Read Paradox Database Files into R.
Rparadox: A Modern Interface for Reading Paradox Databases in R
Rparadox provides a simple and efficient way to read data from Paradox database files (.db) directly into R as modern tibble data frames. It uses the underlying pxlib C library to handle the low-level file format details and provides a clean, user-friendly R interface.
This package is designed to “just work” for the most common use case: extracting the full dataset from a Paradox table, including its associated BLOB/memo file (.mb).
Features
- Direct Reading: Reads Paradox
.dbfiles without needing database drivers or external software. - Tibble Output: Returns data in the
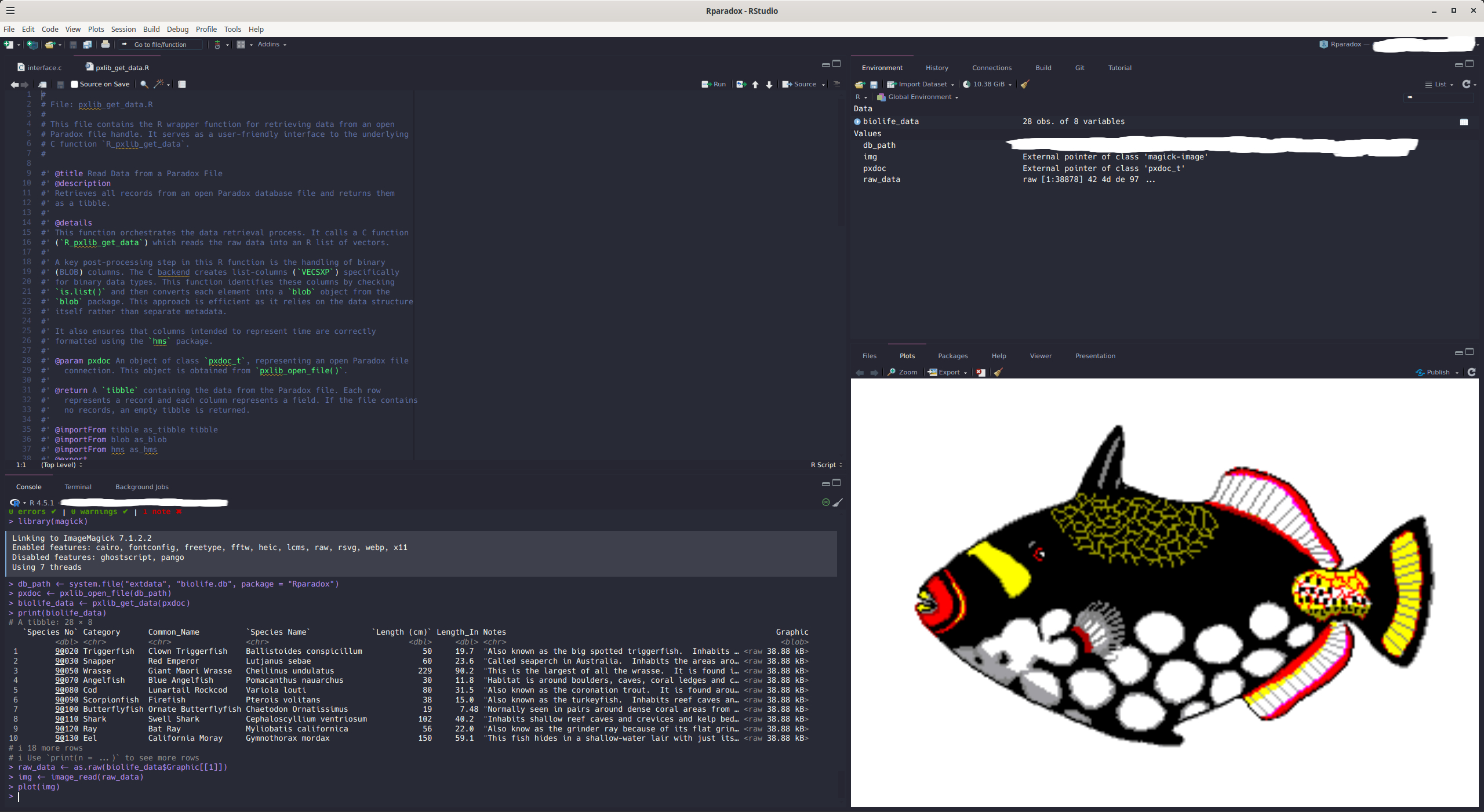
tibbleformat, which is fully compatible with the Tidyverse ecosystem. - Automatic BLOB Handling: Automatically detects, attaches, and reads data from associated memo/BLOB (
.mb) files. - Character Encoding Control: Automatically handles character encoding conversion to UTF-8 and allows the user to manually override the source encoding for files with incorrect headers.
- Type Conversion: Correctly maps Paradox data types to their corresponding R types, including
Date,Time(hms),Timestamp(POSIXct),Logical,Integer,Numeric, and binaryblobobjects.
Installation
# stable version from CRAN
install.packages("Rparadox")
You can install the development version of Rparadox from GitHub using the devtools package.
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("celebithil/Rparadox")
Usage
Basic Usage: The read_paradox() function
The easiest way to read a Paradox file is with the high-level read_paradox() function. It handles opening the file, reading the data, and closing the connection in a single step.
# 1. Load the package
library(Rparadox)
# 2. Get the path to an example database
db_path <- system.file("extdata", "biolife.db", package = "Rparadox")
# 3. Read the data directly into a tibble
# This automatically finds 'biolife.mb' and handles data types.
biolife_data <- read_paradox(db_path)
# 4. View the data
print(biolife_data)
#> # A tibble: 28 × 8
#> `Species No` Category Common_Name `Species Name` `Length (cm)` Length_In
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 90020 Triggerfish Clown Trig… Ballistoides … 50 19.7
#> 2 90030 Snapper Red Emperor Lutjanus sebae 60 23.6
#> 3 90050 Wrasse Giant Maor… Cheilinus und… 229 90.2
#> 4 90070 Angelfish Blue Angel… Pomacanthus n… 30 11.8
#> 5 90080 Cod Lunartail … Variola louti 80 31.5
#> 6 90090 Scorpionfish Firefish Pterois volit… 38 15.0
#> 7 90100 Butterflyfish Ornate But… Chaetodon Orn… 19 7.48
#> 8 90110 Shark Swell Shark Cephaloscylli… 102 40.2
#> 9 90120 Ray Bat Ray Myliobatis ca… 56 22.0
#> 10 90130 Eel California… Gymnothorax m… 150 59.1
#> # ℹ 18 more rows
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: Notes <chr>, Graphic <blob>
Handling Incorrect Character Encoding
If you have a legacy file where the encoding is specified incorrectly in the header, you can manually override it using the encoding parameter with read_paradox().
library(Rparadox)
# This tells the package to interpret the source data as CP866
data <- read_paradox("path/to/your/file.db", encoding = "cp866")
This ensures that all text fields are correctly converted to UTF-8 in the final tibble.
Advanced Usage
For more control, you can use the lower-level functions. This is useful if you want to inspect metadata before reading the full dataset.
library(Rparadox)
db_path <- system.file("extdata", "biolife.db", package = "Rparadox")
# 1. Open the file and get a handle
pxdoc <- pxlib_open_file(db_path)
if (!is.null(pxdoc)) {
# 2. Get metadata without reading all the data
metadata <- pxlib_metadata(pxdoc)
cat("Number of records:", metadata$num_records, "\n")
# 3. Read the actual data
data_table <- pxlib_get_data(pxdoc)
# 4. Always close the file when you're done
pxlib_close_file(pxdoc)
}
#> Number of records: 28
Links
- pxlib C library: https://github.com/steinm/pxlib
- CRAN page: https://cran.r-project.org/package=Rparadox
- Bug reports: https://github.com/celebithil/Rparadox/issues.