The Fudgets Library.
Fudgets is a Graphical User Interface Toolkit built in Haskell on top of the X11 Windows system in the early 1990s. There is an FPCA-93 paper about it. Fudgets also makes it easy to create client/server applications that communicate via the Internet.
This package includes the Fudgets library and a few small examples and demo applications.
For installation instructions, see the last section of the Readme.
¤ Fudgets ¤
Fudgets is primarily a Graphical User Interface Toolkit implemented in Haskell on top of its own binding to the Xlib library of the X Windows system. Fudgets also makes it easy to create client/server applications that communicate via the Internet. The Hello world program fits on a single line:
main = fudlogue (shellF "Hello" (labelF "Hello world!"))
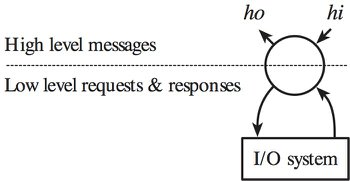
The key abstraction is the fudget. A fudget is a stream processor with high-level and low-level streams. The high level streams are used for communication between fudgets within a program. The low level streams are for communication with the I/O system.
Fudgets are combined using various combinators for parallel composition, serial composition and loops.
Fudgets was originally implemented in Lazy ML in the early 1990s, then converted to Haskell. It was thus designed before monadic IO was introduced in Haskell and early versions did not make use of Haskell's type classes at all.
Documentation
- Your first 8 Fudgets program. Gentle Introduction.
- Fudgets User's Guide. Naming conventions and some other practical things.
- Fudget Library Reference Manual. (Haddock did not exist back when Fudgets were created.)
- Programming with Fudgets: Lecture Notes from the Spring School on Advanced Functional Programming in Båstad 1995. A comprehensive introduction.
- The FPCA-93 paper about Fudgets, the first publication describing Fudgets.
- See the Fudgets home page for more info.
Installing Fudgets from Hackage
On Linux systems
sudo apt install libxext-devcabal install fudgets
(The first command installs Xlib etc on Debian-based distributions, the command and package name may be different on other Linux distributions.)
On macOS
(The preprocessor in clang does not preserve layout, so we use gcc instead. Also, with ghc>=8.10.3 there seems to be problem with the -optP option, so we use a helper script hsrc/fudcpp to call cpp with the correct options.)