Parameter Estimation of Item Response Theory with Estimation of Latent Distribution.
Welcome to IRTest!
Please feel free tocreate an issuefor bug reports or potential improvements.
IRTest is a useful tool for $\mathcal{\color{red}{IRT}}$ (item response theory) parameter $\mathcal{\color{red}{est}}\textrm{imation}$, especially when the violation of normality assumption on latent distribution is suspected.
IRTest deals with uni-dimensional latent variable.
For missing values, IRTest adopts full information maximum likelihood (FIML) approach.
In IRTest, including the conventional usage of Gaussian distribution, several methods are available for estimation of latent distribution:
- empirical histogram method,
- two-component Gaussian mixture distribution,
- Davidian curve,
- kernel density estimation,
- log-linear smoothing.
Installation
The CRAN version of IRTest can be installed on R-console with:
install.packages("IRTest")
For the development version, it can be installed on R-console with:
devtools::install_github("SeewooLi/IRTest")
Functions
Followings are the functions of IRTest.
IRTest_Dichis the estimation function when items are dichotomously scored.IRTest_Polyis the estimation function when items are polytomously scored.IRTest_Contis the estimation function when items are continuously scored.IRTest_Mixis the estimation function for a mixed-format test, a test comprising both dichotomous item(s) and polytomous item(s).factor_scoreestimates factor scores of examinees.coef_sereturns standard errors of item parameter estimates.best_modelselects the best model using an evaluation criterion.item_fittests the statistical fit of all items individually.inform_f_itemcalculates the information value(s) of an item.inform_f_testcalculates the information value(s) of a test.plot_itemdraws item response function(s) of an item.reliabilitycalculates marginal reliability coefficient of IRT.latent_distributionreturns evaluated PDF value(s) of an estimated latent distribution.DataGenerationgenerates several objects that can be useful for computer simulation studies. Among these are simulated item parameters, ability parameters and the corresponding item-response data.dist2is a probability density function of two-component Gaussian mixture distribution.original_par_2GMconverts re-parameterized parameters of two-component Gaussian mixture distribution into original parameters.cat_clpsrecommends category collapsing based on item parameters (or, equivalently, item response functions).recategorizeimplements the category collapsing.For S3 methods,
anova,coef,logLik,plot,print, andsummaryare available.
Example
A simple simulation study for a 2PL model can be done in following manners:
library(IRTest)
- Data generation
An artificial data of 1000 examinees and 20 items.
Alldata <- DataGeneration(seed = 123456789,
model_D = 2,
N=1000,
nitem_D = 10,
latent_dist = "2NM",
m=0, # mean of the latent distribution
s=1, # s.d. of the latent distribution
d = 1.664,
sd_ratio = 2,
prob = 0.3)
data <- Alldata$data_D
item <- Alldata$item_D
theta <- Alldata$theta
colnames(data) <- paste0("item",1:10)
- Analysis
For an illustrative purpose, the two-component Gaussian mixture distribution (2NM) method is used for the estimation of latent distribution.
Mod1 <-
IRTest_Dich(
data = data,
latent_dist = "2NM"
)
- Summary of the result
summary(Mod1)
#> Convergence:
#> Successfully converged below the threshold of 1e-04 on 52nd iterations.
#>
#> Model Fit:
#> log-likeli -4786.734
#> deviance 9573.469
#> AIC 9619.469
#> BIC 9732.347
#> HQ 9662.37
#>
#> The Number of Parameters:
#> item 20
#> dist 3
#> total 23
#>
#> The Number of Items: 10
#>
#> The Estimated Latent Distribution:
#> method - 2NM
#> ----------------------------------------
#>
#>
#>
#> . @ @ .
#> . . @ @ @ @ .
#> @ @ @ . . . @ @ @ @ @ @
#> @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @
#> . @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @
#> @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ .
#> @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @
#> +---------+---------+---------+---------+
#> -2 -1 0 1 2
- Parameter estimation results
colnames(item) <- c("a", "b", "c")
knitr::kables(
list(
### True item parameters
knitr::kable(item, format='simple', caption = "True item parameters", digits = 2)%>%
kableExtra::kable_styling(font_size = 4),
### Estimated item parameters
knitr::kable(coef(Mod1), format='simple', caption = "Estimated item parameters", digits = 2)%>%
kableExtra::kable_styling(font_size = 4)
)
)
True item parameters |
Estimated item parameters |
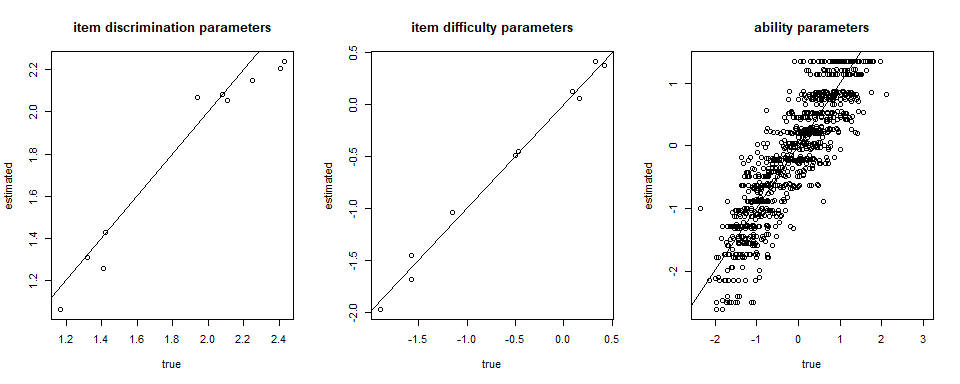
### Plotting
fscores <- factor_score(Mod1, ability_method = "MLE")
par(mfrow=c(1,3))
plot(item[,1], Mod1$par_est[,1], xlab = "true", ylab = "estimated", main = "item discrimination parameters")
abline(a=0,b=1)
plot(item[,2], Mod1$par_est[,2], xlab = "true", ylab = "estimated", main = "item difficulty parameters")
abline(a=0,b=1)
plot(theta, fscores$theta, xlab = "true", ylab = "estimated", main = "ability parameters")
abline(a=0,b=1)
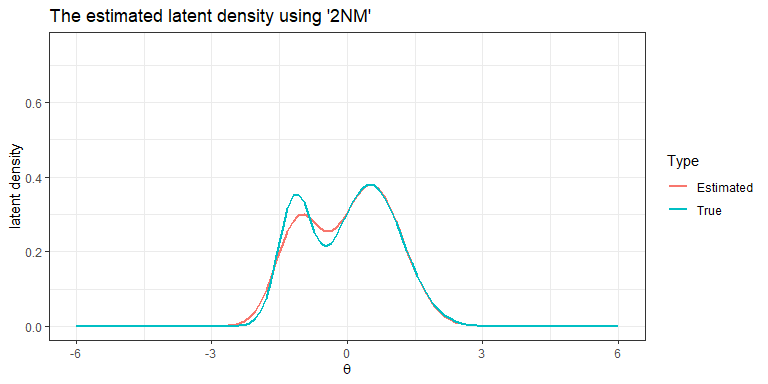
- The result of latent distribution estimation
plot(Mod1, mapping = aes(colour="Estimated"), linewidth = 1) +
stat_function(
fun = dist2,
args = list(prob = .3, d = 1.664, sd_ratio = 2),
mapping = aes(colour = "True"),
linewidth = 1) +
lims(y = c(0, .75)) +
labs(title="The estimated latent density using '2NM'", colour= "Type")+
theme_bw()
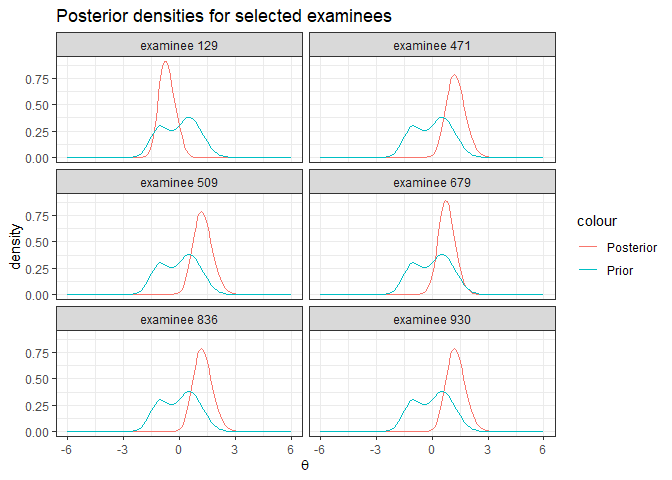
- Posterior distributions for the examinees
Each examinee’s posterior distribution is calculated in the E-step of EM algorithm. Posterior distributions can be found in Mod1$Pk.
set.seed(1)
selected_examinees <- sample(1:1000,6)
post_sample <-
data.frame(
X = rep(seq(-6,6, length.out=121),6),
prior = rep(Mod1$Ak/(Mod1$quad[2]-Mod1$quad[1]), 6),
posterior = 10*c(t(Mod1$Pk[selected_examinees,])),
ID = rep(paste("examinee", selected_examinees), each=121)
)
ggplot(data=post_sample, mapping=aes(x=X))+
geom_line(mapping=aes(y=posterior, group=ID, color='Posterior'))+
geom_line(mapping=aes(y=prior, group=ID, color='Prior'))+
labs(title="Posterior densities for selected examinees", x=expression(theta), y='density')+
facet_wrap(~ID, ncol=2)+
theme_bw()
- Item fit
item_fit(Mod1)
#> stat df p.value
#> item1 21.05639 5 0.0008
#> item2 39.02560 5 0.0000
#> item3 18.38326 5 0.0025
#> item4 26.05405 5 0.0001
#> item5 14.32893 5 0.0136
#> item6 38.58140 5 0.0000
#> item7 25.55899 5 0.0001
#> item8 14.43694 5 0.0131
#> item9 18.29131 5 0.0026
#> item10 65.25700 5 0.0000
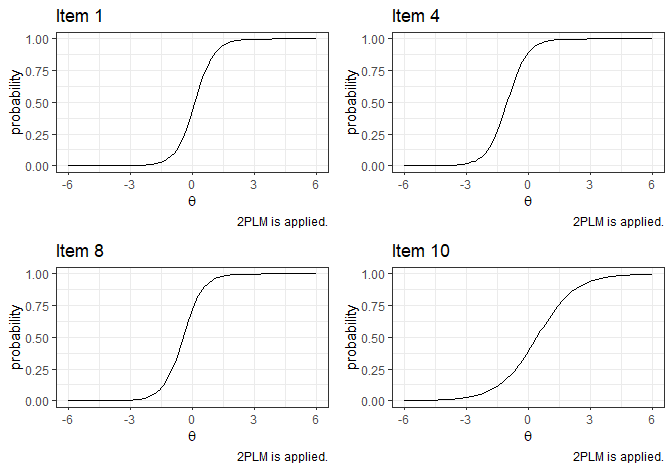
- Item response function
p1 <- plot_item(Mod1,1)
p2 <- plot_item(Mod1,4)
p3 <- plot_item(Mod1,8)
p4 <- plot_item(Mod1,10)
grid.arrange(p1, p2, p3, p4, ncol=2, nrow=2)
- Reliability
reliability(Mod1)
#> $summed.score.scale
#> $summed.score.scale$test
#> test reliability
#> 0.8133725
#>
#> $summed.score.scale$item
#> item1 item2 item3 item4 item5 item6 item7 item8
#> 0.4586843 0.3014154 0.3020563 0.3805659 0.1425990 0.4534580 0.2688948 0.4475414
#> item9 item10
#> 0.2661783 0.1963062
#>
#>
#> $theta.scale
#> test reliability
#> 0.7457047
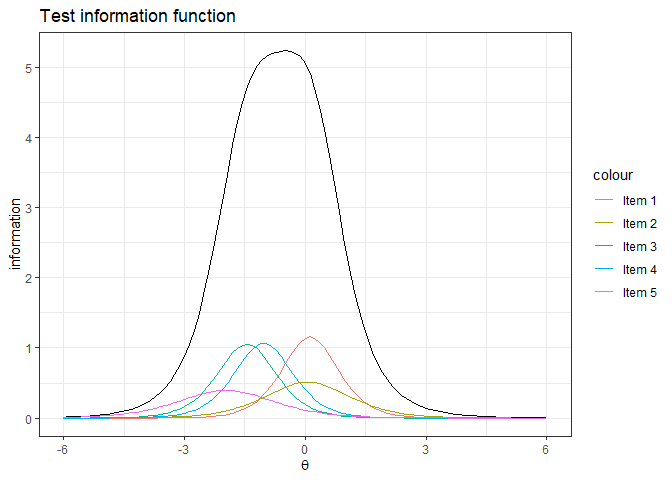
- Test information function
ggplot()+
stat_function(
fun = inform_f_test,
args = list(Mod1)
)+
stat_function(
fun=inform_f_item,
args = list(Mod1, 1),
mapping = aes(color="Item 1")
)+
stat_function(
fun=inform_f_item,
args = list(Mod1, 2),
mapping = aes(color="Item 2")
)+
stat_function(
fun=inform_f_item,
args = list(Mod1, 3),
mapping = aes(color="Item 3")
)+
stat_function(
fun=inform_f_item,
args = list(Mod1, 4),
mapping = aes(color="Item 4")
)+
stat_function(
fun=inform_f_item,
args = list(Mod1, 5),
mapping = aes(color="Item 5")
)+
lims(x=c(-6,6))+
labs(title="Test information function", x=expression(theta), y='information')+
theme_bw()