Console IRC client.
Console IRC client
glirc is a console IRC client with an emphasis on providing dynamic views into the model of your IRC connections.
GLIRC - Advanced Console IRC Client
Client Features
- Support for a wide variety of IRCv3 capabilities.
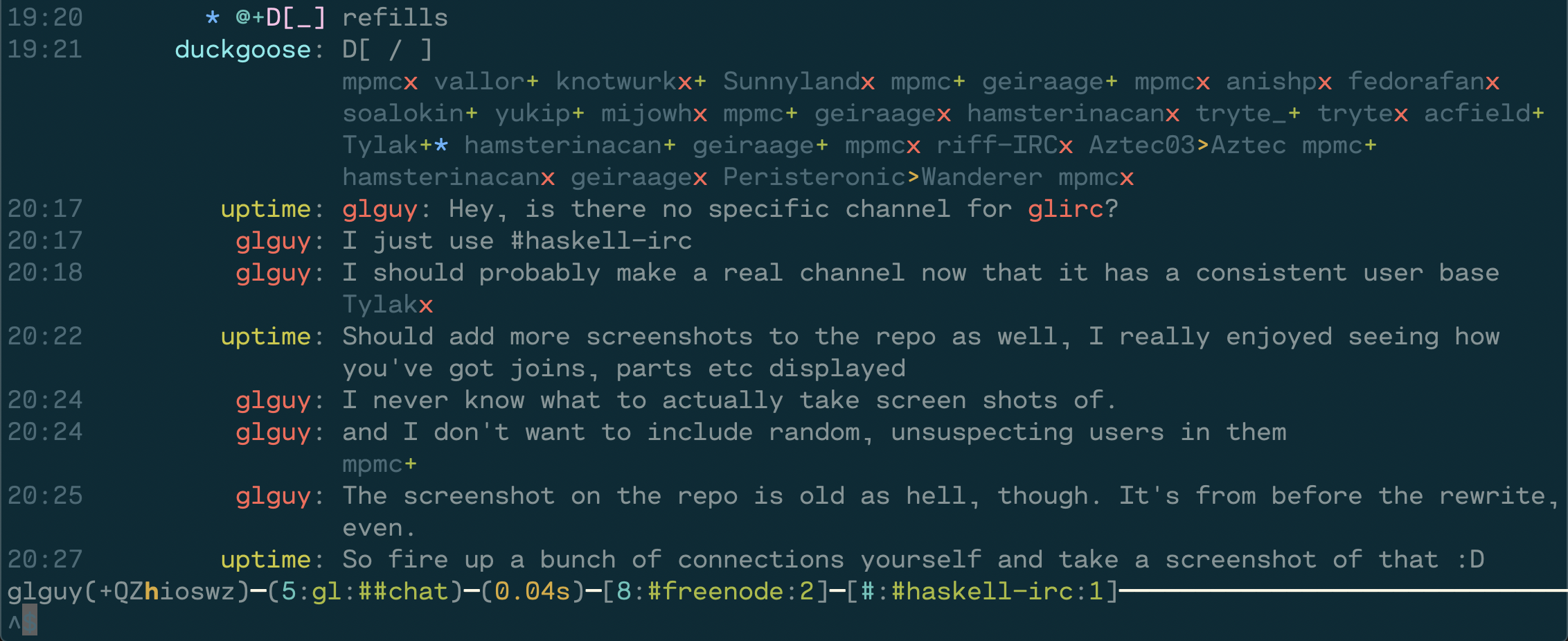
- Joins, parts, and quits fold into one line to save space without sacrificing context. Detailed view (F2) shows additional info, such as part/quit messages.
- Ignore support that folds ignored messages into the joins and parts. Detailed view shows the messages.
- Searchable channel list, who and names list, and list modes (beqI) views separate from chat messages.
- Dynamic, in-place message and list view searching using
/grep. - View and open long URLs with
/url. - Context-sensitive tab completion and command hints.
- WYSIWYG mIRC formatting input.
- Multi-line editing; Enter sends one line at a time.
- Atheme-flavored-ChanServ integration.
- Nicknames in chat messages are colored to match messages from that nickname.
- Correct handling of STATUSMSG, including CTCP ACTIONs.
- Command macros.
- Support for a wide variety of SASL authentication mechanisms, including
ECDSA-NIST256P-CHALLENGE. - Split-screen view.
- Configurable color palette.
- Desktop notifications on important messages while unfocused. Can run arbitrary commands instead (or turn them off).
- Extensions, a Lua plugin system, and trivial piping of IRC messages to arbitrary commands with
/exec. - Plenty more, but this list is getting a bit long.
Building
glirc uses recent versions of packages, make sure your package databases are up-to-date:
$ cabal update
To install the latest version from Hackage using cabal-install:
$ cabal install glirc
Building with cabal-install from source checkout
$ cabal install --dep
$ cabal build
Startup
glirc [FLAGS] INITIAL_NETWORKS...
-c PATH --config=PATH Configuration file path
-! --noconnect Disable autoconnecting
-h --help Show help
--config-format Show configuration file format
-v --version Show version
--full-version Show version and versions of all linked Haskell libraries
Environment variables
USER=<default nickname and username>
IRCPASSWORD=<your irc password>
Configuration file
Most of glirc's settings are specified using a configuration file. The file format is config-value, an indentation-sensitive format that resembles YAML. It has macros which are documented here.
The default configuration file path is ~/.config/glirc/config. Relative paths are relative to the home directory.
To view the full list of configuration variables, run glirc --config-format | less. If any variable is unspecified, a default value will be used instead.
-- vim: filetype=config-value
-- Grab the Vim syntax highlighting file from the config-value package
-- Defaults used when not specified on command line
defaults:
nick: "yournick"
username: "yourusername"
realname: "Your real name"
tls: yes -- or: no, or: starttls
-- enabling tls automatically uses port 6697
-- Override the defaults when connecting to specific servers
servers:
* name: "libera"
hostname: "irc.libera.chat"
sasl:
username: "someuser"
password: "somepass"
log-dir: "/home/myuser/ircLogs"
connect-cmds:
* "join #glirc,#someotherchannel"
* name: "znc"
hostname: "znc.example.com"
port: 7000 -- Override the default port
password: "IRC server password"
tls-verify: no
message-hooks: ["buffextras"] -- Use this when using ZNC's "buffextra" module to get correct playback
flood-penalty: -1 -- Disable flood controls
flood-threshold: -1
macros:
* name: "wipe"
commands:
* "clear"
* "znc *status clearbuffer $channel"
* name: "mysplits"
commands:
* "splits libera:#haskell libera:#haskell-offtopic"
-- Example use of macro in combination with an extension
* name: "extra"
commands:
* "extension Lua somecommand $network $channel"
extra-highlights: ["glirc", "hello"]
nick-padding:
side: left -- Try "right" if you don't like left padding
width: 13
url-opener: "open" -- This works on macOS; use "xdg-open" for most Linuxes
key-bindings:
* bind: "C-M-b"
command: "masks b"
palette:
line-marker: yellow
time:
fg: [10,10,10] -- RGB values for color for timestamps
bg: blue
identifier-colors: -- Used for nicknames and channel names
[ cyan, magenta, green, yellow, blue
, bright-cyan, bright-magenta, bright-green, bright-blue
, 218, 88, 89, 124, 160, 205, 212, 224 -- reds
, 94, 130, 166, 172, 208, 214, 216, 180 -- oranges
, 58, 226, 229, 184, 187, 100, 142, 220 -- yellows
, 22, 34, 40, 82, 70, 64, 48, 85 -- greens
, 25, 27, 33, 39, 51, 80, 81, 75 -- blues
, 69, 61, 56, 54, 129, 93, 99, 147 -- purples
]
notifications: terminal-notifier -- Use terminal-notifier for nicer notifications (macOS only)
Commands
glirc has built-in documentation for all of its commands. To view the full list of commands and what they do, use /help. To view help on a specific command, use /help <command>.
Unlike some other clients, glirc does not send unknown commands to the server. Use /quote to send arbitrary IRC commands.
The following is a curated list of commands for basic use:
/help [command]- Show in-client help/exit- Terminate the client/reload [path]- Load a new configuration file (optional path)/palette- Show the client palette/url [n]- Execute url-opener on the nth URL in the current window (defaults to first)/toggle-activity-bar- toggle channel names in activity bar/toggle-detail- toggle full detail view of messages/toggle-metadata- toggle visibility of channel metadata (joins, parts, quits, nick changes, etc)
Connection
/connect <name>- Connect to the given server/quit [message]- Gracefully terminate connection to the current server/reconnect- Reconnect to the current server/nick <nick>- Change nickname/away [message]- Set away status; no message removes away status
Window management
/windows [filter]- List all open windows (filters: networks, channels, users)/setname [letter]- Assign a one-letter name to the given window./channel <channel>- Change focus to channel/user on current network (alias:/c)/channel <network>:[channel]- Change focus to channel/user on the specified network (alias:/c)/clear [network] [channel]- Clear contents of current or specified window/splits [focuses...]- Enable split-screen view. Focuses should be space delimited list of NETWORK:CHANNEL/splits+ [focuses...]- Incremental addition to splits/splits- [focuses...]- Incremental removal from splits/toggle-layout- toggle split-screen layout between 1 and 2 column view
Chat commands
/join <channel>- Join a channel (alias:/j)/part [msg]- Part from current channel/query <target> [msg]- Switch focus to target window on current server, optionally send message (alias:/q)/msg <target> <msg>- Send a message on the current server to target/me <msg>- Send action message to channel/say <msg>- Send normal message to channel; useful for macros and messages starting with a slash/ignore <mask>...- Toggle ignore status on a list of masks/topic [msg]- Display or set the current topic of a channel
Views
/channelinfo- Show channel topic, creation, url/grep [flags] <regex>- Filter using a regular expression/ignore- Show all ignore masks/list- View the list of public channels on the network/masks <mode>- Show channel bans(b), quiets(q), exempts(e), or invex(I)/mentions- Show all the highlighted lines across all windows/names- Show the user list for the current channel/who [channel] [options]- Perform WHO query, sending options to the server, or show the results of the previous query.
ZNC-specific
/znc <module> <parameters>- send command to ZNC module without echoing to all clients/znc-playback- ZNC playback module - play everything/znc-playback <time>- ZNC playback module - play everything start at the given time today/znc-playback <date> <time>- ZNC playback module - play everything start at the given time
Miscellaneous
/dump <filename>- Dump current window to file/extension <extension name> <params...>- Send the given params to the named extension/exec [-n network] [-c channel] <command> <arguments...>- Execute a command; if no network or channel are provided send output to client window, if network and channel are provided send output as messages, if network is provided send output as raw IRC messages./quote <raw command>- Send a raw IRC command to the server
Keyboard Shortcuts
Note that these keybindings are using Emacs syntax. C-a means "hold control and press A". M-a means "hold meta key and press A". On most modern keyboards the Meta key is labeled Alt or Option.
To view the full list of keybindings and what they do, use /keymap from within glirc.
The following is a curated list of default keybinds for basic use:
Navigation
Page Upscroll upPage Downscroll downC-nnext windowC-pprevious windowC-xnext network windowM-<name>jump to window with the given one-letter nameM-ajump to activityM-sjump to previous windowESCreturn to messages view (from userlist, masklist, help, etc)
Editing
C-bboldC-ccolorC-vinvert foreground/backgroundC-_underlineC-]italicC-oreset formattingTabautocompletionM-kreplace 2 characters before the cursor with a character specified in/digraphsC-abeginning of lineC-eend of lineC-kdelete to endC-udelete to beginningC-ddelete at cursorC-wdelete word backwardsC-ypaste from yank bufferC-tswap characters at cursorM-fforward wordM-bbackward wordM-Rightforward wordM-Leftbackward wordM-Backspacedelete word backwardsM-ddelete word forwardsM-Enterinsert newline
Client settings
F2toggle detailed viewF3toggle detailed activity barF4toggle metadata visibilityF7toggle Enter key lock
Macros
The macros configuration section allows you to define sequences of commands. These commands can contain expansions.
Configuration
name- text - name of macroarguments- text - space separated list of argument names (suffix name with?when optional)commands- list of text - commands to send after expansion
Macro Expansions
Variable names and integer indexes can be used when defining commands. Variables are specified with a leading $. For disambiguation a variable name can be surrounded by {}. $channel and ${channel} are equivalent. Default values can be provided following a pipe: ${var|default}.
channel- current channelnetwork- current network namenick- current nickname
The arguments to a command will be mapped to integer indexes.
0- first argument1- second argument (etc.)


