Bayesian Network Modeling and Analysis.
BayesianNetwork
![]()
BayesianNetwork is a Shiny web application for Bayesian network modeling and analysis, powered by the bnlearn package. To learn more about this project, check out this paper.
Getting Started
To install BayesianNetwork in R:
install.packages("BayesianNetwork")
Or to install the latest developmental version:
devtools::install_github('paulgovan/BayesianNetwork')
To launch the app:
BayesianNetwork::BayesianNetwork()
Or to access the app through a browser, visit paulgovan.shinyapps.io/BayesianNetwork.
Example
Home
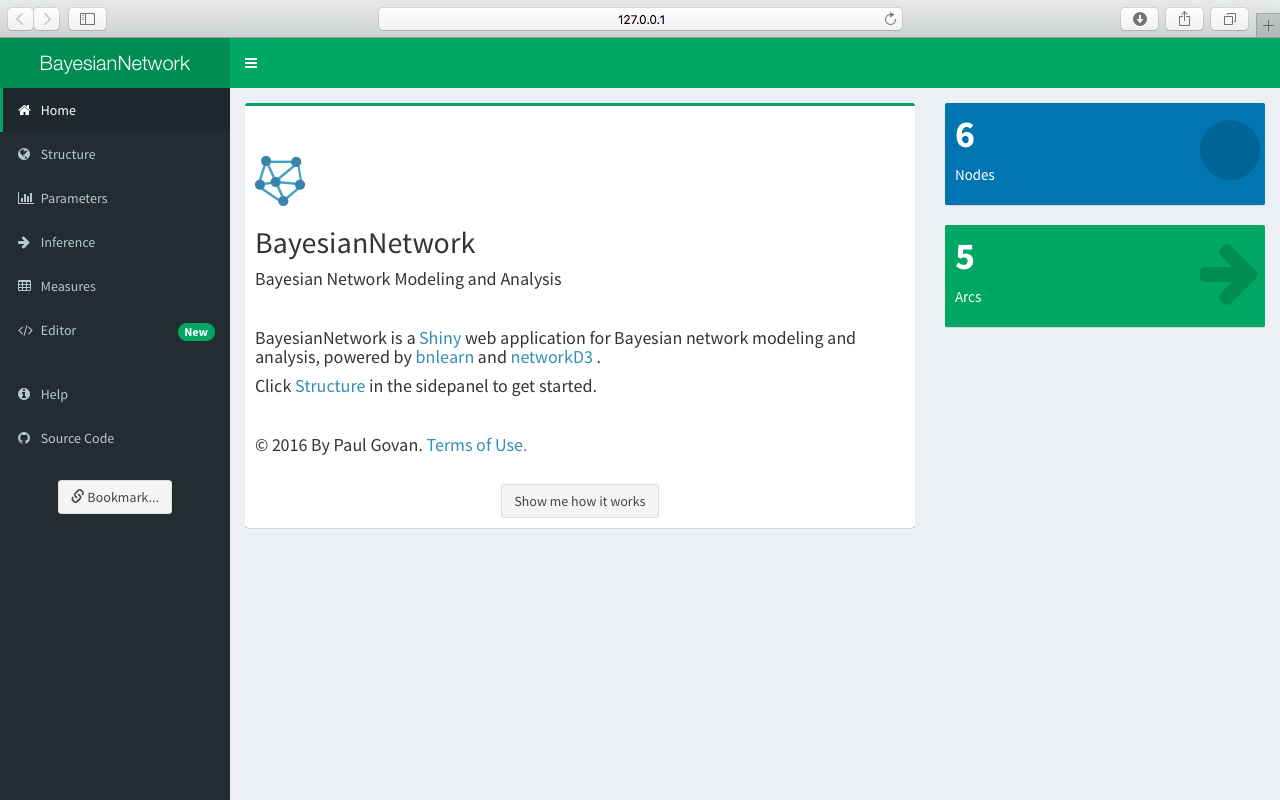
Launching the app brings up the Home tab. The Home tab is basically a landing page that gives a brief introduction to the app and includes two value boxes, one each for the number of nodes and arcs in the network. The following figure shows the basic Home tab.
BayesianNetwork comes with a number of simulated and “real world” data sets. This example will use the “Sample Discrete Network”, which is the selected network by default.
Structure
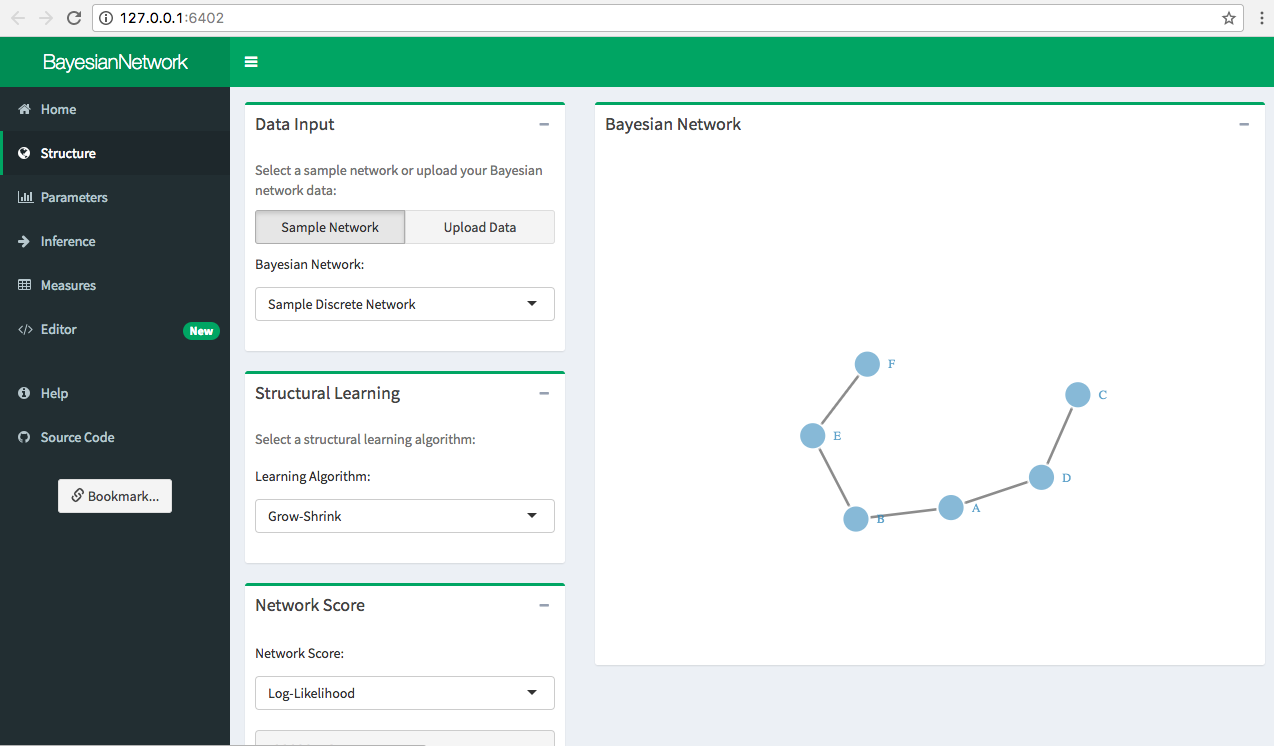
Click Structure in the sidepanel to begin learning the network from the data. The Bayesian network is automatically displayed in the Bayesian Network box.
In order to learn the structure of a network for a given data set, upload the data set in csv format using The Data Input box. Data should be numeric or factored and should not contain any NULL/NaN/NA values. Again, this example uses the “Sample Discrete Network”, which should already be loaded.
Select a learning algorithm from the Structural Learning box. The classes of available structural learning algorithms include:
* Constraint-based algorithms * Score-based algorithms * Hybrid-structure algorithms * Local discovery algorithms
To view the network score, select a score function from the The Network Score box.
“Sample Discrete Network” contains six discrete variables, stored as factors with either 2 or 3 levels. The structure of this simple Bayesian network can be learned using the grow-shrink algorithm, which is the selected algorithm by default.
Try different combinations of structural learning algorithms and score functions in order to see the effect (if any) on the resulting Bayesian network.
Parameters
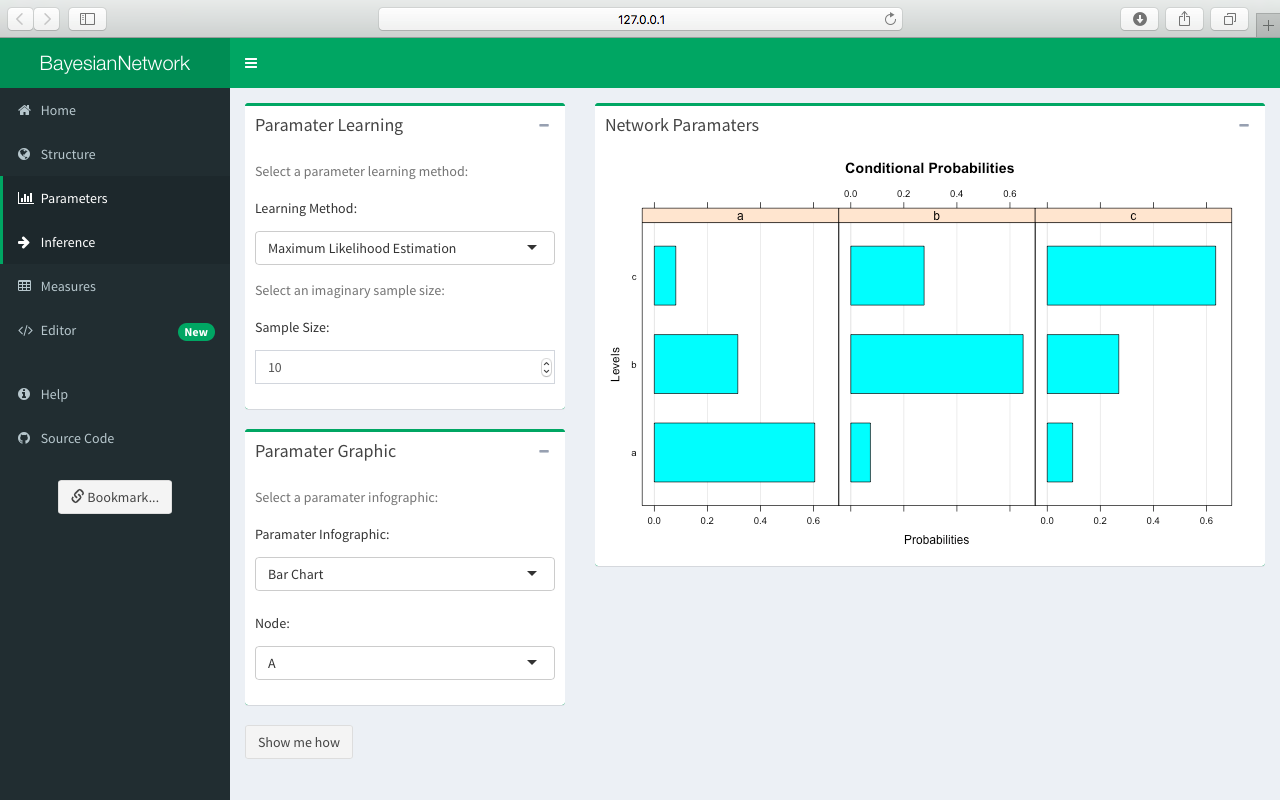
Select the grow-shrink algorithm once again and then click Parameters in the sidepanel in order to learn the parameters of the network. The selected parameters are automically displayed in the Network Parameters box.
Select a learning algorithm from the Parameter Learning box. This app supports both maximum-likelihood and Bayesian estimation of the parameters. Note that Bayesian parameter learning is currently only implemented for discrete data sets. Then select the type of chart to display in the Parameter Infographic box and, for the discrete case, choose the preferred node. For example, the selected node A is a discrete node with three levels: a, b, and c.
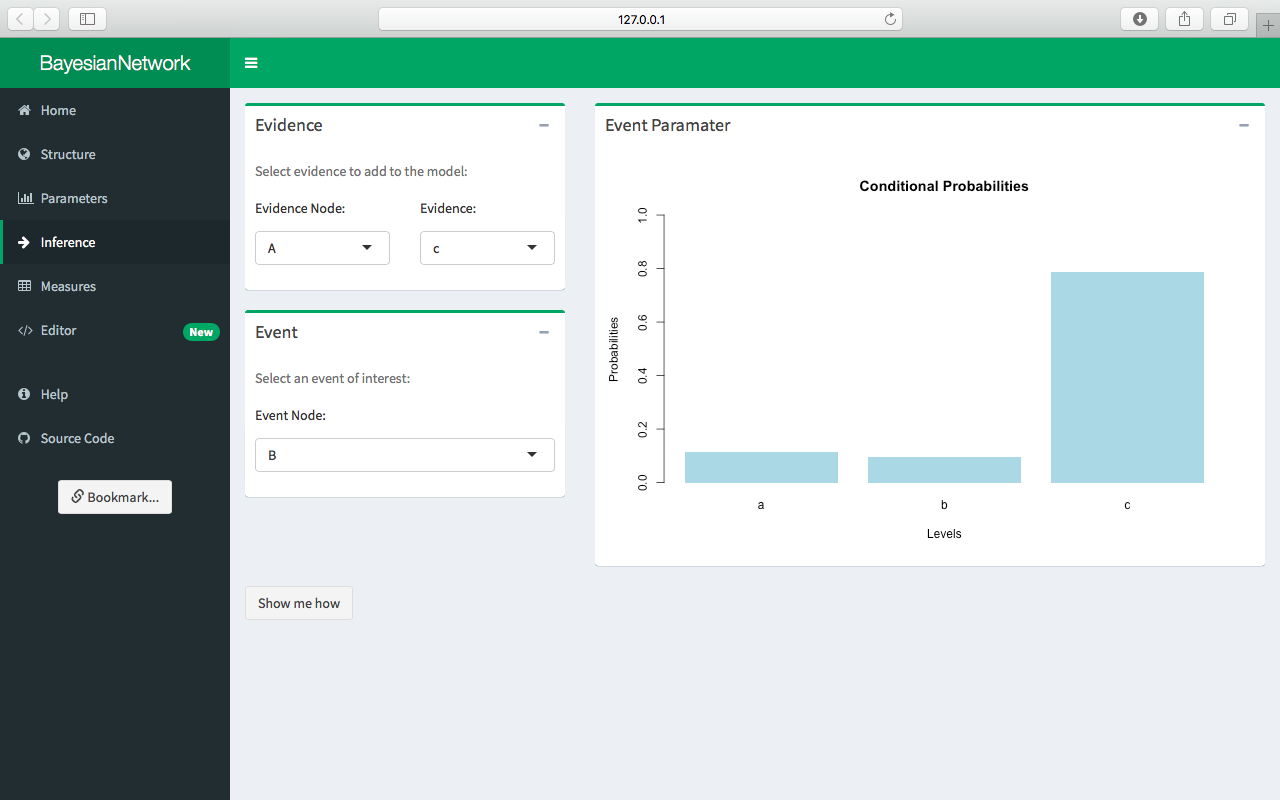
Inference
Click Inference in the sidebar to add evidence to the network. Select evidence to add to the model using the Evidence box and select a conditional event of interest using the Event box. The resulting conditional probabilities are automatically displayed in the Event Parameter box. For example, the following figure shows the conditional probability of event B, given evidence of c for node A. Changing the evidence for node A to a or b similarly changes the conditional probability of event B. Note that inference is currently not supported for continuous variables.
Measures
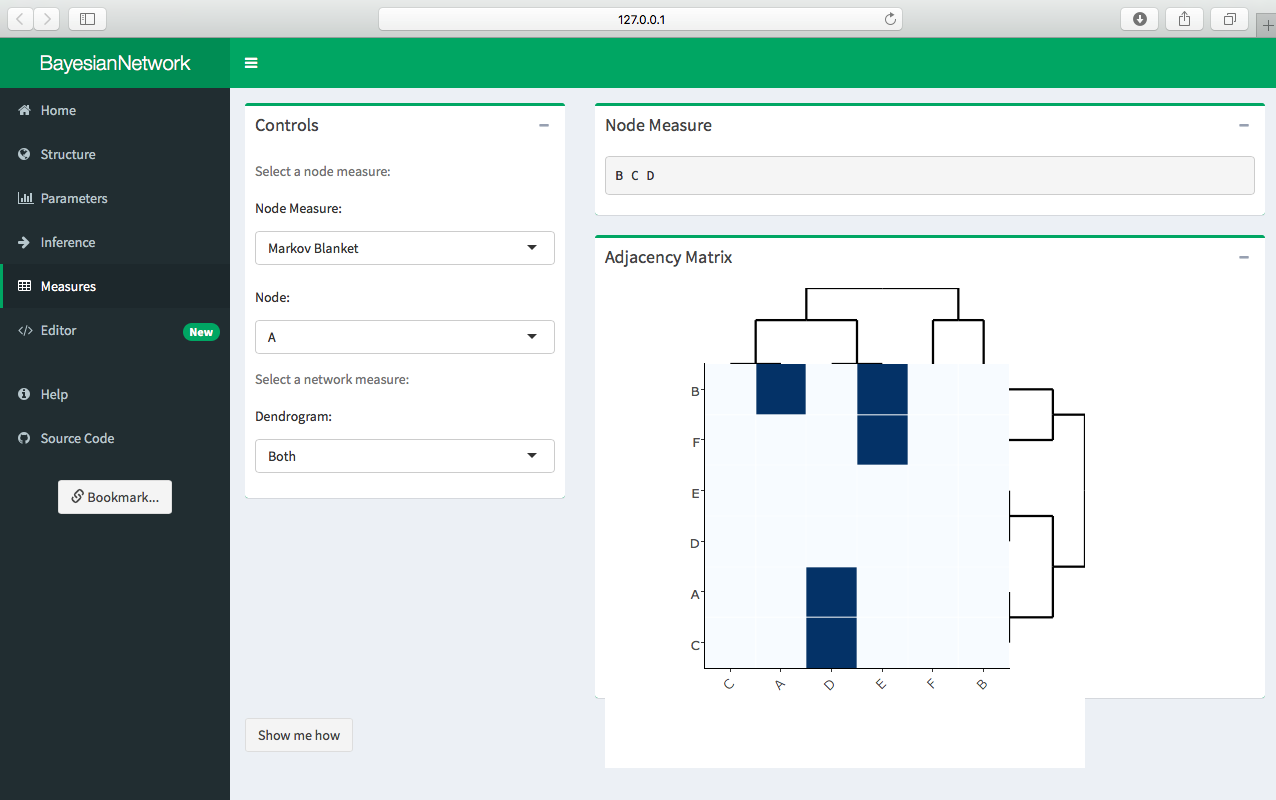
Click Measures in the sidepanel to bring up a number of tools for classic network analysis. The Measures tab has a number of node and network measures. The node measures include: * Markov blanket * Neighborhood * Parents * Children * In degree * Out degree * Incident arcs * Incoming arcs * Outgoing arcs
Select a node measure in the Controls box and the result will be displayed in the Node Measure box.
The Controls box also contains different options for displaying hierarchical clusters/dendograms for the network. Select the type of dendogram to display (row, column, both, or none) and the resulting dendogram(s) will be displayed along with the adjacency matrix in the Adjacency Matrix box.
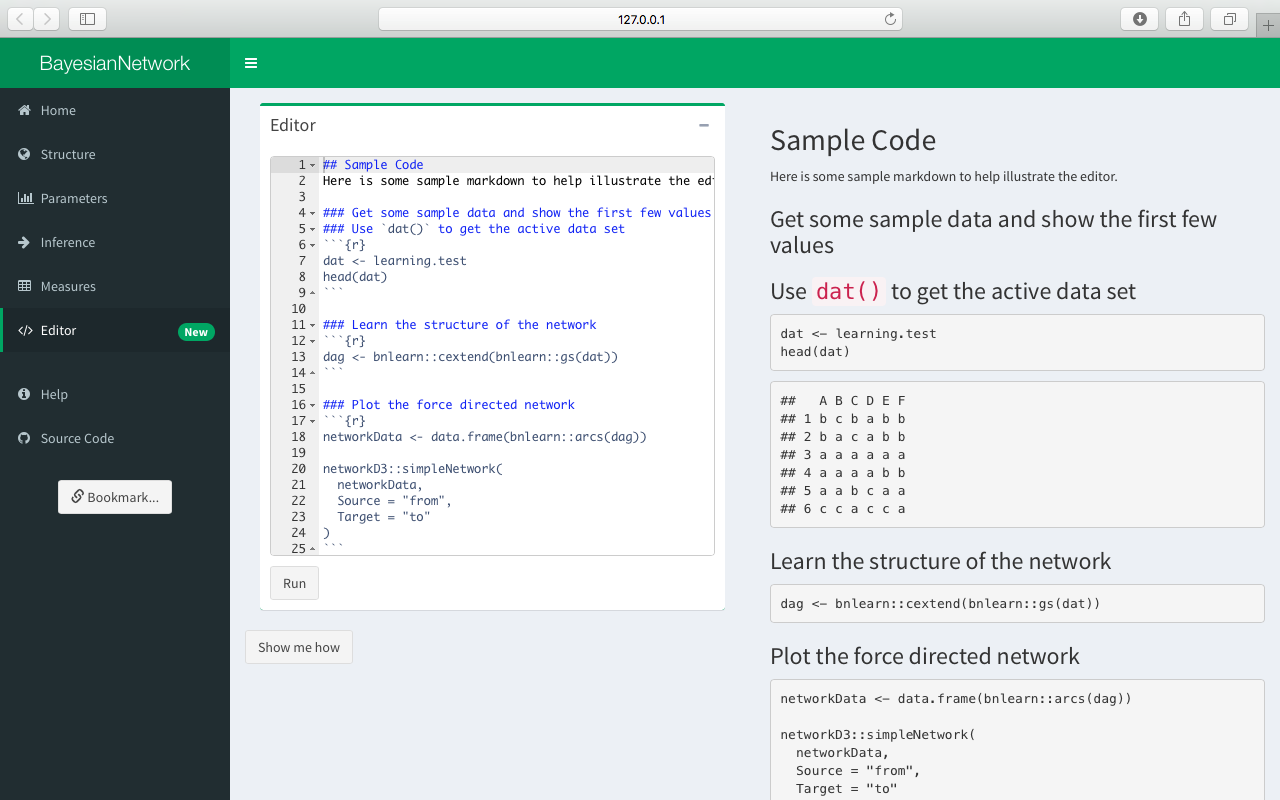
Editor
Finally, click Editor in the sidepanel in order to bring up the interactive code editor. Some example markdown is automatically displayed in the Editor box. Click the Run button to knit the code and the resulting report will be displayed in the body of the app.
Note that the Editor is only available in the package (not on shinyapps.io).
Code of Conduct
Please note that the BayesianNetwork project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.