Label Creation for Tracking and Collecting Data from Biological Samples.
baRcodeR
baRcodeR generates labels for more repeatable workflows with biological samples
Installation
You can install the released version of baRcodeR from CRAN with:
install.packages("baRcodeR")
And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("ropensci/baRcodeR", build_vignettes = T)
# for windows users to build vignettes
# install_github("ropensci/baRcodeR", build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"), build_vignettes = TRUE)
NOTE: Restarting RStudio is necessary for the addin for baRcodeR to appear.
Quick Start
Text identifiers can be created in a sequential or hierarchical pattern.
library(baRcodeR)
## Loading required package: qrcode
example_labels <- uniqID_maker(user = FALSE, string = "Example", level = 1:80)
head(example_labels)
## label ind_string ind_number
## 1 Example001 Example 001
## 2 Example002 Example 002
## 3 Example003 Example 003
## 4 Example004 Example 004
## 5 Example005 Example 005
## 6 Example006 Example 006
Then the text identifiers can be printed out with a laser printer on sticker sheets.
pdf_file_name <- tempfile()
create_PDF(Labels = example_labels, name = pdf_file_name)

Th particular layout above defaults to ULINE 1.75” * 0.5” labels but other layouts can be specified through parameters in the custom_create_PDF function.
Introduction
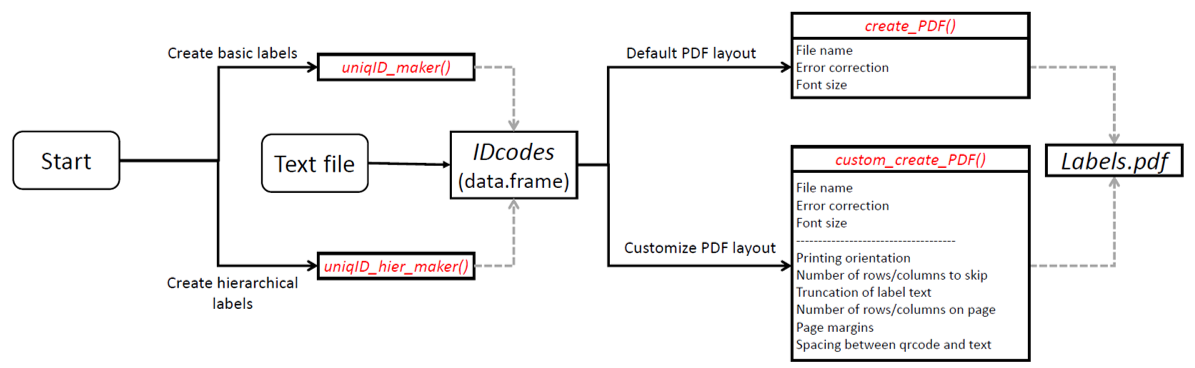
baRcodeR is a R package for generating unique identifier strings and printable 2D (QR) barcodes, with the aim of improving repeatability of labelling, tracking and curating data from biological samples. Specifically, users can:
- generate simple ID codes (Ex001, Ex002, Ex003 …),
- generate hierarchical (i.e. nested) ID codes (A01-B01, A01-B02, A02-B01, A02-B02, A03-B01 …),
- generate printable PDF files of paired ID codes and QR barcodes with default spacing for ULINE 1.75” * 0.5” WEATHER RESISTANT LABEL for laser printer; item # S-19297 (uline.ca)
- customize the PDF layout for any type of printable format (e.g, vinyl stickers, waterproof paper)
- generate reproducible code for archival purposes (e.g. in publications or online repositories)
- create CSV files to link unique IDs and sampling hierarchy with downstream data collection workflows. For example, the PyTrackDat pipeline can be used to set up a web-based data collection platform: https://github.com/pytrackdat/pytrackdat
Creating unique, scannable barcodes generally involves two steps:
- Generate unique ID codes with
uniqID_maker()oruniqID_hier_maker() - Create a PDF file containing unique ID codes coupled with 2D barcode using
create_PDF()
If you already have ID codes saved in a CSV file, the csv can be read into a data.frame() in R. The label column, if it exists will be used as input to generate barcodes. Otherwise, the first column in the data frame will be used.
NOTE: When printing from pdf, ensure that ‘anti-aliasing’ or ‘smoothing’ options are turned OFF, and that you are not using ‘fit to page’ or similar options that will re-scale the output.
Cheat Sheet
A 2-page, quick-reference guide is available via Figshare
Usage with RStudio addin
Please load the vignette “Use Addin”.
library(baRcodeR)
vignette("use-addin")
Usage from the console
Please load the vignette “Using-baRcodeR” for console use.
vignette("Using-baRcodeR")
Contribution
Please note that the ‘baRcodeR’ project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
Please document issues with a description, a minimal reproducible example, and the sessionInfo().
sessionInfo()
## R version 4.1.3 (2022-03-10)
## Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit)
## Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 22000)
##
## Matrix products: default
##
## locale:
## [1] LC_COLLATE=English_Canada.1252 LC_CTYPE=English_Canada.1252
## [3] LC_MONETARY=English_Canada.1252 LC_NUMERIC=C
## [5] LC_TIME=English_Canada.1252
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] baRcodeR_0.1.7 qrcode_0.1.4
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] png_0.1-7 assertthat_0.2.1 digest_0.6.29 R.methodsS3_1.8.1
## [5] magrittr_2.0.2 evaluate_0.15 highr_0.9 rlang_1.0.2
## [9] stringi_1.7.6 cli_3.2.0 rstudioapi_0.13 R.oo_1.24.0
## [13] R.utils_2.11.0 rmarkdown_2.13 tools_4.1.3 stringr_1.4.0
## [17] xfun_0.30 yaml_2.3.5 fastmap_1.1.0 compiler_4.1.3
## [21] htmltools_0.5.2 knitr_1.38
See also:
zintris an R interface to the C zint library. Use zintr if you want to create single barcode images. zintr does not include functions for (i) automating the creation of biologically-relevant, unique ID codes or (ii) customizable layouts for printing multiple barcodes.
zint is a C library that generates a variety of different barcodes. Just like zintr, zint produces single barcode images.