Law-abiding lenses for Aeson, using microlens.
microlens-aeson
microlens-aeson provides Traversals for the Aeson library's Value type, while obeying the Traversal laws.
microlens-aeson is derived from lens-aeson, but is based upon microlens to reduce the amount of dependencies involved.
Here is the dependency graph for lens-aeson:
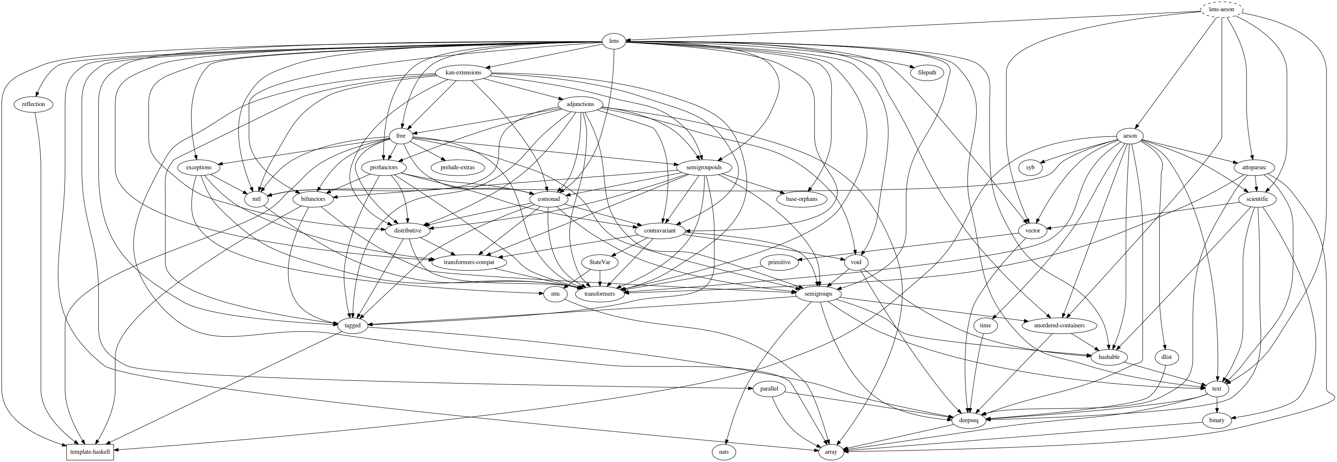
And that for microlens-aeson:
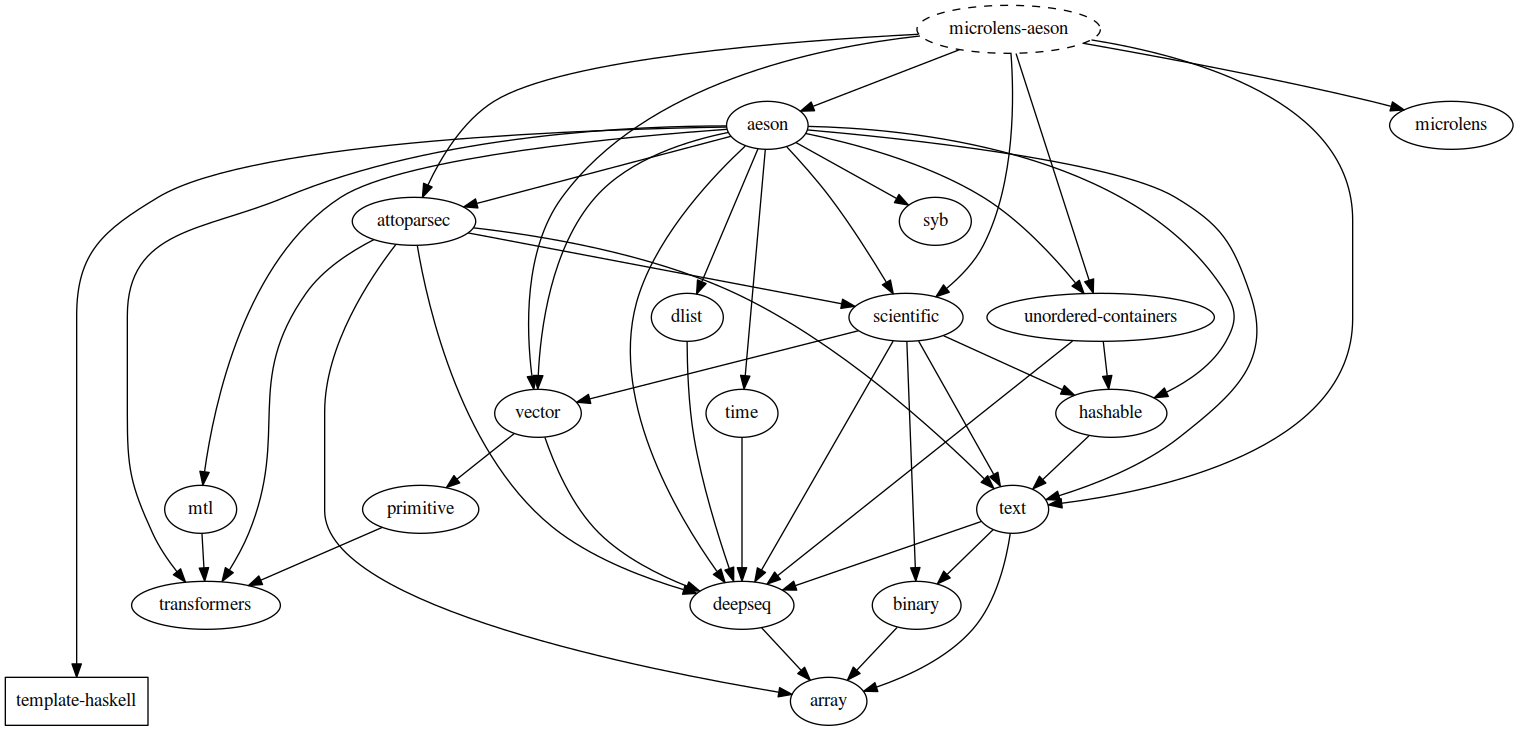
Usage
microlens-aeson provides Traversals into both lazy and strict variants of all the text types. Here are some examples:
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}
import Data.Aeson
import Data.Text (Text)
import Lens.Micro.Aeson
--------------------------
-- Manipulating primatives
--------------------------
-- | Optionally getting one value
a :: Maybe Int
a = ("37" :: Text) ^? _Integer -- Just 37
-- | Setting one value within encoded JSON
b :: Maybe Text
b = "true" & _Bool .~ False -- "false"
----------------------
-- Manipulating arrays
----------------------
-- | Get all values as an Aeson type.
c :: [Value]
c = "[1, 2, 3]" ^.. values -- [Number 1.0, Number 2.0, Number 3.0]
-- | Get all values cast to some simpler number type.
d :: [Double]
d = "[1, 2, 3]" ^.. values . _Double -- [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
-- | Access a specific index, and set a `Value` directly.
e :: Text
e = "[1,2,3]" & nth 1 .~ Number 20 -- "[1,20,3]"
-----------------------
-- Manipulating objects
-----------------------
-- | Access all values of the key/value pairs.
f :: Text
f = "{\"a\":4,\"b\":7}" & members . _Number %~ (*10) -- "{\"a\":40,\"b\":70}"
-- | Access via a given key.
g :: Maybe Value
g = ("{\"a\": 100, \"b\": 200}" :: Text) ^? key "a" -- Just (Number 100.0)
-----------------------------------
-- Aeson `Value`s from encoded JSON
-----------------------------------
h :: Maybe Text
h = "{\"a\":4,\"b\":7}" ^? _Value
-- Just (Object (fromList [("a",Number 4.0),("b",Number 7.0)]))
See the Haddock documentation for a full API specification.
Migration from Data.Aeson.Lens
The functions provided here are Traversals, not Prisms, therefore creation of encoded JSON from Haskell types like:
>>> _Bool # True :: String
"true"
is no longer possible. Otherwise, if your use cases are strictly like those listed in the Usage section above, then you need only to switch the import from Data.Aeson.Lens to Lens.Micro.Aeson.
