Change-in-Estimate Approach to Assess Confounding Effects.
Change-in-Estimate (chest) Approach to Assess Confounding Effects
chest package
The ‘chest’ package can be used to assess confounding effects by comparing effect estimates from many models. It calculates the changes in effect estimates by adding one of many variables (potential confounding factors) to the model sequentially in a stepwise fashion. Effect estimates can be regression coefficients, odds ratios and hazard ratios depending on the modelling methods. At each step, only one variable that causes the largest change in the effect estimates among the remaining variables is added to the model. Effect estimates and change (%) values are presented in a graph and data frame table. This approach can be used for assessing confounding effects in epidemiological studies and bio-medical research including clinical trials.
Installation
You can install the released version of chest from CRAN with:
install.packages("chest")
Examples
Data: diabetes and mortality
A data frame ‘diab_df’ is used to examine the association between diabetes (Diabetes) and mortality (Endpoint). The purpose of using this data set is to demonstrate the use of the functions in this package rather than answering any research questions. Assuming it is a cohort design for Cox Proportional Hazards Models, cross-sectional design for Logistic Regression Model and matched cohort design for Conditional logistic regression Models.
chest_glm: Logistic regression using (generalized linear models, ‘glm’).
‘chest_glm’ is slow. We can use ‘indicate = TRUE’ to monitor the progress.
chest_glm(crude = "Endpoint ~ Diabetes", xlist = vlist, data = diab_df, indicate = TRUE)
chest_cox: Using Cox Proportional Hazards Models: ‘coxph’ of ‘survival’ package
chest_cox(crude = "Surv(t0, t1, Endpoint) ~ Diabetes", xlist = vlist,
na_omit = TRUE, data = diab_df, zero = 1)
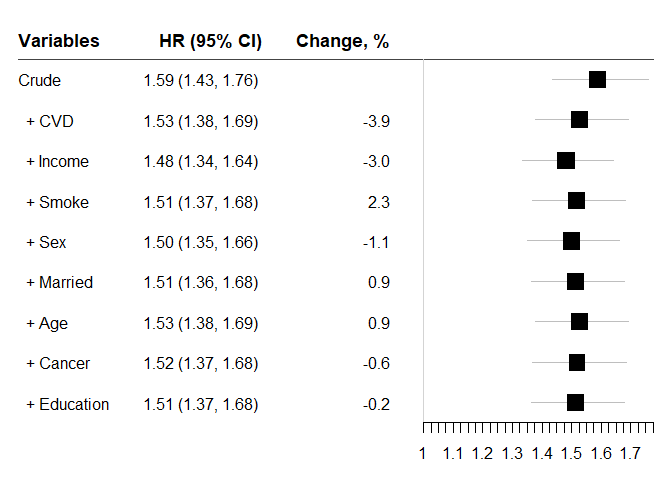
#> variables HR lb ub Change p n
#> 1 Crude 1.588134 1.434544 1.758167 NA 4.950249e-19 2048
#> 2 + CVD 1.526276 1.377192 1.691499 -3.8949795 7.454317e-16 2048
#> 3 + Income 1.480726 1.335380 1.641891 -2.9844079 9.581156e-14 2048
#> 4 + Smoke 1.514956 1.366037 1.680108 2.3116907 3.596810e-15 2048
#> 5 + Sex 1.498963 1.351879 1.662049 -1.0556582 1.571022e-14 2048
#> 6 + Married 1.512616 1.363974 1.677456 0.9108110 4.451213e-15 2048
#> 7 + Age 1.526426 1.376076 1.693202 0.9129952 1.305521e-15 2048
#> 8 + Cancer 1.517896 1.368399 1.683726 -0.5587865 3.050629e-15 2048
#> 9 + Education 1.514437 1.365204 1.679982 -0.2279234 4.453189e-15 2048
‘chest_clogit’: Conditional logistic regression: ‘clogit’ of ‘survival’ package
chest_clogit(crude = "Endpoint ~ Diabetes + strata(mid)",
xlist = vlist, data = diab_df, indicate= TRUE, zero = 1)
#> 2 out of 9 3 out of 9 4 out of 9 5 out of 9 6 out of 9 7 out of 9 8 out of 9 9 out of 9
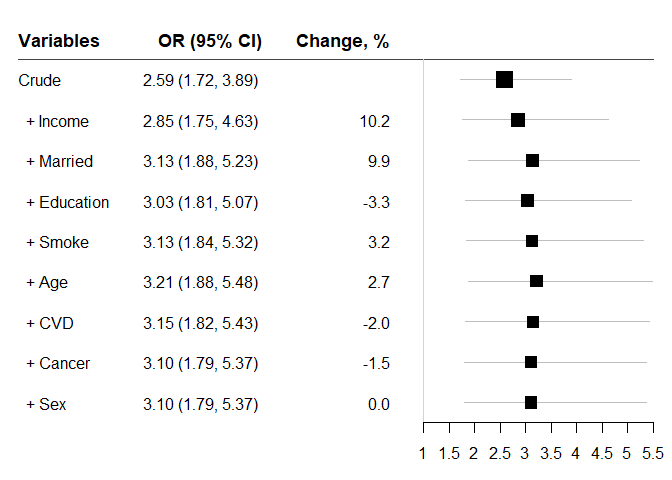
#> variables OR lb ub Change p n
#> 1 Crude 2.586950 1.719871 3.891170 NA 5.033866e-06 2372
#> 2 + Income 2.850010 1.752942 4.633671 10.168718 2.405822e-05 2061
#> 3 + Married 3.133480 1.875838 5.234301 9.946296 1.283423e-05 2058
#> 4 + Education 3.030468 1.810620 5.072149 -3.287484 2.452619e-05 2048
#> 5 + Smoke 3.128331 1.839469 5.320260 3.229314 2.559384e-05 2048
#> 6 + Age 3.212487 1.883223 5.480007 2.690121 1.844153e-05 2048
#> 7 + CVD 3.148114 1.824571 5.431754 -2.003848 3.776568e-05 2048
#> 8 + Cancer 3.100427 1.790709 5.368067 -1.514782 5.340664e-05 2048
#> 9 + Sex 3.100427 1.790709 5.368067 0.000000 5.340664e-05 2048
Note:
Because ‘chest’ fits many models and compares effect estimates, some analyses may take long time to complete.