Easier CUSUM Control Charts.
cusumcharter 
The goal of cusumcharter is to create both simple CUSUM charts, with and without control limits from a vector, or to create multiple CUSUM charts, with or without control limits, from a grouped dataframe, tibble or data.table.
CUSUM charts detect small changes over time, and will alert quicker than a Statistical Process Control chart. They are an excellent alternative to run and control charts, particularly where data is scarce, infrequent, or expensive to obtain.
They monitor the difference between each data point, relative to a target value, which is often the mean of all the currently available data points. Using these variances and targets, control limits are calculated. Any points outside these limits are an indication that the process is out of control.
Installation
Install the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("johnmackintosh/cusumcharter")
A Simple CUSUM calculation
This returns the CUSUM statistics for a single vector, centred on a supplied target value:
library(cusumcharter)
test_vec <- c(0.175, 0.152, 0.15, 0.207, 0.136, 0.212, 0.166)
cusum_res <- cusum_single(test_vec, target = 0.16)
cusum_res
#> [1] 0.175 0.167 0.157 0.204 0.180 0.232 0.238
Expanded outputs with cusum_single_df
This function takes a single vector as input and returns a data.frame with additional information used to calculate the CUSUM statistic
test_vec2 <- c(0.175, 0.152, 0.15, 0.207, 0.136, 0.212, 0.166)
cusum_single_df(test_vec2, target = 0.16)
#> x target si cusumx cusum_target
#> 1 0.175 0.16 0.015 0.015 0.175
#> 2 0.152 0.16 -0.008 0.007 0.167
#> 3 0.150 0.16 -0.010 -0.003 0.157
#> 4 0.207 0.16 0.047 0.044 0.204
#> 5 0.136 0.16 -0.024 0.020 0.180
#> 6 0.212 0.16 0.052 0.072 0.232
#> 7 0.166 0.16 0.006 0.078 0.238
Here we don’t supply a target, so the mean is used
test_vec3 <- c(1,1,2,11,3,5,7,2,4,3,5)
cusum_single_df(test_vec3)
#> x target si cusumx cusum_target
#> 1 1 4 -3 -3 1
#> 2 1 4 -3 -6 -2
#> 3 2 4 -2 -8 -4
#> 4 11 4 7 -1 3
#> 5 3 4 -1 -2 2
#> 6 5 4 1 -1 3
#> 7 7 4 3 2 6
#> 8 2 4 -2 0 4
#> 9 4 4 0 0 4
#> 10 3 4 -1 -1 3
#> 11 5 4 1 0 4
CUSUM control limits
Two additional functions allow you to calculate control limits from a single vector and plot a CUSUM chart with control limits. As before, the mean is used to determine the target if none is provided. Alternate functions are available if you wish to use the median instead.
test_vec3 <- c(1,1,2,3,5,7,11,7,5,7,8,9,5)
controls <- cusum_control(test_vec3, target = 4)
controls
#> x target variance std_dev cusum cplus cneg cum_nplus cum_nneg
#> 1 1 4 -3 1.77305 -3 0.0000000 -2.113475 0 1
#> 2 1 4 -3 1.77305 -6 0.0000000 -4.226950 0 2
#> 3 2 4 -2 1.77305 -8 0.0000000 -5.340426 0 3
#> 4 3 4 -1 1.77305 -9 0.0000000 -5.453901 0 4
#> 5 5 4 1 1.77305 -8 0.1134752 -3.567376 1 5
#> 6 7 4 3 1.77305 -5 2.2269504 0.000000 2 0
#> 7 11 4 7 1.77305 2 8.3404255 0.000000 3 0
#> 8 7 4 3 1.77305 5 10.4539007 0.000000 4 0
#> 9 5 4 1 1.77305 6 10.5673759 0.000000 5 0
#> 10 7 4 3 1.77305 9 12.6808511 0.000000 6 0
#> 11 8 4 4 1.77305 13 15.7943262 0.000000 7 0
#> 12 9 4 5 1.77305 18 19.9078014 0.000000 8 0
#> 13 5 4 1 1.77305 19 20.0212766 0.000000 9 0
#> ucl lcl centre obs
#> 1 7.092199 -7.092199 0 1
#> 2 7.092199 -7.092199 0 2
#> 3 7.092199 -7.092199 0 3
#> 4 7.092199 -7.092199 0 4
#> 5 7.092199 -7.092199 0 5
#> 6 7.092199 -7.092199 0 6
#> 7 7.092199 -7.092199 0 7
#> 8 7.092199 -7.092199 0 8
#> 9 7.092199 -7.092199 0 9
#> 10 7.092199 -7.092199 0 10
#> 11 7.092199 -7.092199 0 11
#> 12 7.092199 -7.092199 0 12
#> 13 7.092199 -7.092199 0 13
Also see the cusum_control_median function
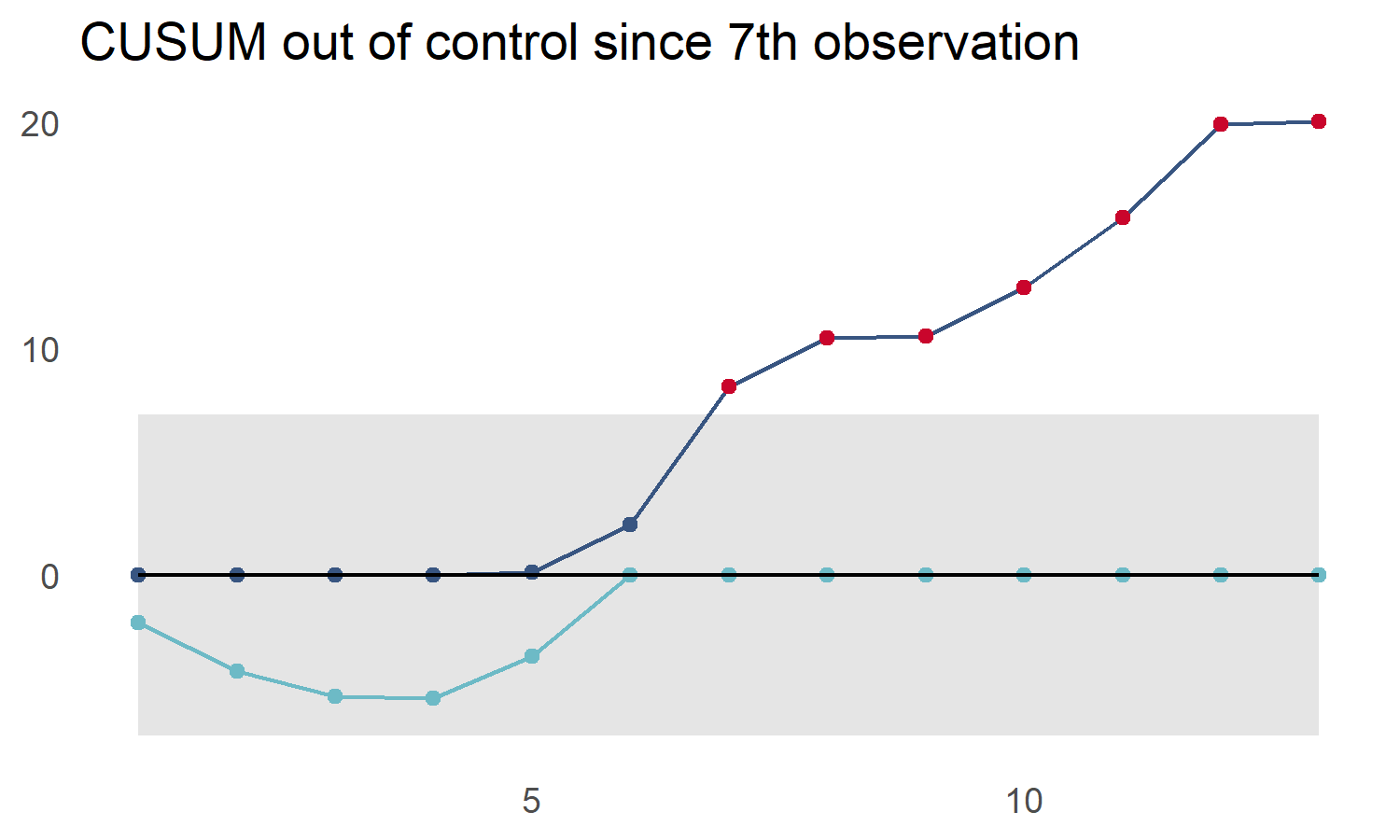
CUSUM Control Chart
test_vec3 <- c(1,1,2,3,5,7,11,7,5,7,8,9,5)
controls <- cusum_control(test_vec3, target = 4)
cusum_control_plot(controls,
xvar = obs,
title_text = "CUSUM out of control since 7th observation")
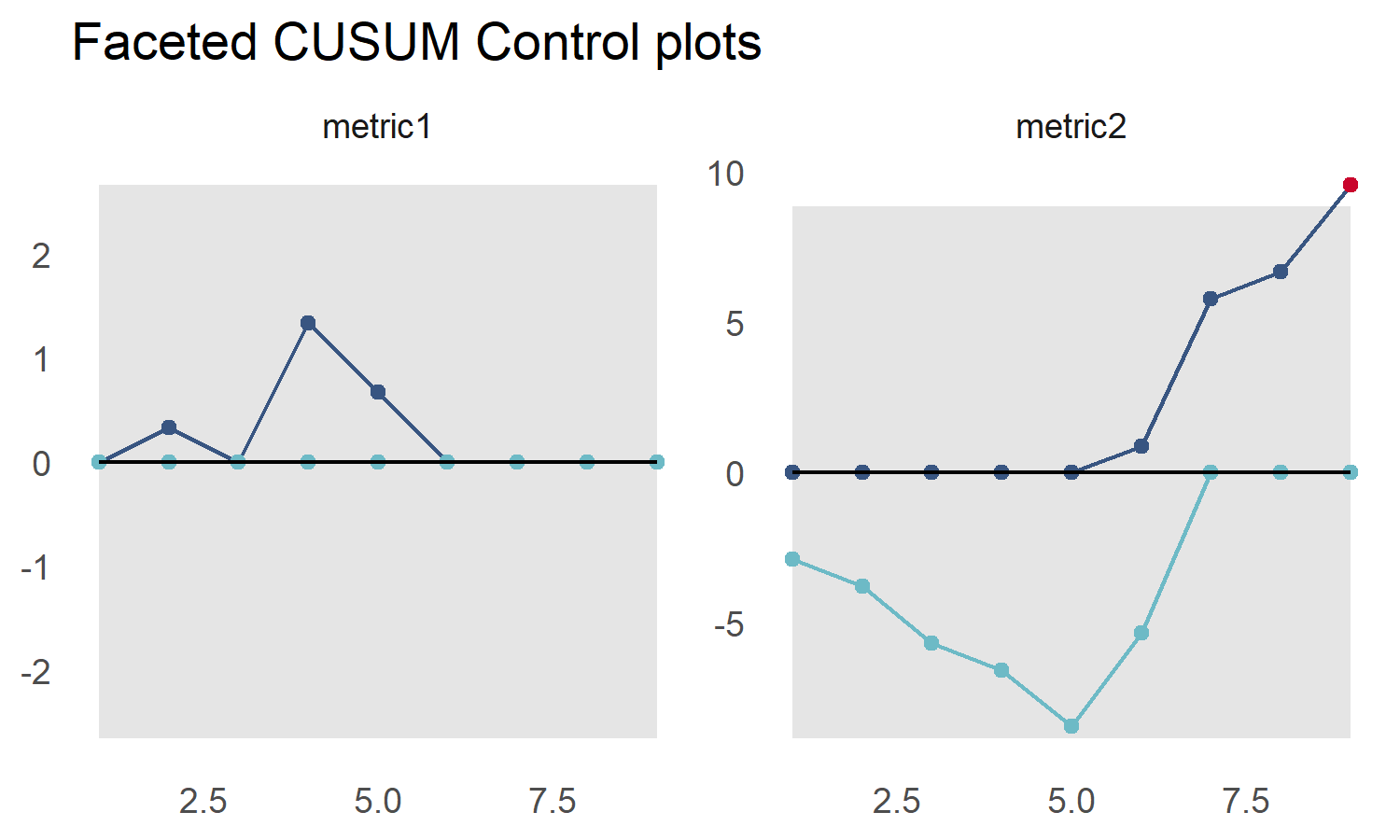
Multiple CUSUM Control Charts
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
library(tibble)
library(ggplot2)
library(cusumcharter)
testdata <- tibble::tibble(
N = c(1L,2L,1L,3L,1L,1L,1L,1L,1L,
1L,3L,2L,3L,2L,7L,11L,7L,9L),
metric = c("metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1",
"metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2"))
testres <- testdata %>%
dplyr::group_by(metric) %>%
dplyr::mutate(cusum_control(N)) %>%
dplyr::ungroup()
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
p <- cusum_control_plot(testres,
xvar = obs,
facet_var = metric,
title_text = "Faceted CUSUM Control plots")
p
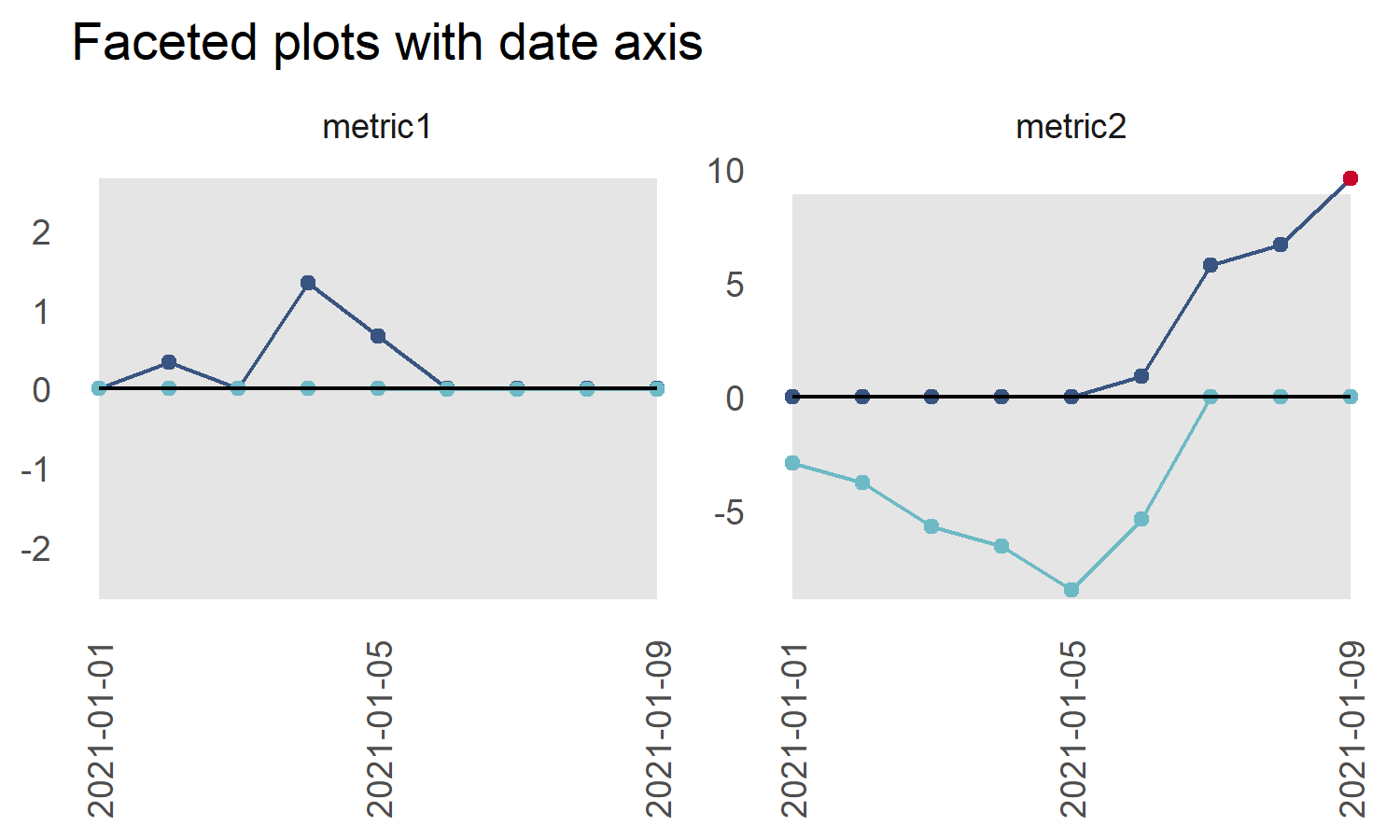
Flexible x axis
Here we add a date column, specify that the scale_type is 'date', and provide the datebreaks argument to plot our data over time
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(cusumcharter)
testdata <- tibble::tibble(
N = c(1L,2L,1L,3L,1L,1L,1L,1L,1L,
1L,3L,2L,3L,2L,7L,11L,7L,9L),
metric = c("metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1",
"metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2"))
datecol <- as.Date(c("2021-01-01","2021-01-02", "2021-01-03", "2021-01-04" ,
"2021-01-05", "2021-01-06","2021-01-07", "2021-01-08",
"2021-01-09"))
testres <- testdata %>%
dplyr::group_by(metric) %>%
dplyr::mutate(cusum_control(N)) %>%
dplyr::ungroup() %>%
dplyr::group_by(metric) %>%
dplyr::mutate(report_date = datecol) %>%
ungroup()
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
p2 <- cusum_control_plot(testres,
xvar = report_date,
facet_var = metric,
title_text = "Faceted plots with date axis",
scale_type = "date",
datebreaks = '4 days')
p2 <- p2 + ggplot2::theme(axis.text.x = ggplot2::element_text(angle = 90,
hjust = 1,
vjust = 0.5))
p2
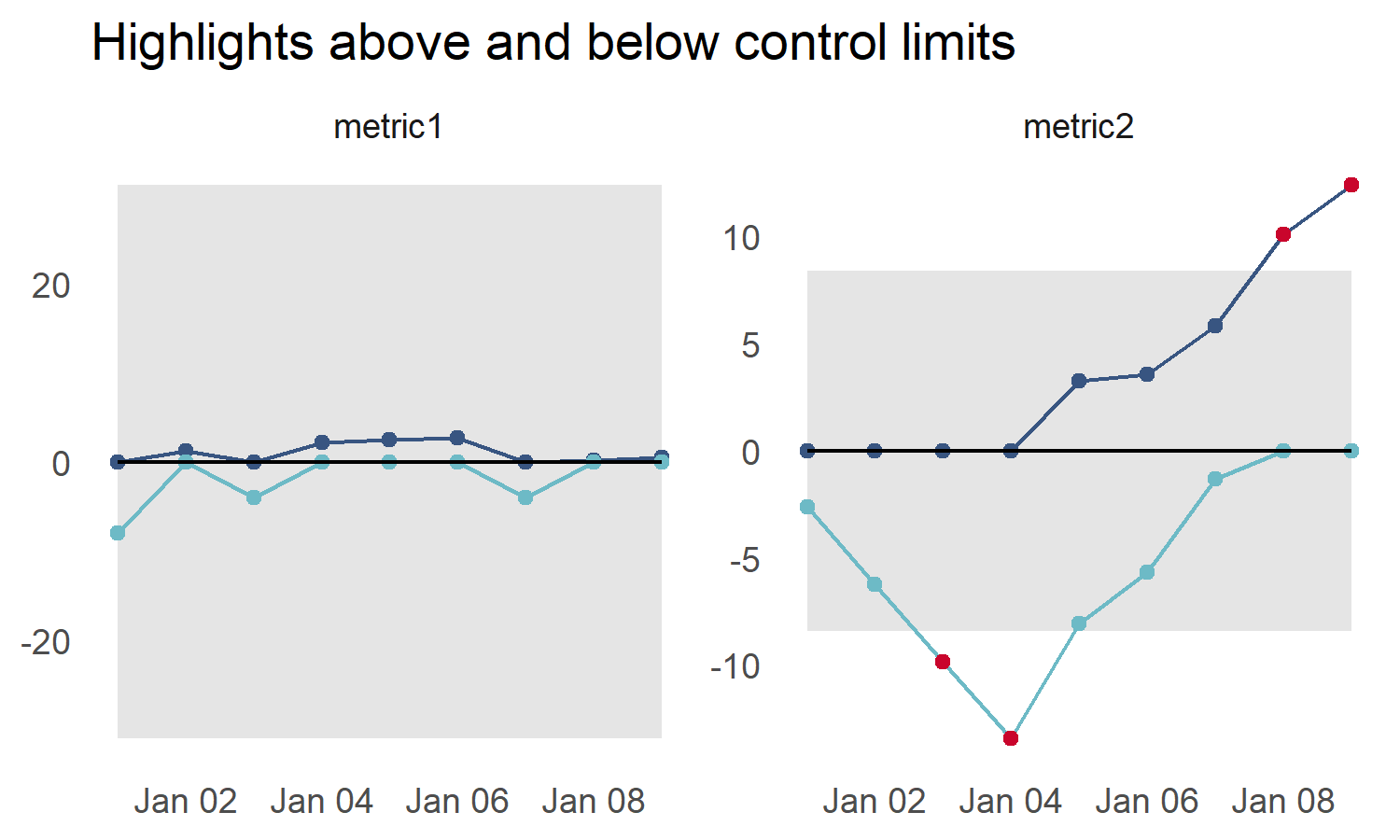
Highlight above and below control limits
Points outside the Upper Control Limit are always highlighted. Use the show_below option to enable highlighting points below the Lower Control Limit
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(cusumcharter)
testdata <- tibble::tibble(
N = c(-15L,2L,-11L,3L,1L,1L,-11L,1L,1L,
2L,1L,1L,1L,10L,7L,9L,11L,9L),
metric = c("metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1",
"metric1","metric1","metric1","metric1","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2","metric2",
"metric2","metric2","metric2"))
datecol <- as.Date(c("2021-01-01","2021-01-02", "2021-01-03", "2021-01-04" ,
"2021-01-05", "2021-01-06","2021-01-07", "2021-01-08",
"2021-01-09"))
testres <- testdata %>%
dplyr::group_by(metric) %>%
dplyr::mutate(cusum_control(N)) %>%
dplyr::ungroup() %>%
dplyr::group_by(metric) %>%
dplyr::mutate(report_date = datecol) %>%
ungroup()
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
#> no target value supplied, so using the mean of x
p5 <- cusum_control_plot(testres,
xvar = report_date,
show_below = TRUE,
facet_var = metric,
title_text = "Highlights above and below control limits")
p5