Description
Fit Univariate Mixed and Usual Distributions.
Description
Extends the fitdist() (from 'fitdistrplus') adding the Anderson-Darling ad.test() (from 'ADGofTest') and Kolmogorov Smirnov Test ks.test() inside, trying the distributions from 'stats' package by default and offering a second function which uses mixed distributions to fit, this distributions are split with unsupervised learning, with Mclust() function (from 'mclust').
README.md
FitUltD
The goal of FitUltD is to fit data that can’t be fitted with ordinary density functions
Installation
You can install the released version of FitUltD from CRAN with:
install.packages(“FitUltD”)
Example
This is a basic example which shows you how to fit a multimodal random variable:
library(FitUltD)
#> Loading required package: mclust
#> Package 'mclust' version 5.4.5
#> Type 'citation("mclust")' for citing this R package in publications.
#random Variable
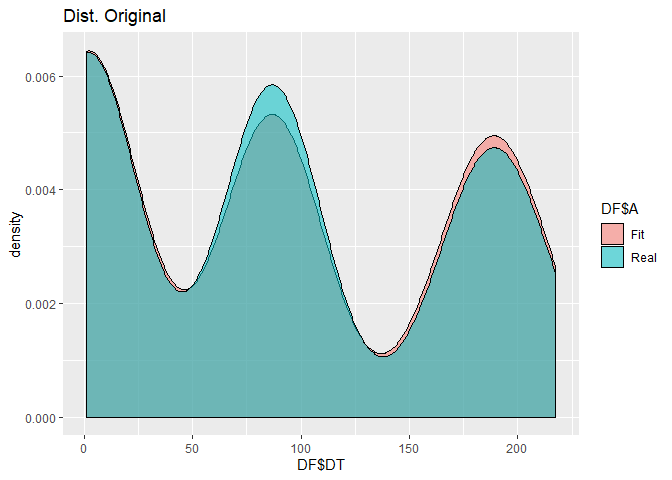
RV<-c(rnorm(73,189,12),rweibull(82,401,87),rgamma(90,40,19))
FIT1<-FDistUlt(RV, plot=TRUE, subplot = TRUE)
#> <simpleError in optim(par = vstart, fn = fnobj, fix.arg = fix.arg, obs = data, gr = gradient, ddistnam = ddistname, hessian = TRUE, method = meth, lower = lower, upper = upper, ...): non-finite finite-difference value [2]>
#> <simpleError in optim(par = vstart, fn = fnobj, fix.arg = fix.arg, obs = data, gr = gradient, pdistnam = pdistname, hessian = TRUE, method = meth, lower = lower, upper = upper, ...): non-finite finite-difference value [2]>
What is special about using README.Rmd instead of just README.md? You can include R chunks like so:
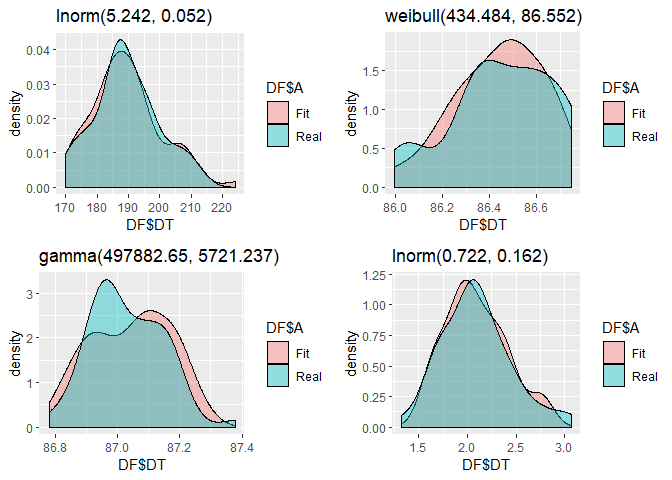
FIT1[[3]]
#> Distribucion Prop_dist AD_p.v KS_p.v Chs_p.v
#> AD6 lnorm(5.242, 0.052) 0.29795918 0.8372311 0.8985857 0
#> AD8 weibull(434.484, 86.552) 0.09387755 0.8861584 0.7938189 0
#> AD2 gamma(497882.65, 5721.237) 0.24081633 0.7523182 0.7705192 0
#> AD61 lnorm(0.722, 0.162) 0.36734694 0.9807500 0.9616154 0
You’ll still need to render README.Rmd regularly, to keep README.md up-to-date.
You can also embed plots, for example: