Genomic Breeding Tools: Genetic Variance Prediction and Cross-Validation.
PopVar
Introduction
To make progress in breeding, populations should have a favorable mean and high genetic variance (Bernardo 2010). These two parameters can be combined into a single measure called the usefulness criterion (Schnell and Utz 1975), visualized in Figure 1.
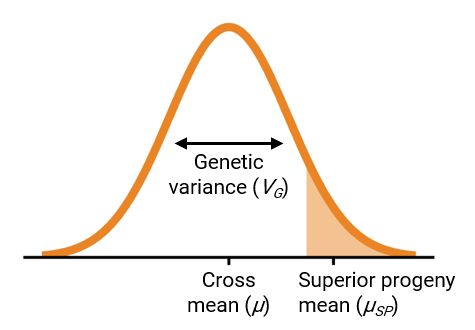
Ideally, breeders would identify the set of parent combinations that, when realized in a cross, would give rise to populations meeting these requirements. PopVar is a package that uses phenotypic and genomewide marker data on a set of candidate parents to predict the mean, genetic variance, and superior progeny mean in bi-parental or multi-parental populations. Thre package also contains functionality for performing cross-validation to determine the suitability of different statistical models. More details are available in Mohammadi, Tiede, and Smith (2015) A dataset think_barley is included for reference and examples.
Installation
You can install the released version of PopVar from CRAN with:
install.packages("PopVar")
And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("UMN-BarleyOatSilphium/PopVar")
Functions
Below is a description of the functions provided in PopVar:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
pop.predict | Uses simulations to make predictions in recombinant inbred line populations; can internally perform cross-validation for model selections; can be quite slow. |
pop.predict2 | Uses deterministic equations to make predictions in populations of complete or partial selfing and with or without the induction of doubled haploids; is much faster than pop.predict; does not perform cross-validation or model selection internally. |
pop_predict2 | Has the same functionality as pop.predict2, but accepts genomewide marker data in a simpler matrix format. |
x.val | Performs cross-validation to estimate model performance. |
mppop.predict | Uses deterministic equations to make predictions in 2- or 4-way populations of complete or partial selfing and with or without the induction of doubled haploids; does not perform cross-validation or model selection internally. |
mpop_predict2 | Has the same functionality as mppop.predict, but accepts genomewide marker data in a simpler matrix format. |
Examples
Examples are outlined in the package vignette.
References
Bernardo, Rex. 2010. Breeding for Quantitative Traits in Plants. Woodbury, Minnesota: Stemma Press.
Mohammadi, Mohsen, Tyler Tiede, and Kevin P Smith. 2015. “PopVar: A Genome-Wide Procedure for Predicting Genetic Variance and Correlated Response in Biparental Breeding Populations.” Crop Sci. 55 (5): 2068–77. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2015.01.0030.
Schnell, F W, and H F Utz. 1975. “F1-Leistung Und Elternwahl Euphyder züchtung von Selbstbefruchtern.” In Bericht über Die Arbeitstagung Der Vereinigung Österreichischer Pflanzenzüchter, 243–48. Gumpenstein, Austria: BAL Gumpenstein.