Description
Useful Functions for Data Processing.
Description
In ancient Chinese mythology, Bai Ze is a divine creature that knows the needs of everything. 'baizer' provides data processing functions frequently used by the author. Hope this package also knows what you want!
README.md
baizer 
- In ancient Chinese mythology, Bai Ze is a divine creature that knows the needs of everything.
baizerprovides data processing functions frequently used by the author.- Hope this package also knows what you want!
installation
universal installation
You can install the stable version of baizer like so:
install.packages("baizer")
Or install the development version of baizer like so:
devtools::install_github("william-swl/baizer")
specific installation
If you prefer Macports on MacOS:
sudo port install R-baizer
basic utils
- load packages as a batch
pkglib(dplyr, purrr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
- versions of packages
pkgver(dplyr, purrr)
#> $dplyr
#> [1] "1.1.1"
#>
#> $purrr
#> [1] "1.0.1"
# case-insensitive input
pkgver(DplyR)
#> $dplyr
#> [1] "1.1.1"
- information of packages
# pkginfo(dplyr)
# case-insensitive input
# pkginfo(DplyR)
- use
%nin%to get ‘not in’ logical value
1 %nin% c(1, 2, 3)
#> [1] FALSE
1 %nin% c(2, 3)
#> [1] TRUE
- use
%neq%to getNAsupported ‘not equal’ logical value
NA != 0
#> [1] NA
NA != NA
#> [1] NA
NA %neq% 0
#> [1] TRUE
NA %neq% NA
#> [1] FALSE
- not NA/NULL
not.na(NA)
#> [1] FALSE
not.null(NULL)
#> [1] FALSE
- dump a vector into string
collapse_vector(c("A" = 2, "B" = 3, "C" = 4), front_name = TRUE, collapse = ";")
#> [1] "A(2);B(3);C(4)"
collapse_vector(c("A" = 2, "B" = 3, "C" = 4), front_name = FALSE, collapse = ",")
#> [1] "2(A),3(B),4(C)"
- slice character vector
x <- c("A", "B", "C", "D", "E")
slice_char(x, "A", "D")
#> [1] "A" "B" "C" "D"
slice_char(x, "D", "A")
#> [1] "D" "C" "B" "A"
x <- c("A", "B", "C", "C", "A", "D", "D", "E", "A")
slice_char(x, "B", "E")
#> [1] "B" "C" "C" "A" "D" "D" "E"
# duplicated element as boundary will throw an error
# slice_char(x, 'A', 'E')
# unique=TRUE to remove the duplicated boundary characters
slice_char(x, "A", "E", unique = TRUE)
#> [1] "A" "B" "C" "C" "D" "D" "E"
- the index of different character
diff_index("AAAA", "ABBA")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 2 3
# ignore case
diff_index("AAAA", "abba", ignore_case = TRUE)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 2 3
# only the index of nth different character, NA if unaccessible
diff_index("AAAA", "ABBA", nth = 2)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 3
diff_index("AAAA", "ABBA", 10)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] NA
# second and third indices
diff_index("AAAA", "ABBB", nth = 2:3)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 3 4
# support vectorized operations
diff_index(c("ABBA", "AABB"), "AAAA")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 2 3
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 3 4
- the index of same character
# just like diff_index
same_index(c("ABBA", "AABB"), "AAAA")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 1 4
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 1 2
- fetch character from strings
fetch_char(rep("ABC", 3), list(1, 2, 3))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "A"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "B"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "C"
# accept the output of `diff_index` or `same_index`
str1 <- c("ABCD", "AAEF")
str2 <- c("AAAA", "AAAA")
fetch_char(str1, diff_index(str1, str2))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "B" "C" "D"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "E" "F"
# if the output of `diff_index` have NA, also return NA
fetch_char(str1, diff_index(str1, str2, nth = 1:3), na.rm = FALSE)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "B" "C" "D"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "E" "F" NA
# remove NA
fetch_char(str1, diff_index(str1, str2, nth = 1:5), na.rm = TRUE)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "B" "C" "D"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "E" "F"
# collapse the characters from a same string
fetch_char(str1, diff_index(str1, str2, nth = 1:5), na.rm = TRUE, collapse = ",")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "B,C,D"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "E,F"
- trans fixed string into regular expression string
fix_to_regex("ABC|?(*)")
#> [1] "ABC\\|\\?\\(\\*\\)"
- detect possible duplication in a vector, ignore case, blank and special character
detect_dup(c("a", "B", "C_", "c -", "#A"))
#> [1] "a" "#A" "C_" "c -"
- extract key and values for a character vector
extract_kv(c("x: 1", "y: 2"))
#> x y
#> "1" "2"
- farthest point sampling (FPS) for a vector
fps_vector(1:10, 2)
#> [1] 1 10
fps_vector(1:10, 4)
#> [1] 1 4 7 10
fps_vector(c(1, 2, NULL), 2)
#> [1] 1 2
fps_vector(c(1, 2, NA), 2)
#> [1] 1 NA
- regex match
v <- stringr::str_c("id", 1:3, c("A", "B", "C"))
v
#> [1] "id1A" "id2B" "id3C"
# return first group as default
reg_match(v, "id(\\d+)(\\w)")
#> [1] "1" "2" "3"
reg_match(v, "id(\\d+)(\\w)", group = 2)
#> [1] "A" "B" "C"
# when group=-1, return full matched tibble
reg_match(v, "id(\\d+)(\\w)", group = -1)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 3
#> match group1 group2
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 id1A 1 A
#> 2 id2B 2 B
#> 3 id3C 3 C
- join the matched parts into string
reg_join(c("A_12.B", "C_3.23:2"), "[A-Za-z]+")
#> [1] "AB" "C"
reg_join(c("A_12.B", "C_3.23:2"), "\\w+")
#> [1] "A_12B" "C_3232"
reg_join(c("A_12.B", "C_3.23:2"), "\\d+", sep = ",")
#> [1] "12" "3,23,2"
reg_join(c("A_12.B", "C_3.23:2"), "\\d", sep = ",")
#> [1] "1,2" "3,2,3,2"
- split vector into list
split_vector(1:10, c(3, 7))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 1 2 3
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 4 5 6 7
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] 8 9 10
vec <- stringr::str_split("ABCDEFGHIJ", "") %>% unlist()
vec
#> [1] "A" "B" "C" "D" "E" "F" "G" "H" "I" "J"
split_vector(vec, breaks = c(3, 7), bounds = "[)")
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "A" "B"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "C" "D" "E" "F"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "G" "H" "I" "J"
- group character vector by a regex pattern
v <- c(
stringr::str_c("A", c(1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, 99, 101, 102)),
stringr::str_c("B", c(1, 2, 9, 10, 21, 32, 99, 101, 102))
) %>% sample()
v
#> [1] "B2" "A10" "A99" "A9" "A2" "B102" "B1" "B101" "A101" "A1"
#> [11] "B10" "B9" "A11" "B21" "B32" "A12" "A102" "B99"
group_vector(v)
#> $A
#> [1] "A10" "A99" "A9" "A2" "A101" "A1" "A11" "A12" "A102"
#>
#> $B
#> [1] "B2" "B102" "B1" "B101" "B10" "B9" "B21" "B32" "B99"
group_vector(v, pattern = "\\w\\d")
#> $A1
#> [1] "A10" "A101" "A1" "A11" "A12" "A102"
#>
#> $A2
#> [1] "A2"
#>
#> $A9
#> [1] "A99" "A9"
#>
#> $B1
#> [1] "B102" "B1" "B101" "B10"
#>
#> $B2
#> [1] "B2" "B21"
#>
#> $B3
#> [1] "B32"
#>
#> $B9
#> [1] "B9" "B99"
# the pattern rules are just same as reg_match()
group_vector(v, pattern = "\\w(\\d)")
#> $`1`
#> [1] "A10" "B102" "B1" "B101" "A101" "A1" "B10" "A11" "A12" "A102"
#>
#> $`2`
#> [1] "B2" "A2" "B21"
#>
#> $`3`
#> [1] "B32"
#>
#> $`9`
#> [1] "A99" "A9" "B9" "B99"
# unmatched part will alse be stored
group_vector(v, pattern = "\\d{2}")
#> $`10`
#> [1] "A10" "B102" "B101" "A101" "B10" "A102"
#>
#> $`11`
#> [1] "A11"
#>
#> $`12`
#> [1] "A12"
#>
#> $`21`
#> [1] "B21"
#>
#> $`32`
#> [1] "B32"
#>
#> $`99`
#> [1] "A99" "B99"
#>
#> $unmatch
#> [1] "B2" "A9" "A2" "B1" "A1" "B9"
- sort by a function
sortf(c(-2, 1, 3), abs)
#> [1] 1 -2 3
v <- stringr::str_c("id", c(1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, 99, 101, 102)) %>% sample()
v
#> [1] "id10" "id99" "id1" "id12" "id101" "id102" "id9" "id2" "id11"
sortf(v, function(x) reg_match(x, "\\d+") %>% as.double())
#> [1] "id1" "id2" "id9" "id10" "id11" "id12" "id99" "id101" "id102"
# you can also use purrr functions
sortf(v, ~ reg_match(.x, "\\d+") %>% as.double())
#> [1] "id1" "id2" "id9" "id10" "id11" "id12" "id99" "id101" "id102"
# group before sort
v <- c(
stringr::str_c("A", c(1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, 99, 101, 102)),
stringr::str_c("B", c(1, 2, 9, 10, 21, 32, 99, 101, 102))
) %>% sample()
v
#> [1] "A2" "B101" "A99" "A102" "A1" "B2" "A10" "B102" "A11" "A101"
#> [11] "B9" "A12" "B10" "B1" "B32" "B21" "A9" "B99"
sortf(v, ~ reg_match(.x, "\\d+") %>% as.double(), group_pattern = "\\w")
#> [1] "A1" "A2" "A9" "A10" "A11" "A12" "A99" "A101" "A102" "B1"
#> [11] "B2" "B9" "B10" "B21" "B32" "B99" "B101" "B102"
- pileup another logical vector on the TRUE values of first vector
# first vector have 2 TRUE value
v1 <- c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE)
# the length of second vector should also be 2
v2 <- c(FALSE, TRUE)
pileup_logical(v1, v2)
#> [1] FALSE FALSE TRUE
- only keep unique vector values and its names
v <- c(a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, b = 2, a = 1)
# unique will lost the names
unique(v)
#> [1] 1 2 3
# uniq can keep them
uniq(v)
#> a b c
#> 1 2 3
- replace the items of one object by another
x <- list(A = 1, B = 3)
y <- list(A = 9, C = 10)
replace_item(x, y)
#> $A
#> [1] 9
#>
#> $B
#> [1] 3
replace_item(x, y, keep_extra = TRUE)
#> $A
#> [1] 9
#>
#> $B
#> [1] 3
#>
#> $C
#> [1] 10
x <- list(a = 1, b = list(c = "a", d = FALSE, f = list(x = 0, z = 30)))
y <- list(a = 3, e = 2, b = list(d = TRUE, f = list(x = 10, y = 20)))
replace_item(x, y, keep_extra = TRUE)
#> $a
#> [1] 3
#>
#> $b
#> $b$c
#> [1] "a"
#>
#> $b$d
#> [1] TRUE
#>
#> $b$f
#> $b$f$x
#> [1] 10
#>
#> $b$f$z
#> [1] 30
#>
#> $b$f$y
#> [1] 20
#>
#>
#>
#> $e
#> [1] 2
- generate characters
gen_char(from = "g", n = 5)
#> [1] "g" "h" "i" "j" "k"
gen_char(to = "g", n = 5)
#> [1] "c" "d" "e" "f" "g"
gen_char(from = "g", to = "j")
#> [1] "g" "h" "i" "j"
gen_char(from = "t", n = 5, random = TRUE)
#> [1] "z" "y" "t" "u" "y"
gen_char(from = "x", n = 5, random = TRUE, allow_dup = FALSE, add = c("+", "-"))
#> [1] "y" "z" "-" "+" "x"
- trans range character into seq characters
rng2seq(c("1-5", "2"))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "1" "2" "3" "4" "5"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "2"
- return top n items with highest frequency
top_item(c("a", "b", "c", "b"))
#> [1] "b"
top_item(c(1, 2, 3, 2, 2))
#> [1] 2
- melt a vector into single value
melt_vector(c(NA, 2, 3), method = "first")
#> [1] 2
melt_vector(c(NA, 2, 3), method = "sum")
#> [1] 5
melt_vector(c(NA, 2, 3), method = ",")
#> [1] "2,3"
melt_vector(c(NA, 2, Inf), invalid = c(NA, Inf))
#> [1] 2
- combine multiple vectors into one
x1 <- c(1, 2, NA, NA)
x2 <- c(3, NA, 2, NA)
x3 <- c(4, NA, NA, 3)
combn_vector(x1, x2, x3, method = "sum")
#> [1] 8 2 2 3
- broadcast the vector into length n
broadcast_vector(1:3, 5)
#> [1] 1 2 3 1 2
- replace specific characters in a string by their locations
str_replace_loc("abcde", 1, 3, "A")
#> [1] "Ade"
- swap the names and values of a vector
v <- c("a" = "A", "b" = "B", "c" = "C")
swap_vecname(v)
#> A B C
#> "a" "b" "c"
numbers
- from float number to fixed digits character
round(2.1951, 2)
#> [1] 2.2
round_string(2.1951, 2)
#> [1] "2.20"
signif(2.1951, 3)
#> [1] 2.2
signif_string(2.1951, 3)
#> [1] "2.20"
- signif or round string depend on the character length
signif_round_string(20.526, 2, "short")
#> [1] "21"
signif_round_string(20.526, 2, "long")
#> [1] "20.53"
# if you want keep the very small value
signif_round_string(0.000002654, 3, full_small = TRUE)
#> [1] "0.00000265"
- signif while use floor/ceiling
signif_floor(3.19, 2)
#> [1] 3.1
signif_ceiling(3.11, 2)
#> [1] 3.2
- whether the number string only has zero
is.zero("0.000")
#> [1] TRUE
is.zero("0.0001")
#> [1] FALSE
- float and percent trans
float_to_percent(0.123, digits = 1)
#> [1] "12.3%"
percent_to_float("123%", digits = 3)
#> [1] "1.230"
percent_to_float("123%", digits = 3, to_double = TRUE)
#> [1] 1.23
- wrapper of the functions to process number string with prefix and suffix
number_fun_wrapper(">=2.134%", function(x) round(x, 2))
#> [1] ">=2.13%"
- expand a number vector according to the adjacent two numbers
adjacent_div(10^c(1:3), n_div = 10)
#> [1] 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500
#> [16] 600 700 800 900 1000
# only keep the unique numbers
adjacent_div(10^c(1:3), n_div = 10, .unique = TRUE)
#> [1] 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 200 300 400 500 600
#> [16] 700 800 900 1000
- correct the numbers to a target ratio
correct_ratio(c(10, 10), c(3, 5))
#> [1] 6 10
# support ratio as a float
correct_ratio(c(100, 100), c(0.2, 0.8))
#> [1] 25 100
# more numbers
correct_ratio(10:13, c(2, 3, 4, 6))
#> [1] 4 6 9 13
# with digits after decimal point
correct_ratio(c(10, 10), c(1, 4), digits = 1)
#> [1] 2.5 10.0
- the ticks near a number
near_ticks(3462, level = 10)
#> [1] 3460 3465 3470
- the nearest ticks around a number
nearest_tick(3462, level = 10)
#> [1] 3460
- generate ticks for a number vector
generate_ticks(c(176, 198, 264))
#> [1] 175 185 195 205 215 225 235 245 255 265
- split a positive integer number as a number vector
pos_int_split(12, 3, method = "average")
#> [1] 4 4 4
pos_int_split(12, 3, method = "random")
#> [1] 6 1 5
# you can also assign the ratio of output
pos_int_split(12, 3, method = c(1, 2, 3))
#> [1] 2 4 6
- generate outliers from a series of number
x <- seq(0, 100, 1)
gen_outlier(x, 10)
#> [1] -104 -112 -115 -145 -179 219 253 210 263 189
# generation limits
gen_outlier(x, 10, lim = c(-80, 160))
#> [1] -64 -68 -60 -75 -66 157 153 154 158 159
# assign the low and high outliers
gen_outlier(x, 10, lim = c(-80, 160), assign_n = c(0.1, 0.9))
#> [1] -70 156 159 156 153 155 151 156 151 157
# just generate low outliers
gen_outlier(x, 10, side = "low")
#> [1] -190 -164 -196 -161 -105 -144 -149 -110 -102 -89
# return with raw vector
gen_outlier(x, 10, only_out = FALSE)
#> [1] -143 -122 -61 -76 -54 161 199 276 251 195 0 1 2 3 4
#> [16] 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
#> [31] 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
#> [46] 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49
#> [61] 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64
#> [76] 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79
#> [91] 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94
#> [106] 95 96 97 98 99 100
- max-min normalization
mm_norm(c(1, 3, 4))
#> [1] 0.0000000 0.6666667 1.0000000
dataframe
- a minimal dataset
head(mini_diamond)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 4 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 5 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 6 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
- shortcut of
dplyr::column_to_rownamesanddplyr::rownames_to_column
head(mini_diamond) %>% c2r("id")
#> carat cut clarity price x y
#> id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
# use column index
head(mini_diamond) %>% c2r(1)
#> carat cut clarity price x y
#> id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
head(mini_diamond) %>%
c2r("id") %>%
r2c("id")
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 4 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 5 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 6 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
- fancy count to show an extended column
# count one column
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 3
#> cut n r
#> <chr> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35
#> 2 Good 31 0.31
#> 3 Ideal 34 0.34
# count an extended column
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, ext = clarity)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> cut n r clarity
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35 I1(5),IF(4),SI1(5),SI2(4),VS1(3),VS2(5),VVS1(5),VVS2(4)
#> 2 Good 31 0.31 I1(5),IF(5),SI1(4),SI2(4),VS1(2),VS2(4),VVS1(4),VVS2(3)
#> 3 Ideal 34 0.34 I1(4),IF(4),SI1(5),SI2(4),VS1(5),VS2(2),VVS1(5),VVS2(5)
# change format
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, ext = clarity, ext_fmt = "ratio")
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> cut n r clarity
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35 I1(0.14),IF(0.11),SI1(0.14),SI2(0.11),VS1(0.09),VS2(0.14),V…
#> 2 Good 31 0.31 I1(0.16),IF(0.16),SI1(0.13),SI2(0.13),VS1(0.06),VS2(0.13),V…
#> 3 Ideal 34 0.34 I1(0.12),IF(0.12),SI1(0.15),SI2(0.12),VS1(0.15),VS2(0.06),V…
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, ext = clarity, ext_fmt = "clean")
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> cut n r clarity
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35 I1,IF,SI1,SI2,VS1,VS2,VVS1,VVS2
#> 2 Good 31 0.31 I1,IF,SI1,SI2,VS1,VS2,VVS1,VVS2
#> 3 Ideal 34 0.34 I1,IF,SI1,SI2,VS1,VS2,VVS1,VVS2
# count an extended column, in an order by n
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, ext = clarity, sort = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> cut n r clarity
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35 I1(5),SI1(5),VS2(5),VVS1(5),IF(4),SI2(4),VVS2(4),VS1(3)
#> 2 Ideal 34 0.34 SI1(5),VS1(5),VVS1(5),VVS2(5),I1(4),IF(4),SI2(4),VS2(2)
#> 3 Good 31 0.31 I1(5),IF(5),SI1(4),SI2(4),VS2(4),VVS1(4),VVS2(3),VS1(2)
# extended column after a two-column count
fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, clarity, ext = id) %>% head(5)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 5
#> cut clarity n r id
#> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair I1 5 0.05 id-20(1),id-23(1),id-28(1),id-32(1),id-48(1)
#> 2 Fair IF 4 0.04 id-12(1),id-45(1),id-89(1),id-95(1)
#> 3 Fair SI1 5 0.05 id-1(1),id-64(1),id-65(1),id-68(1),id-76(1)
#> 4 Fair SI2 4 0.04 id-25(1),id-40(1),id-6(1),id-99(1)
#> 5 Fair VS1 3 0.03 id-36(1),id-43(1),id-85(1)
- count two columns as a cross-tabulation table
cross_count(mini_diamond, cut, clarity)
#> I1 IF SI1 SI2 VS1 VS2 VVS1 VVS2
#> Fair 5 4 5 4 3 5 5 4
#> Good 5 5 4 4 2 4 4 3
#> Ideal 4 4 5 4 5 2 5 5
# show the ratio in the row
cross_count(mini_diamond, cut, clarity, method = "rowr")
#> I1 IF SI1 SI2 VS1 VS2 VVS1 VVS2
#> Fair 0.14 0.11 0.14 0.11 0.09 0.14 0.14 0.11
#> Good 0.16 0.16 0.13 0.13 0.06 0.13 0.13 0.10
#> Ideal 0.12 0.12 0.15 0.12 0.15 0.06 0.15 0.15
# show the ratio in the col
cross_count(mini_diamond, cut, clarity, method = "colr")
#> I1 IF SI1 SI2 VS1 VS2 VVS1 VVS2
#> Fair 0.36 0.31 0.36 0.33 0.3 0.45 0.36 0.33
#> Good 0.36 0.38 0.29 0.33 0.2 0.36 0.29 0.25
#> Ideal 0.29 0.31 0.36 0.33 0.5 0.18 0.36 0.42
- split a column and return a longer tibble
df <- fancy_count(mini_diamond, cut, ext = clarity)
head(df)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> cut n r clarity
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 Fair 35 0.35 I1(5),IF(4),SI1(5),SI2(4),VS1(3),VS2(5),VVS1(5),VVS2(4)
#> 2 Good 31 0.31 I1(5),IF(5),SI1(4),SI2(4),VS1(2),VS2(4),VVS1(4),VVS2(3)
#> 3 Ideal 34 0.34 I1(4),IF(4),SI1(5),SI2(4),VS1(5),VS2(2),VVS1(5),VVS2(5)
split_column(df, name_col = cut, value_col = clarity)
#> # A tibble: 24 × 2
#> cut clarity
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 Fair I1(5)
#> 2 Fair IF(4)
#> 3 Fair SI1(5)
#> 4 Fair SI2(4)
#> 5 Fair VS1(3)
#> 6 Fair VS2(5)
#> 7 Fair VVS1(5)
#> 8 Fair VVS2(4)
#> 9 Good I1(5)
#> 10 Good IF(5)
#> # … with 14 more rows
- move selected rows to target location
# move row 3-5 after row 8
move_row(mini_diamond, 3:5, .after = 8)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 4 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07
#> 5 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 6 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 7 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 8 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 9 id-9 1.01 Ideal SI1 5590 6.43 6.4
#> 10 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41
#> # … with 90 more rows
# move row 3-5 before the first row
move_row(mini_diamond, 3:5, .before = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 3 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 4 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 5 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 6 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 7 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07
#> 8 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 9 id-9 1.01 Ideal SI1 5590 6.43 6.4
#> 10 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41
#> # … with 90 more rows
# move row 3-5 after the last row
move_row(mini_diamond, 3:5, .after = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 4 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07
#> 5 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 6 id-9 1.01 Ideal SI1 5590 6.43 6.4
#> 7 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41
#> 8 id-11 1.02 Good VVS1 7861 6.37 6.4
#> 9 id-12 0.71 Fair IF 3205 5.87 5.81
#> 10 id-13 0.56 Ideal SI1 1633 5.31 5.32
#> # … with 90 more rows
- slice a tibble by an ordered vector
ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2"))
#> # A tibble: 2 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
# support NA and known values in ordered vector
ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", "id-3", NA))
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> NA values!
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> duplicated values!
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 <NA> NA <NA> <NA> NA NA NA
#> 4 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 5 <NA> NA <NA> <NA> NA NA NA
# remove NA
ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", "id-3", NA),
na.rm = TRUE
)
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> NA values!
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> duplicated values!
#> # A tibble: 3 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
# remove duplication
ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", "id-3", NA),
dup.rm = TRUE
)
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> NA values!
#> Warning in ordered_slice(mini_diamond, id, c("id-3", "id-2", "unknown_id", : 2
#> duplicated values!
#> # A tibble: 3 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 <NA> NA <NA> <NA> NA NA NA
- remove columns by the ratio of
NA, default to remove the columns only haveNA
df_with_nacol <- dplyr::bind_cols(
mini_diamond,
tibble::tibble(na1 = NA, na2 = NA)
)
df_with_nacol
#> # A tibble: 100 × 9
#> id carat cut clarity price x y na1 na2
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl> <lgl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18 NA NA
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18 NA NA
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18 NA NA
#> 4 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45 NA NA
#> 5 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77 NA NA
#> 6 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37 NA NA
#> 7 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07 NA NA
#> 8 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08 NA NA
#> 9 id-9 1.01 Ideal SI1 5590 6.43 6.4 NA NA
#> 10 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41 NA NA
#> # … with 90 more rows
remove_nacol(df_with_nacol)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 4 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 5 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 6 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 7 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07
#> 8 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 9 id-9 1.01 Ideal SI1 5590 6.43 6.4
#> 10 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41
#> # … with 90 more rows
# only keep the columns that have less than 20% NA values
# remove_nacol(df_with_nacol, max_ratio=0.2)
- remove rows by the ratio of NA
# remove_narow(df)
- remove columns by the ratio of an identical single value (NA supported)
df_with_monocol <- tibble::tibble(
x = c(1, 1, 1, 2),
y = c(1, 1, 2, 2),
z = c(1, 1, 1, 1),
x1 = c(1, 1, 1, NA),
y1 = c(1, 1, NA, NA),
z1 = c(NA, NA, NA, NA),
x2 = c(NA, NA, NA, 1),
y2 = c(NA, NA, 1, 1)
)
df_with_monocol
#> # A tibble: 4 × 8
#> x y z x1 y1 z1 x2 y2
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 1 1 1 1 NA NA NA
#> 2 1 1 1 1 1 NA NA NA
#> 3 1 2 1 1 NA NA NA 1
#> 4 2 2 1 NA NA NA 1 1
remove_monocol(df_with_monocol)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 6
#> x y x1 y1 x2 y2
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 1 1 1 NA NA
#> 2 1 1 1 1 NA NA
#> 3 1 2 1 NA NA 1
#> 4 2 2 NA NA 1 1
# only keep the columns that have less than 60% identical values
remove_monocol(df_with_monocol, max_ratio = 0.6)
#> # A tibble: 4 × 3
#> y y1 y2
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 1 NA
#> 2 1 1 NA
#> 3 2 NA 1
#> 4 2 NA 1
- separate numeric vector into bins
vector <- dplyr::pull(mini_diamond, price, id)
hist_bins(vector)
#> # A tibble: 100 × 5
#> id value start end bin
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 id-1 3027 2218. 3975. 2
#> 2 id-2 11746 11000. 12757. 7
#> 3 id-3 2029 462 2218. 1
#> 4 id-4 9452 9244 11000. 6
#> 5 id-5 2498 2218. 3975. 2
#> 6 id-6 14080 12757. 14513. 8
#> 7 id-7 752 462 2218. 1
#> 8 id-8 1029 462 2218. 1
#> 9 id-9 5590 3975. 5731. 3
#> 10 id-10 1691 462 2218. 1
#> # … with 90 more rows
# set the max and min limits
hist_bins(vector, bins = 20, lim = c(0, 20000))
#> # A tibble: 100 × 5
#> id value start end bin
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 id-1 3027 3000 4000 4
#> 2 id-2 11746 11000 12000 12
#> 3 id-3 2029 2000 3000 3
#> 4 id-4 9452 9000 10000 10
#> 5 id-5 2498 2000 3000 3
#> 6 id-6 14080 14000 15000 15
#> 7 id-7 752 0 1000 1
#> 8 id-8 1029 1000 2000 2
#> 9 id-9 5590 5000 6000 6
#> 10 id-10 1691 1000 2000 2
#> # … with 90 more rows
# or pass breaks directly
hist_bins(vector, breaks = seq(0, 20000, length.out = 11))
#> # A tibble: 100 × 5
#> id value start end bin
#> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
#> 1 id-1 3027 2000 4000 2
#> 2 id-2 11746 10000 12000 6
#> 3 id-3 2029 2000 4000 2
#> 4 id-4 9452 8000 10000 5
#> 5 id-5 2498 2000 4000 2
#> 6 id-6 14080 14000 16000 8
#> 7 id-7 752 0 2000 1
#> 8 id-8 1029 0 2000 1
#> 9 id-9 5590 4000 6000 3
#> 10 id-10 1691 0 2000 1
#> # … with 90 more rows
- trans a table in markdown format into tibble
x <- "
| col1 | col2 | col3 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| v1 | v2 | v3 |
| r1 | r2 | r3 |
"
as_tibble_md(x)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> col1 col2 col3
#> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 v1 v2 v3
#> 2 r1 r2 r3
- trans a tibble into markdown format table
mini_diamond %>%
head(5) %>%
as_md_table()
#> | id | carat | cut | clarity | price | x | y |
#> | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
#> | id-1 | 1.02 | Fair | SI1 | 3027 | 6.25 | 6.18 |
#> | id-2 | 1.51 | Good | VS2 | 11746 | 7.27 | 7.18 |
#> | id-3 | 0.52 | Ideal | VVS1 | 2029 | 5.15 | 5.18 |
#> | id-4 | 1.54 | Ideal | SI2 | 9452 | 7.43 | 7.45 |
#> | id-5 | 0.72 | Ideal | VS1 | 2498 | 5.73 | 5.77 |
- relevel a target column by another reference column
cut_level <- mini_diamond %>%
pull(cut) %>%
unique()
df <- mini_diamond %>%
dplyr::mutate(cut = factor(cut, cut_level)) %>%
dplyr::mutate(cut0 = stringr::str_c(cut, "xxx"))
levels(df$cut)
#> [1] "Fair" "Good" "Ideal"
levels(df$cut0)
#> NULL
# after relevel
df <- ref_level(df, cut0, cut)
levels(df$cut)
#> [1] "Fair" "Good" "Ideal"
levels(df$cut0)
#> [1] "Fairxxx" "Goodxxx" "Idealxxx"
- trans list into tibble
x <- list(
c("a", "1"),
c("b", "2"),
c("c", "3")
)
list2df(x, colnames = c("char", "num"))
#> char num
#> It1 a 1
#> It2 b 2
#> It3 c 3
x <- list(
c("a", "b", "c"),
c("1", "2", "3")
)
list2df(x, method = "col")
#> It1 It2
#> 1 a 1
#> 2 b 2
#> 3 c 3
- generate a matrix to show whether the item in each element of a list
x <- 1:5 %>% map(~ gen_char(to = "k", n = 5, random = TRUE, seed = .x))
x
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "i" "d" "g" "a" "b"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "e" "f" "f" "h" "a"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "e" "j" "g" "d" "j"
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] "h" "k" "c" "c" "g"
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] "b" "k" "i" "k" "i"
exist_matrix(x)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 11
#> g i k a b c d e f h j
#> * <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl>
#> 1 TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> 2 FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE
#> 3 TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
#> 4 TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE
#> 5 FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE
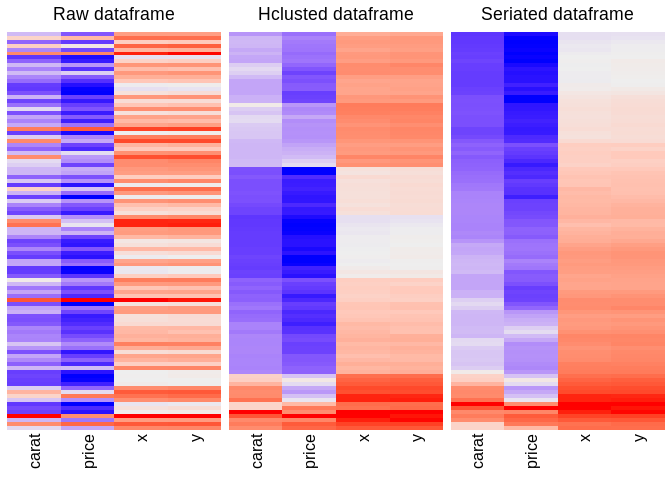
- dataframe rows seriation, which will reorder the rows in a better pattern. Sometimes clearer than
hclust
seriated_df <- seriate_df(df)
- diagnosis a tibble for character NA, NULL, all T/F column, blank in cell
x <- tibble(
c1 = c("NA", NA, "a", "b"),
c2 = c("c", "d", "e", "NULL"),
c3 = c("T", "F", "F", "T"),
c4 = c("T", "F", "F", NA),
c5 = c("", " ", "\t", "\n")
)
x
#> # A tibble: 4 × 5
#> c1 c2 c3 c4 c5
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 NA c T T ""
#> 2 <NA> d F F " "
#> 3 a e F F "\t"
#> 4 b NULL T <NA> "\n"
dx_tb(x)
#> $chr_na
#> # A tibble: 1 × 2
#> row col
#> <int> <int>
#> 1 1 1
#>
#> $chr_null
#> # A tibble: 1 × 2
#> row col
#> <int> <int>
#> 1 4 2
#>
#> $only_tf
#> [1] 3 4
#>
#> $blank_in_cell
#> [1] " " "\t" "\n"
#>
#> $stat
#> chr_na chr_null only_tf blank_in_cell
#> 1 1 2 3
#>
#> $pass
#> [1] FALSE
- generate tibbles
gen_tb()
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> V1 V2 V3 V4
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 -3.19 0.406 -1.44 0.240
#> 2 -0.196 1.36 0.466 -0.304
#> 3 -0.326 0.262 0.705 1.31
gen_tb(fill = "str", nrow = 3, ncol = 4, len = 3)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> V1 V2 V3 V4
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 slt imb kou cha
#> 2 xce qbu dlx qmr
#> 3 yhh xir fze egv
- differences between two tibbles
tb1 <- gen_tb(fill = "int", seed = 1)
tb1
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> V1 V2 V3 V4
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 -7 15 4 -4
#> 2 1 3 7 15
#> 3 -9 -9 5 3
tb2 <- gen_tb(fill = "int", seed = 3)
tb2
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> V1 V2 V3 V4
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 -10 -12 0 12
#> 2 -3 1 11 -8
#> 3 2 0 -13 -12
diff_tb(tb1, tb2)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 6
#> .diff_type .diff V1 V2 V3 V4
#> <chr> <glue> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 c -old[1, ] -7 15 4 -4
#> 2 c +new[1, ] -10 -12 0 12
#> 3 c -old[2, ] 1 3 7 15
#> 4 c +new[2, ] -3 1 11 -8
#> 5 c -old[3, ] -9 -9 5 3
#> 6 c +new[3, ] 2 0 -13 -12
- transpose a dataframe
tdf(c2r(head(mini_diamond), "id"))
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> item `id-1` `id-2` `id-3` `id-4` `id-5` `id-6`
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 carat "1.02" 1.51 "0.52" "1.54" "0.72" 2.02
#> 2 cut "Fair" Good "Ideal" "Ideal" "Ideal" Fair
#> 3 clarity "SI1" VS2 "VVS1" "SI2" "VS1" SI2
#> 4 price " 3027" 11746 " 2029" " 9452" " 2498" 14080
#> 5 x "6.25" 7.27 "5.15" "7.43" "5.73" 8.33
#> 6 y "6.18" 7.18 "5.18" "7.45" "5.77" 8.37
- count unique values in each column
uniq_in_cols(mini_diamond)
#> # A tibble: 7 × 2
#> col uniqe_values
#> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 id 100
#> 2 carat 57
#> 3 cut 3
#> 4 clarity 8
#> 5 price 99
#> 6 x 89
#> 7 y 87
- like
left_join(), full_join(), inner_join()while ignore the same columns in right tibble
tb1 <- head(mini_diamond, 4)
tb2 <- tibble(
id = c("id-2", "id-4", "id-5"),
carat = 1:3,
price = c(1000, 2000, 3000),
newcol = c("new2", "new4", "new5")
)
left_expand(tb1, tb2, by = "id")
#> # A tibble: 4 × 8
#> id carat cut clarity price x y newcol
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18 <NA>
#> 2 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18 new2
#> 3 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18 <NA>
#> 4 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45 new4
inner_expand(tb1, tb2, by = "id")
#> # A tibble: 2 × 8
#> id carat cut clarity price x y newcol
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18 new2
#> 2 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45 new4
- rewrite the NA values in a tibble by another tibble
tb1 <- tibble(
id = c("id-1", "id-2", "id-3", "id-4"),
group = c("a", "b", "a", "b"),
price = c(0, -200, 3000, NA),
type = c("large", "none", "small", "none")
)
tb2 <- tibble(
id = c("id-1", "id-2", "id-3", "id-4"),
group = c("a", "b", "a", "b"),
price = c(1, 2, 3, 4),
type = c("l", "x", "x", "m")
)
rewrite_na(tb1, tb2, by = c("id", "group"))
#> # A tibble: 4 × 4
#> id group price type
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 id-1 a 0 large
#> 2 id-2 b -200 none
#> 3 id-3 a 3000 small
#> 4 id-4 b 4 none
- remove outliers and NA
out <- tibble(
id = stringr::str_c("out-", 1:20),
price = gen_outlier(mini_diamond %>% dplyr::pull(price), n = 20)
)
dim(bind_rows(mini_diamond, out))
#> [1] 120 7
res <- bind_rows(mini_diamond, out) %>%
remove_outliers(price)
dim(res)
#> [1] 93 7
stat
- generate all combinations
gen_combn(1:4, n = 2)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 1 2
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] 1 3
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] 1 4
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] 2 3
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] 2 4
#>
#> [[6]]
#> [1] 3 4
- statistical test which returns a extensible tibble
stat_test(mini_diamond, y = price, x = cut, .by = clarity)
#> # A tibble: 24 × 9
#> y clarity group1 group2 n1 n2 p plim psymbol
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 price I1 Fair Good 5 5 0.31 1.01 NS
#> 2 price I1 Fair Ideal 5 4 0.90 1.01 NS
#> 3 price I1 Good Ideal 5 4 0.19 1.01 NS
#> 4 price IF Fair Good 4 5 0.063 1.01 NS
#> 5 price IF Fair Ideal 4 4 0.059 1.01 NS
#> 6 price IF Good Ideal 5 4 1.0 1.01 NS
#> 7 price SI1 Fair Good 5 4 1.0 1.01 NS
#> 8 price SI1 Fair Ideal 5 5 1.0 1.01 NS
#> 9 price SI1 Good Ideal 4 5 0.41 1.01 NS
#> 10 price SI2 Fair Good 4 4 0.057 1.01 NS
#> # … with 14 more rows
- fold change calculation which returns a extensible tibble
stat_fc(mini_diamond, y = price, x = cut, .by = clarity)
#> # A tibble: 24 × 8
#> y clarity group1 group2 y1 y2 fc fc_fmt
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 price I1 Fair Good 4695. 2760. 1.70 1.7x
#> 2 price I1 Fair Ideal 4695. 4249 1.11 1.1x
#> 3 price I1 Good Ideal 2760. 4249 0.649 0.65x
#> 4 price IF Fair Good 2016 1044. 1.93 1.9x
#> 5 price IF Fair Ideal 2016 962. 2.10 2.1x
#> 6 price IF Good Ideal 1044. 962. 1.09 1.1x
#> 7 price SI1 Fair Good 5844. 3227. 1.81 1.8x
#> 8 price SI1 Fair Ideal 5844. 3877. 1.51 1.5x
#> 9 price SI1 Good Ideal 3227. 3877. 0.832 0.83x
#> 10 price SI2 Fair Good 13162. 6539. 2.01 2.0x
#> # … with 14 more rows
- calculate phi coefficient of two binary variables
data <- matrix(c(10, 8, 14, 18), nrow = 2)
stat_phi(data)
#> [1] 0.1134241
IO
- get the command line arguments
cmdargs()
#> $wd
#> [1] "/home/william/rpkg/baizer"
#>
#> $R_env
#> [1] "/home/william/software/mambaforge/envs/baizer/lib/R/bin/exec/R"
#>
#> $script_path
#> character(0)
#>
#> $script_dir
#> character(0)
#>
#> $env_configs
#> [1] "--slave"
#> [2] "--no-save"
#> [3] "--no-restore"
#> [4] "-f"
#> [5] "/tmp/Rtmpus1DLR/callr-scr-73b34fef3f99"
cmdargs("R_env")
#> [1] "/home/william/software/mambaforge/envs/baizer/lib/R/bin/exec/R"
- detect whether directory is empty recursively, and detect whether file is empty recursively
# create an empty directory
dir.create("some/deep/path/in/a/folder", recursive = TRUE)
empty_dir("some/deep/path/in/a/folder")
#> [1] TRUE
# create an empty file
file.create("some/deep/path/in/a/folder/there_is_a_file.txt")
#> [1] TRUE
empty_dir("some/deep/path/in/a/folder")
#> [1] FALSE
empty_file("some/deep/path/in/a/folder/there_is_a_file.txt", strict = TRUE)
#> [1] TRUE
# create a file with only character of length 0
write("", "some/deep/path/in/a/folder/there_is_a_file.txt")
empty_file("some/deep/path/in/a/folder/there_is_a_file.txt", strict = TRUE)
#> [1] FALSE
empty_file("some/deep/path/in/a/folder/there_is_a_file.txt")
#> [1] TRUE
# clean
unlink("some", recursive = TRUE)
- read excel file
# read_excel("mini_diamond.xlsx")
- write a tibble, or a list of tibbles into an excel file
# write_excel(mini_diamond, "mini_diamond.xlsx")
# Ldf <- list(mini_diamond[1:3, ], mini_diamond[4:6, ])
# write_excel(Ldf, '2sheets.xlsx')
- read multi-sheet excel file as a list of tibbles
# read_excel_list("mini_diamond.xlsx")
- read front matter markdown
# read_fmmd("markdown_file.md")
- fetch remote files via sftp
# sftp_con <- sftp_connect(server='remote_host', port=22,
# user='username', password = "password", wd='~')
#
# sftp_download(sftp_con,
# path=c('t1.txt', 't2.txt'),
# to=c('path1.txt', 'path2.txt')
# )
- list files from remote server via sftp
# sftp_ls(sftp_con, 'your/dir')
S3 classes in baizer
tbflt
- save a series of filter conditions, and support logical operation among conditions
- use
filterCto applytbfltondplyr::filter
c1 <- tbflt(cut == "Fair")
c2 <- tbflt(x > 8)
c1 | c2
#> <quosure>
#> expr: ^cut == "Fair" | x > 8
#> env: 0x55f4a327c4e0
mini_diamond %>%
filterC(c1) %>%
head(5)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-1 1.02 Fair SI1 3027 6.25 6.18
#> 2 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 3 id-10 0.7 Fair VVS1 1691 5.56 5.41
#> 4 id-12 0.71 Fair IF 3205 5.87 5.81
#> 5 id-18 0.34 Fair VVS1 1012 4.8 4.76
mini_diamond %>%
filterC(!c1) %>%
head(5)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-2 1.51 Good VS2 11746 7.27 7.18
#> 2 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 3 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 4 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 5 id-7 0.27 Good VVS1 752 4.1 4.07
mini_diamond %>% filterC(c1 & c2)
#> # A tibble: 3 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 2 id-48 2.01 Fair I1 7294 8.3 8.19
#> 3 id-68 2.32 Fair SI1 18026 8.47 8.31
- stricter limitation to avoid the unexpected default behavior
# default behavior of dplyr::filter, use column in data at first
x <- 8
mini_diamond %>% dplyr::filter(y > x)
#> # A tibble: 53 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 3 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 4 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 5 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 6 id-11 1.02 Good VVS1 7861 6.37 6.4
#> 7 id-13 0.56 Ideal SI1 1633 5.31 5.32
#> 8 id-14 0.3 Ideal VVS2 812 4.33 4.39
#> 9 id-15 0.28 Good IF 612 4.09 4.12
#> 10 id-16 0.41 Good I1 467 4.7 4.74
#> # … with 43 more rows
# so the default behavior of filterC is just like that
# but if you want y > 8, and the defination of cond is far away from
# its application, the results may be unexpected
x <- 8
cond <- tbflt(y > x)
mini_diamond %>% filterC(cond)
#> # A tibble: 53 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-3 0.52 Ideal VVS1 2029 5.15 5.18
#> 2 id-4 1.54 Ideal SI2 9452 7.43 7.45
#> 3 id-5 0.72 Ideal VS1 2498 5.73 5.77
#> 4 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 5 id-8 0.51 Good SI2 1029 5.05 5.08
#> 6 id-11 1.02 Good VVS1 7861 6.37 6.4
#> 7 id-13 0.56 Ideal SI1 1633 5.31 5.32
#> 8 id-14 0.3 Ideal VVS2 812 4.33 4.39
#> 9 id-15 0.28 Good IF 612 4.09 4.12
#> 10 id-16 0.41 Good I1 467 4.7 4.74
#> # … with 43 more rows
cond <- tbflt(y > 8)
mini_diamond %>% filterC(cond)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 2 id-48 2.01 Fair I1 7294 8.3 8.19
#> 3 id-49 2.16 Ideal I1 8709 8.31 8.26
#> 4 id-68 2.32 Fair SI1 18026 8.47 8.31
#> 5 id-97 2.61 Good SI2 13784 8.66 8.57
# to avoid this, set usecol=FALSE. An error will be raised for warning you
# to change the variable name
# mini_diamond %>% filterC(cond, usecol=FALSE)
# you can always ignore this argument if you know how to use .env or !!
x <- 8
cond1 <- tbflt(y > !!x)
mini_diamond %>% filterC(cond1)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 2 id-48 2.01 Fair I1 7294 8.3 8.19
#> 3 id-49 2.16 Ideal I1 8709 8.31 8.26
#> 4 id-68 2.32 Fair SI1 18026 8.47 8.31
#> 5 id-97 2.61 Good SI2 13784 8.66 8.57
cond2 <- tbflt(y > .env$x)
mini_diamond %>% filterC(cond1)
#> # A tibble: 5 × 7
#> id carat cut clarity price x y
#> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 id-6 2.02 Fair SI2 14080 8.33 8.37
#> 2 id-48 2.01 Fair I1 7294 8.3 8.19
#> 3 id-49 2.16 Ideal I1 8709 8.31 8.26
#> 4 id-68 2.32 Fair SI1 18026 8.47 8.31
#> 5 id-97 2.61 Good SI2 13784 8.66 8.57
dev
- add
#'into each line of codes for roxygen examples
roxygen_fmt(
"
code line1
code line2
"
)
#>
#> #' code line1
#> #' code line2
#> #'
- use aliases for function arguments
# set y, z as aliases of x when create a function
func <- function(x = 1, y = NULL, z = NULL) {
x <- alias_arg(x, y, z, default = x)
return(x)
}
func()
#> [1] 1
func(x = 8)
#> [1] 8
func(z = 10)
#> [1] 10
- check arguments by custom function
x <- 1
y <- 3
z <- NULL
func <- function(x = NULL, y = NULL, z = NULL) {
if (check_arg(x, y, z, n = 2)) {
print("As expected, two arguments is not NULL")
}
if (check_arg(x, y, z, n = 1, method = ~ .x < 2)) {
print("As expected, one argument less than 2")
}
}
Code of Conduct
Please note that the baizer project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
