Feature Attributions for ClusTering.
FACT - (Feature Attributions for Clustering)
To get value from a clustering algorithm, it is important to understand the mapping procedure of an algorithm that assigns instances to clusters. FACT is an algorithm agnostic framework that provides feature attribution while preserving the integrity of the data.
Features
SMART(Scoring Metric After Permutation) permutes feature sets to measure the sensitivity of algorithms to changes in cluster assignments.IDEA(Isolated Effect on Assignment) visualizes local and global changes in cluster assignments over one- and two-dimensional feature spaces.
Installation
You can install the development version of FACT like so:
# Development version
remotes::install_github("henrifnk/FACT")
Quickstart
We aim to divide American states by their standardized crime rates in 3 clusters.
library(FACT)
library(mlr3cluster)
#> Lade nötiges Paket: mlr3
attributes_scale = attributes(scale(USArrests))
| Murder | Assault | UrbanPop | Rape | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 1.24 | 0.78 | -0.52 | 0.00 |
| Alaska | 0.51 | 1.11 | -1.21 | 2.48 |
| Arizona | 0.07 | 1.48 | 1.00 | 1.04 |
| Arkansas | 0.23 | 0.23 | -1.07 | -0.18 |
| California | 0.28 | 1.26 | 1.76 | 2.07 |
| Colorado | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.86 | 1.86 |
USArrests Data Set
Therefore, we use a c-means algorithm from mlr3cluster.
tsk_usa = TaskClust$new(id = "usarest", backend = data.frame(scale(USArrests)))
c_lrn = lrn("clust.cmeans", centers = 3, predict_type = "prob")
c_lrn$train(tsk_usa)
Then, we create a ClustPredictor that wraps the information needed for our methods.
predictor = ClustPredictor$new(c_lrn, data = tsk_usa$data(), y = c_lrn$model$membership)
How does Assault effect the partitions created by c-means clustering?
The sIDEA plot shows:
- x-Axis: The domain in the feature space of
Assaultwere realizations of observations can be found (visualized by thegeom_rug). - y-Axis: The associated soft labels score of cluster k,
f(k). - solid line: The estimated marginal, global effect of a cluster k over the feature space.
- transparent area: 50% of the mass of the individual effects. This area represents the variance of the effects across feature space.
idea_assault = IDEA$new(predictor, "Assault", grid.size = 50)
idea_assault$plot_globals(0.5)
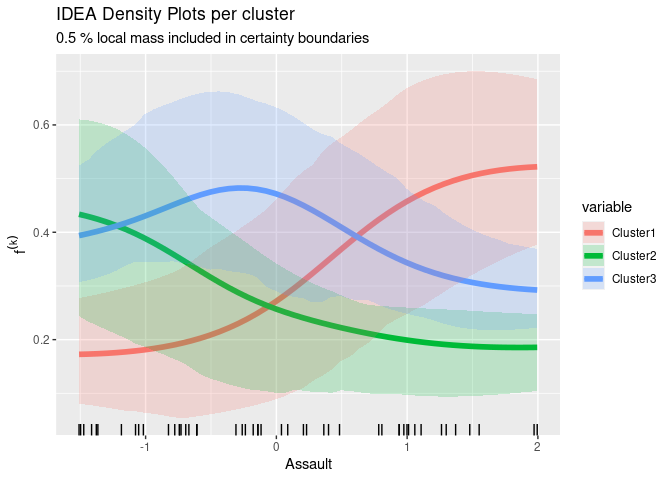
Short Interpretation:
- States in cluster 1 (red) are marginally associated with the lowest
Assaultrate. - States in cluster 3 (blue) are marginally associated with a relatively low
Assaultrate. - States in cluster 2 (green) are marginally associated with a relatively high
Assaultrate.
Citation
If you use FACT in a scientific publication, please cite it as:
Scholbeck, C.A., Funk, H., Casalicchio, G. (2023). Algorithm-Agnostic Feature Attributions for Clustering. In: Longo, L. (eds) Explainable Artificial Intelligence. xAI 2023. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1901. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44064-9_13
BibTeX:
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-44064-9_13,
author="Scholbeck, Christian A.
and Funk, Henri
and Casalicchio, Giuseppe",
editor="Longo, Luca",
title="Algorithm-Agnostic Feature Attributions for Clustering",
booktitle="Explainable Artificial Intelligence",
year="2023",
publisher="Springer Nature Switzerland",
address="Cham",
pages="217--240",
abstract="Understanding how assignments of instances to clusters can be attributed to the features can be vital in many applications. However, research to provide such feature attributions has been limited. Clustering algorithms with built-in explanations are scarce. Common algorithm-agnostic approaches involve dimension reduction and subsequent visualization, which transforms the original features used to cluster the data; or training a supervised learning classifier on the found cluster labels, which adds additional and intractable complexity. We present FACT (feature attributions for clustering), an algorithm-agnostic framework that preserves the integrity of the data and does not introduce additional models. As the defining characteristic of FACT, we introduce a set of work stages: sampling, intervention, reassignment, and aggregation. Furthermore, we propose two novel FACT methods: SMART (scoring metric after permutation) measures changes in cluster assignments by custom scoring functions after permuting selected features; IDEA (isolated effect on assignment) indicates local and global changes in cluster assignments after making uniform changes to selected features.",
isbn="978-3-031-44064-9"
}