Serialize Model Objects with a Consistent Interface.
bundle
Typically, models in R exist in memory and can be saved as .rds files. However, some models store information in locations that cannot be saved using save() or saveRDS() directly. The goal of bundle is to provide a common interface to capture this information, situate it within a portable object, and restore it for use in new settings.
Installation
You can install the released version of bundle from CRAN with:
install.packages("bundle")
And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("rstudio/bundle")
Overview
We often imagine a trained model as a somewhat “standalone” R object—given some new data, the R object can generate predictions on its own. In reality, some types of model objects also make use of references to generate predictions. A reference is a piece of information that a model object refers to that isn’t part of the object itself; this could be anything from a connection with a server to an internal function in the package used to train the model. When we call predict(), model objects know where to look to retrieve that data, but saving model objects can sometimes disrupt those references. Thus, if we want to train a model, save it, re-load it into memory in a production setting, and generate predictions with it, we may run into issues because those references do not exist in the new computational environment.
We need some way to preserve access to those references. The bundle package provides a consistent interface for bundling model objects with their references so that they can be safely saved and re-loaded in production:
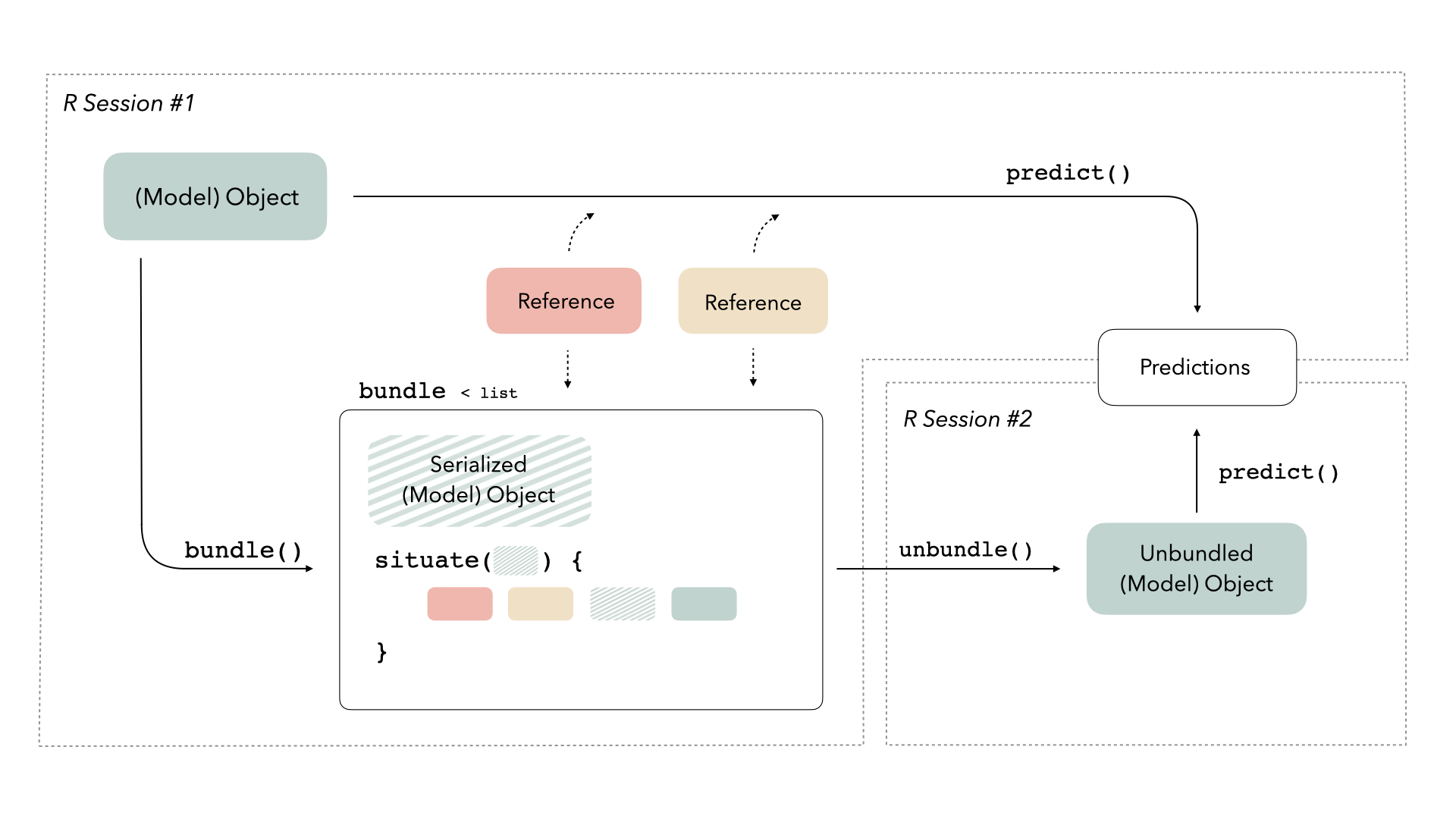
For more on this diagram, see the main bundle vignette.
When you’re ready to save your model, bundle() it first. Once you’ve loaded it in a new setting, unbundle() it!
Example
The bundle package prepares model objects so that they can be effectively saved and re-loaded for use in new R sessions. To demonstrate using bundle, we will train a boosted tree model using XGBoost, bundle it, and then pass the bundle into another R session to generate predictions on new data.
First, load needed packages:
library(bundle)
library(parsnip)
library(callr)
library(waldo)
Fit the boosted tree model:
# fit an boosted tree with xgboost via parsnip
mod <-
boost_tree(trees = 5, mtry = 3) %>%
set_mode("regression") %>%
set_engine("xgboost") %>%
fit(mpg ~ ., data = mtcars[1:25,])
mod
#> parsnip model object
#>
#> ##### xgb.Booster
#> raw: 8.1 Kb
#> call:
#> xgboost::xgb.train(params = list(eta = 0.3, max_depth = 6, gamma = 0,
#> colsample_bytree = 1, colsample_bynode = 0.3, min_child_weight = 1,
#> subsample = 1), data = x$data, nrounds = 5, watchlist = x$watchlist,
#> verbose = 0, nthread = 1, objective = "reg:squarederror")
#> params (as set within xgb.train):
#> eta = "0.3", max_depth = "6", gamma = "0", colsample_bytree = "1", colsample_bynode = "0.3", min_child_weight = "1", subsample = "1", nthread = "1", objective = "reg:squarederror", validate_parameters = "TRUE"
#> xgb.attributes:
#> niter
#> callbacks:
#> cb.evaluation.log()
#> # of features: 10
#> niter: 5
#> nfeatures : 10
#> evaluation_log:
#> iter training_rmse
#> 1 14.640496
#> 2 10.927976
#> 3 8.217181
#> 4 6.262192
#> 5 4.796391
Note that simply saving and loading the model results in changes to the fitted model:
temp_file <- tempfile()
saveRDS(mod, temp_file)
mod2 <- readRDS(temp_file)
compare(mod, mod2, ignore_formula_env = TRUE)
#> `old$fit$handle` is <pointer: 0x12fa5adc0>
#> `new$fit$handle` is <pointer: 0x0>
#>
#> `old$fit$handle` is attr(,"class")
#> `new$fit$handle` is attr(,"class")
#>
#> `old$fit$handle` is [1] "xgb.Booster.handle"
#> `new$fit$handle` is [1] "xgb.Booster.handle"
Saving and reloading mod2 didn’t preserve XGBoost’s reference to its pointer, which may result in failures later in the modeling process.
We thus need to prepare the fitted model to be saved before passing it to another R session. We can do so by bundling it:
# bundle the model
bundled_mod <-
bundle(mod)
bundled_mod
#> bundled model_fit object.
Passing the model to another R session and generating predictions on new data:
# load the model in a fresh R session and predict on new data
r(
func = function(bundled_mod) {
library(bundle)
library(parsnip)
unbundled_mod <-
unbundle(bundled_mod)
predict(unbundled_mod, new_data = mtcars[26:32,])
},
args = list(
bundled_mod = bundled_mod
)
)
#> # A tibble: 7 × 1
#> .pred
#> <dbl>
#> 1 22.2
#> 2 20.9
#> 3 19.1
#> 4 13.3
#> 5 16.6
#> 6 13.3
#> 7 17.2
For a more in-depth demonstration of the package, see the main vignette with vignette("bundle").
Contributing
This project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
For questions and discussions about our packages, modeling, and machine learning, please post on RStudio Community.
If you think you have encountered a bug, please submit an issue.
Either way, learn how to create and share a reprex (a minimal, reproducible example), to clearly communicate about your code.
