Retrieve Archived Web Pages from the 'Internet Archive'.
archiveRetriever 
R-Package to retrieve web data from the Internet Archive
The goal of the archiveRetriever package is to provide a systematic workflow for retrieving web data from mementos stored in the Internet Archive. Currently, the package includes the following functions:
archive_overviewgenerates a calendar providing an overview of the available mementos of the homepage in the Internet Archive within a specific time range. This function is very useful for getting a quick glimpse of the web data available when planning to retrieve a comprehensive coverage of the homepage from the Internet Archiveretrieve_urlsgenerates a vector of links to mementos of the homepage stored in the Internet Archive within a specific time range.retrieve_linksgenerates a tibble with two columns including the link to the memento of the homepage stored in the Internet Archive as well as all links within the memento. The two column translate to the parent link with its child references. This function is useful to fully cover the content within a homepage for retrieval.scrape_urlsgenerates a tibble including the link of the memento being scraped as well as the scraped content structured in different columns. The number of columns for the scraped content amounts to the length of the XPath or CSS selectors used to scrape the content.
We present a short step-by-step guide as well as the functions in more detail below.
How to cite this package
To cite the archiveRetriever package, you can use:
Isermann, Lukas; Gavras, Konstantin. (2024). archiveRetriever: Retrieve Archived Web Pages from the ‘Internet Archive’. R package version 0.4.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=archiveRetriever.
You can also access the preferred citation as well as the bibtex entry for the archiveRetriever Package via R:
citation("archiveRetriever")
#> To cite archiveRetriever in publications, please use:
#>
#> Lukas Isermann, & Konstantin Gavras. (2024). Archive Retriever:
#> Retrieve Archived Web Pages from the 'Internet Archive'.R package
#> version 0.4.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=archiveRetriever.
#>
#> Ein BibTeX-Eintrag für LaTeX-Benutzer ist
#>
#> @Misc{,
#> title = {Archive Retriever: Retrieve Archived Web Pages from the 'Internet Archive'},
#> author = {Lukas Isermann and Konstantin Gavras},
#> year = {2024},
#> note = {R package version 0.4.0},
#> doi = {10.5281/zenodo.11548776},
#> url = {https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=archiveRetriever},
#> }
Installation
A stable version of archiveRetriever can be directly accessed on CRAN:
install.packages("archiveRetriever", force = TRUE)
To install the latest development version of archiveRetriever directly from GitHub use:
library(devtools) # Tools to Make Developing R Packages Easier
devtools::install_github("liserman/archiveRetriever")
How to use this package
First, load the package
library(archiveRetriever) # Systematically retrieving web data from the Internet Archive
In the following, we are going to exemplify the workflow of the package using the mementos of the New York Times online version stored in the Internet Archive.
The workflow of the package follows a simple rule:
Get an overview of data availability in the Internet Archive
Retrieve the mementos of the base url from the Internet Archive
Retrieve the links within the base url from the memento stored in the Internet Archive (only necessary when scraping complete homepages)
Scrape the content and get it conveniently stored in tibbles.
Here, the functions retrieve_urls, retrieve_links and scrape_urls can build on each other, each function can take the output of the previous function as input to continue the work process.
archive_overview
As the Internet Archive is not able to archive the complete internet it is always important to check whether the memento of the homepage you want to scrape is actually available in the Internet Archive.
nytimes_overview <- archive_overview(homepage = "https://www.nytimes.com/",
startDate = "2020-10-01",
endDate = "2020-12-31")
The archive_overview function creates a calendar providing an overview of the homepage’s availability in the Internet Archive.
nytimes_overview
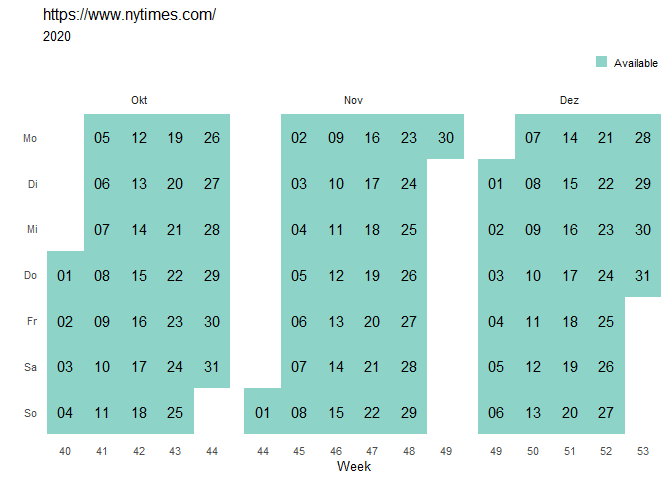
For the New York Times, we find that the Internet Archive save a memento of their homepage every day, which is highly reasonable as this homepage is one of the most visited homepages on the internet.
Next to base urls, the Internet Archive also stores child urls as mementos. Using the archive_overview function, it is of course also possible to get a calendar showing the availability of mementos of specific child urls (for example the article of the New York Times on the election of Joe Biden as 46. President of the USA).
nytimesArticle_overview <- archive_overview(homepage = "https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/07/us/politics/biden-election.html",
startDate = "2020-10-01",
endDate = "2020-12-31")
nytimesArticle_overview
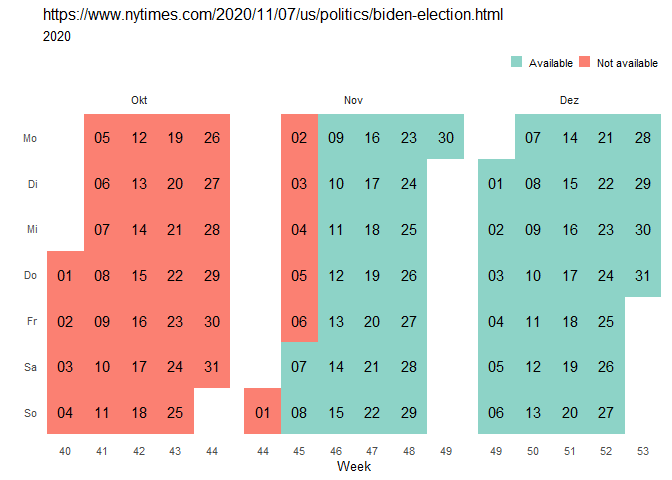
As the article has been published on November 07, there are of course no mementos available before that date.
retrieve_urls
The Internet Archive stores mementos of homepages in their archive which allows researchers to retrieve historical content from the internet or examine changes to existing homepages. Scraping content from the Internet Archive often requires retrieving mementos from a certain time range or specific points in time.
Applying the retrieve_urls function on a homepage results in a character vector of mementos of the homepage available from the Internet Archive.
nytimes_mementos <- retrieve_urls(homepage = "https://www.nytimes.com/",
startDate = "2020-10-01",
endDate = "2020-12-31")
nytimes_mementos[1:10]
#> [1] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/"
#> [2] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201002000016/http://nytimes.com/"
#> [3] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201003000006/https://nytimes.com/"
#> [4] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201004000201/https://www.nytimes.com/"
#> [5] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201005000047/http://nytimes.com/"
#> [6] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201006000036/http://nytimes.com/"
#> [7] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201007000202/https://www.nytimes.com/"
#> [8] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201008000222/https://www.nytimes.com/"
#> [9] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201009000201/https://www.nytimes.com/"
#> [10] "http://web.archive.org/web/20201010000605/http://nytimes.com/"
In the Internet Archive often more than one memento is stored each day. For convenience, retrieve_urls only retrieves one memento for each day. If you would like to retrieve all mementos stored in the Internet Archive in your requested time frame, you can use the option collapseDate to disable the automatic collapsing of the mementos.
nytimes_mementos <- retrieve_urls(homepage = "https://www.nytimes.com/",
startDate = "2020-10-01",
endDate = "2020-12-31",
collapseDate = FALSE)
retrieve_links
For many scraping applications, researchers aim to extract information from all links within a homepage to get a complete picture of the information stored, e.g. when scraping news content from online newspapers, blogs on Reddit or press releases published by political parties.
Sticking to the example of the New York Times, we extract all links of the memento stored on October 01, 2020 using the retrieve_links function. Please be aware that by default the retrieve_links function only takes mementos of the Internet Archive as input. If you want to use retrieve_links on web pages not on the Internet Archive, you can disable this limitation by setting the option nonArchive = TRUE.
nytimes_links <- retrieve_links(ArchiveUrls = "http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/")
The retrieve_links function results in a tibble with two columns, including the base url of the memento in the first column and all links in the second column. By default, the function filters links to be subpages to the top-level domain that has been scraped. This filtering can be disabled using the option filter = FALSE. Alternatively, the function also allows users to set a custom pattern by which links are filtered before output. However, users of this function might also decide to filter out links which do not point to content relevant for analysis using packages for string operations, such as stringr.
head(nytimes_links)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 2
#> baseUrl links
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
#> 2 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
#> 3 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
#> 4 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
#> 5 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
#> 6 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/ http://web…
Sometimes, some of the retrieved urls are unable to access, producing an error message. Especially when retrieving links from a larger body of archive-urls, you may not want your process to break due to these inaccessible urls. For this purpose, you can use the ignoreErrors option.
nytimes_links <- retrieve_links(ArchiveUrls = "http://web.archive.org/web/20201001000041/https://www.nytimes.com/", ignoreErrors = TRUE)
For some applications, it might not be necessary to include the retrieve_links function into the workflow. When only interested in one specific homepage, it can be sufficient to only retrieve the mementos using the retrieve_urls function.
scrape_urls
The scrape_urls function is the main function of the ArchiveRetriever package. The function takes a memento of the Internet Archive and a XPath (or CSS) vector as obligatory inputs and results in a tibble with the content scraped using the XPath/CSS selectors. Similarly to retrieve_links, the limitation to Internet Archive mementos in scrape_urls can be disabled using the option nonArchive = TRUE. There is one important point to consider when entering the Paths for scraping: The option only takes named vectors, in order to provide meaningful column names for the resulting tibbles.
nytimes_article <- scrape_urls(Urls = "http://web.archive.org/web/20201001004918/https://www.nytimes.com/2020/09/30/opinion/biden-trump-2020-debate.html",
Paths = c(title = "//h1[@itemprop='headline']",
author = "//span[@itemprop='name']",
date = "//time//text()",
article = "//section[@itemprop='articleBody']//p"))
nytimes_article
#> # A tibble: 1 × 5
#> Urls title author date article
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 http://web.archive.org/web/20201001004918/https://… Afte… Frank… Sept… "I was…
When using the scrape_urls function to scrape large amounts of urls, we added some important (optional) features, ensuring that the scraping process works smoothly. Most importantly, the process breaks when no content could be scraped for a certain number of urls (default is 10) - most often meaning that the XPaths have not been selected correctly. Additionally, the process breaks when only some elements of the Paths could be scraped - implying that the XPaths have changed for parts of the content aimed to be scraped. After break-off, the function still outputs a tibble, ensuring that the process does not need to be started anew. After break-off, users need to identify the element position of break-off, fix the error in the Paths and are able to re-start the scrape_urls function exactly where it broke off. The scraping process until break-off can be attached to the new process via the attachto option. Lastly, we also added a length warning for long url vector inserted to the scrape_urls raising awareness that a large chunk of data is now going to be scraped.
All these different break-offs can be deactivated using the optional arguments ignoreErrors = TRUE and stopatempty = FALSE. However, we advise to use these options with care. The cutoff point for the number of urls without content in a row until break-off can be set using emptylim. In order to facilitate the automation of the scraping process, we also added the optional argument lengthwarning = FALSE to deactivate the length warning.
In many scraping projects it is very convenient to collapse similar html-nodes into a single observation. We have also done this in the example outlined so far. This enabled us to retrieve the clean article text, filtering out all figures, advertisements, teasers and other annoying things newspapers put in between paragraphs. However, for some applications, we may want to treat similar html-nodes as independent observations. One example for this is the retrieving of article headlines and teasers from overview pages. For this purpose, scrape_urls offers the option collapse = FALSE. Instead of collapsing the content of similar html-nodes into one observation, different nodes are treated as independent observations. Yet, in order for this to work as intended, it is necessary that for all different Paths you extract in the same process, the number of retrieved nodes matches.
nytimes_teaser <- scrape_urls(Urls = "https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.com/section/politics",
Paths = c(title = "//article/div/h2//text()",
teaser = "//article/div/p/text()"),
collapse = FALSE)
nytimes_teaser
#> # A tibble: 4 × 3
#> Urls title teaser
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.c… Tues… Presi…
#> 2 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.c… Take… A New…
#> 3 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.c… Bide… A day…
#> 4 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.c… Six … It wa…
If we want to have even more control over what content gets collapsed into one observation and when scrape_urls starts a new observation, we can also set collapse to a structuring Xpath. This Xpath should be a parent node of the nodes we want to collapse. To demonstrate this, we take the example above, but this time use the article node as structuring Xpath.
nytimes_teaser <- scrape_urls(Urls = "https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://www.nytimes.com/section/politics",
Paths = c(title = "//h2//text()",
teaser = "//p/text()"),
collapse = "//article",
archiveDate = TRUE)
nytimes_teaser
#> # A tibble: 4 × 4
#> Urls title teaser archiveDate
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <date>
#> 1 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://w… Tues… Presi… 2020-10-01
#> 2 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://w… Take… A New… 2020-10-01
#> 3 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://w… Bide… A day… 2020-10-01
#> 4 https://web.archive.org/web/20201001000859/https://w… Six … It wa… 2020-10-01
Lastly, scrape_urls comes with a handy option archiveDate, to add a column indicating the date of the retrieved Internet Archive memento.