Query Data from the 'EIA' API.
EIAapi
The EIAapi package provides functions to query and pull tidy data from EIA API v2.
Introduction to the EIAapi package available here.
Requirments
To pull data from the API using this package, you will need the following:
- jq - The package uses jq to parse the API output from JSON to tabular format. To download and install jq follow the instructions on the download page.
- API key - To query the EIA API, you will need to register to the service to receive the API key.
To register to to the API go to https://www.eia.gov/opendata/ and click the Register button, and follow the instruction.
Installation
Install the stable version from [CRAN]:
install.packages("EIAapi")
Or, install the development version from Github:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("RamiKrispin/EIAapi")
Query data
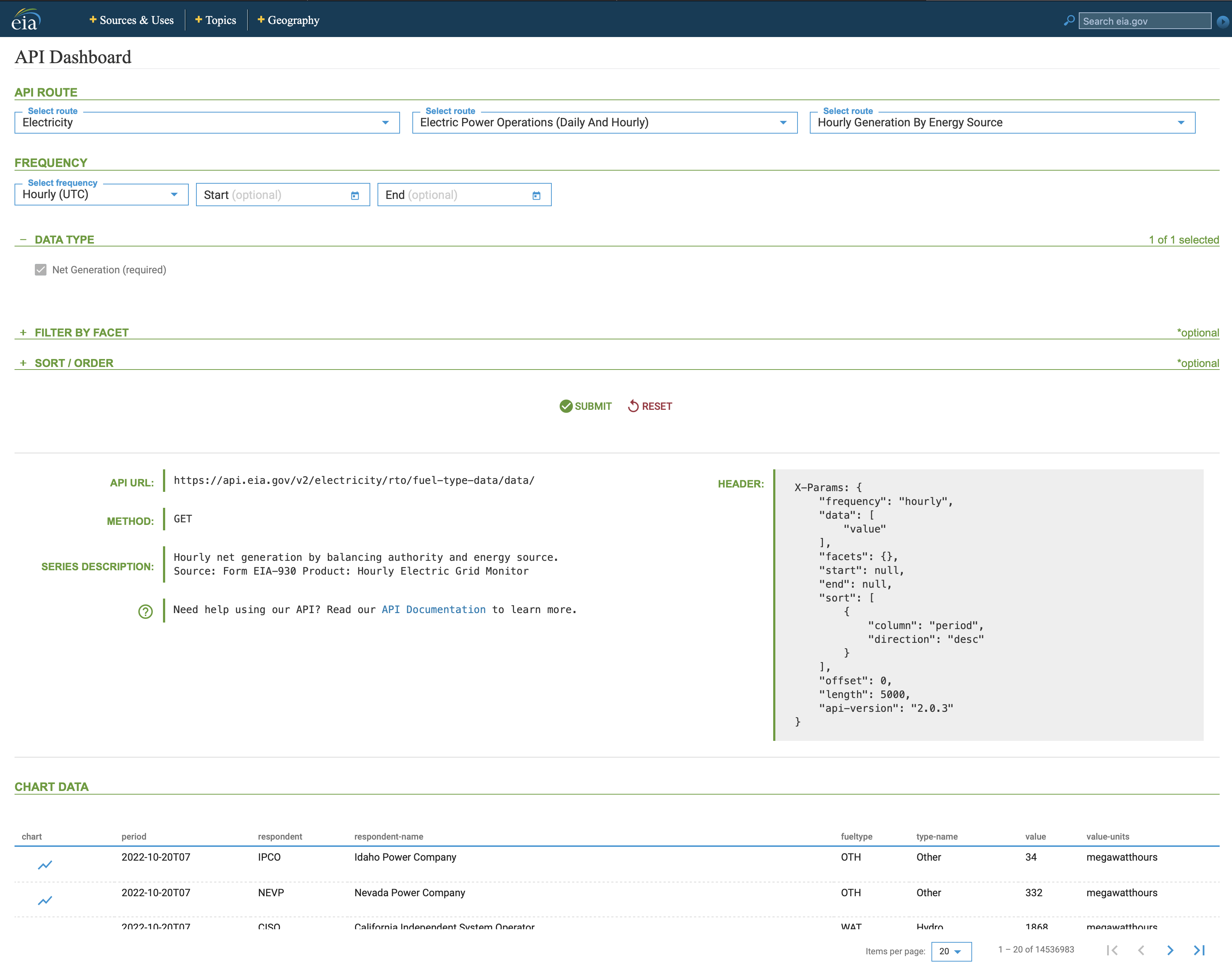
A suggested workflow to query data from the EIA API with the eia_get function:
- Go to the EIA API Dashboard website
- Select the API Route and define filters
- Submit the query and extract the query information from the query metadata:
- API URL
- Header
In the example above:
- The API URL:
https://api.eia.gov/v2/electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/, and - The query header:
{
"frequency": "hourly",
"data": [
"value"
],
"facets": {},
"start": null,
"end": null,
"sort": [
{
"column": "period",
"direction": "desc"
}
],
"offset": 0,
"length": 5000,
"api-version": "2.0.3"
}
Using the URL and header information, we can submit the GET request with the eia_get function:
library(EIAapi)
# Pulling the API key from my renviron file
api_key <- Sys.getenv("eia_key")
df1 <- eia_get(
api_key = api_key,
api_path = "electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/",
data = "value"
)
nrow(df1)
#> [1] 5000
head(df1)
#> period respondent respondent-name fueltype
#> 1 2019-09-02T06 FPC Duke Energy Florida, Inc. SUN
#> 2 2019-09-03T04 PSEI Puget Sound Energy, Inc. WAT
#> 3 2019-09-02T11 MIDA Mid-Atlantic NG
#> 4 2019-09-02T18 NW Northwest OTH
#> 5 2019-09-02T21 AECI Associated Electric Cooperative, Inc. NG
#> 6 2019-09-02T12 CENT Central NUC
#> type-name value value-units
#> 1 Solar 0 megawatthours
#> 2 Hydro 497 megawatthours
#> 3 Natural gas 24868 megawatthours
#> 4 Other 795 megawatthours
#> 5 Natural gas 1551 megawatthours
#> 6 Nuclear 2001 megawatthours
Note: The api_path argument defines by the query of the path that following the endpoint of the API - https://api.eia.gov/v2/. In the example above the API full URL is:
https://api.eia.gov/v2/electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/
Therefore, the query’s path is set to electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/.
The eia_get function leverages the jq tool to parse the return JSON object from the API into CSV format and the data.table package to read and parse the object into R. By default, the function returns a data.frame object, but you can use the format argument and set the output object as data.table:
df2 <- eia_get(
api_key = api_key,
api_path = "electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/",
data = "value",
format = "data.table"
)
df2
#> period respondent respondent-name fueltype
#> 1: 2019-09-02T06 FPC Duke Energy Florida, Inc. SUN
#> 2: 2019-09-03T04 PSEI Puget Sound Energy, Inc. WAT
#> 3: 2019-09-02T11 MIDA Mid-Atlantic NG
#> 4: 2019-09-02T18 NW Northwest OTH
#> 5: 2019-09-02T21 AECI Associated Electric Cooperative, Inc. NG
#> ---
#> 4996: 2019-09-01T15 HST City of Homestead NG
#> 4997: 2019-09-01T18 AEC PowerSouth Energy Cooperative WAT
#> 4998: 2019-09-01T17 SC South Carolina Public Service Authority NG
#> 4999: 2019-09-02T04 PSEI Puget Sound Energy, Inc. WND
#> 5000: 2019-09-01T05 FPC Duke Energy Florida, Inc. OIL
#> type-name value value-units
#> 1: Solar 0 megawatthours
#> 2: Hydro 497 megawatthours
#> 3: Natural gas 24868 megawatthours
#> 4: Other 795 megawatthours
#> 5: Natural gas 1551 megawatthours
#> ---
#> 4996: Natural gas 0 megawatthours
#> 4997: Hydro 0 megawatthours
#> 4998: Natural gas 780 megawatthours
#> 4999: Wind 239 megawatthours
#> 5000: Petroleum 0 megawatthours
If you wish to pull more than the length upper limit, you can use the offset to offset the query by limit and pull the next observations:
df3 <- eia_get(
api_key = api_key,
api_path = "electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/",
data = "value",
length = 5000,
offset = 5000,
format = "data.table"
)
df3
#> period respondent respondent-name
#> 1: 2019-09-01T10 TAL City of Tallahassee
#> 2: 2019-09-01T23 SE Southeast
#> 3: 2019-09-01T16 SWPP Southwest Power Pool
#> 4: 2019-09-01T09 PSCO Public Service Company of Colorado
#> 5: 2019-09-01T23 CPLW Duke Energy Progress West
#> ---
#> 4996: 2019-09-08T13 SCEG Dominion Energy South Carolina, Inc.
#> 4997: 2019-09-09T02 SC South Carolina Public Service Authority
#> 4998: 2019-09-09T03 YAD Alcoa Power Generating, Inc. - Yadkin Division
#> 4999: 2019-09-08T17 TIDC Turlock Irrigation District
#> 5000: 2019-09-09T00 SE Southeast
#> fueltype type-name value value-units
#> 1: NG Natural gas 277 megawatthours
#> 2: NG Natural gas 21452 megawatthours
#> 3: COL Coal 13539 megawatthours
#> 4: COL Coal 1835 megawatthours
#> 5: WAT Hydro 32 megawatthours
#> ---
#> 4996: WAT Hydro 15 megawatthours
#> 4997: SUN Solar 2 megawatthours
#> 4998: WAT Hydro 1 megawatthours
#> 4999: NG Natural gas 193 megawatthours
#> 5000: OIL Petroleum 0 megawatthours
You can narrow down your pull by using the facets argument and applying some filters. For example, in the example above, let’s filter data by the fuletype field and select energy source as Natural gas (NG) and the region as United States Lower 48 (US48), and then extract the header:
{
"frequency": "hourly",
"data": [
"value"
],
"facets": {
"respondent": [
"US48"
],
"fueltype": [
"NG"
]
},
"start": null,
"end": null,
"sort": [
{
"column": "period",
"direction": "desc"
}
],
"offset": 0,
"length": 5000,
"api-version": "2.0.3"
}
Updating the query with the facets information:
facets <- list(respondent = "US48", fueltype = "NG")
df4 <- eia_get(
api_key = api_key,
api_path = "electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/",
data = "value",
length = 5000,
format = "data.table",
facets = facets
)
df4
#> period respondent respondent-name fueltype type-name
#> 1: 2019-09-03T02 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2: 2019-09-02T08 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 3: 2019-09-02T06 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 4: 2019-09-03T03 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 5: 2019-09-02T16 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> ---
#> 4996: 2018-11-09T20 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 4997: 2018-11-09T21 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 4998: 2018-11-07T11 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 4999: 2018-11-07T12 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 5000: 2018-11-07T13 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> value value-units
#> 1: 238622 megawatthours
#> 2: 149180 megawatthours
#> 3: 164671 megawatthours
#> 4: 217190 megawatthours
#> 5: 206225 megawatthours
#> ---
#> 4996: 145412 megawatthours
#> 4997: 147572 megawatthours
#> 4998: 109269 megawatthours
#> 4999: 123157 megawatthours
#> 5000: 132755 megawatthours
unique(df4$fueltype)
#> [1] "NG"
unique(df4$respondent)
#> [1] "US48"
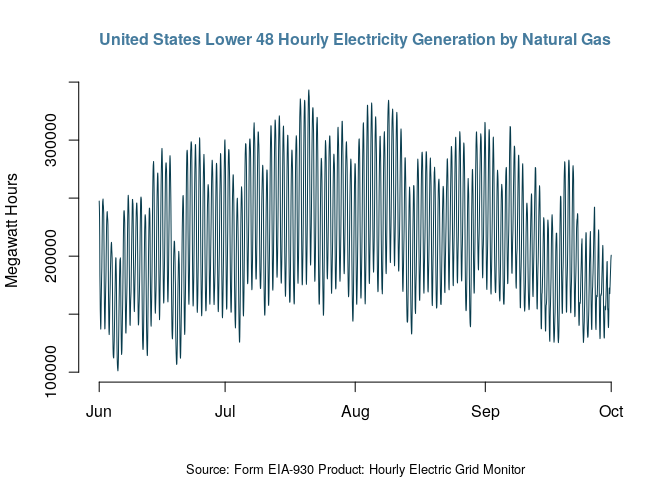
Last but not least, you can set the starting and ending time of the query. For example, let’s set a window between June 1st and October 1st, 2022:
df5 <- eia_get(
api_key = api_key,
api_path = "electricity/rto/fuel-type-data/data/",
data = "value",
length = 5000,
format = "data.table",
facets = facets,
start = "2022-06-01T00",
end = "2022-10-01T00"
)
df5
#> period respondent respondent-name fueltype type-name
#> 1: 2022-06-01T00 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2: 2022-06-01T01 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 3: 2022-06-01T02 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 4: 2022-06-01T03 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 5: 2022-06-01T04 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> ---
#> 2925: 2022-09-30T20 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2926: 2022-09-30T21 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2927: 2022-09-30T22 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2928: 2022-09-30T23 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> 2929: 2022-10-01T00 US48 United States Lower 48 NG Natural gas
#> value value-units
#> 1: 247460 megawatthours
#> 2: 242340 megawatthours
#> 3: 233394 megawatthours
#> 4: 215728 megawatthours
#> 5: 183732 megawatthours
#> ---
#> 2925: 186416 megawatthours
#> 2926: 190630 megawatthours
#> 2927: 196122 megawatthours
#> 2928: 198929 megawatthours
#> 2929: 200809 megawatthours
df5$time <- as.POSIXct(paste(substr(df5$period, start = 1, stop = 10)," ",
substr(df5$period, start = 12, stop = 13), ":00:00",
sep = ""))
plot(x = df5$time, y = df5$value,
main = "United States Lower 48 Hourly Electricity Generation by Natural Gas",
col.main = "#457b9d",
col = "#073b4c",
sub = "Source: Form EIA-930 Product: Hourly Electric Grid Monitor",
xlab = "",
ylab = "Megawatt Hours",
cex.main=1,
cex.lab=1,
cex.sub=0.8,
frame=FALSE,
type = "l")
API Resources
- EIA API documentation: https://www.eia.gov/opendata/documentation.php
- EIA APIv2 Webinar: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1VsSp1XG-Pg&t=1671s&ab_channel=EIAgov.