Diverse Cluster Ensemble in R.
diceR 
Overview
The goal of diceR is to provide a systematic framework for generating diverse cluster ensembles in R. There are a lot of nuances in cluster analysis to consider. We provide a process and a suite of functions and tools to implement a systematic framework for cluster discovery, guiding the user through the generation of a diverse clustering solutions from data, ensemble formation, algorithm selection and the arrival at a final consensus solution. We have additionally developed visual and analytical validation tools to help with the assessment of the final result. We implemented a wrapper function dice() that allows the user to easily obtain results and assess them. Thus, the package is accessible to both end user with limited statistical knowledge. Full access to the package is available for informaticians and statisticians and the functions are easily expanded. More details can be found in our companion paper published at BMC Bioinformatics.
Installation
You can install diceR from CRAN with:
install.packages("diceR")
Or get the latest development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("AlineTalhouk/diceR")
Example
The following example shows how to use the main function of the package, dice(). A data matrix hgsc contains a subset of gene expression measurements of High Grade Serous Carcinoma Ovarian cancer patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas publicly available datasets. Samples as rows, features as columns. The function below runs the package through the dice() function. We specify (a range of) nk clusters over reps subsamples of the data containing 80% of the full samples. We also specify the clustering algorithms to be used and the ensemble functions used to aggregated them in cons.funs.
library(diceR)
data(hgsc)
obj <- dice(hgsc, nk = 4, reps = 5, algorithms = c("hc", "diana"),
cons.funs = c("kmodes", "majority"))
The first few cluster assignments are shown below:
knitr::kable(head(obj$clusters))
| kmodes | majority | |
|---|---|---|
| TCGA.04.1331_PRO.C5 | 2 | 2 |
| TCGA.04.1332_MES.C1 | 2 | 2 |
| TCGA.04.1336_DIF.C4 | 4 | 2 |
| TCGA.04.1337_MES.C1 | 2 | 2 |
| TCGA.04.1338_MES.C1 | 2 | 2 |
| TCGA.04.1341_PRO.C5 | 2 | 2 |
You can also compare the base algorithms with the cons.funs using internal evaluation indices:
knitr::kable(obj$indices$ii$`4`)
| Algorithms | calinski_harabasz | dunn | gamma | c_index | davies_bouldin | sd | s_dbw | silhouette | Compactness | Connectivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC_Euclidean | HC_Euclidean | 3.104106 | 0.2608547 | 0.6349401 | 0.2844073 | 1.839182 | 2.846480 | 1.678968 | -0.1418603 | 24.83225 | 41.62183 |
| DIANA_Euclidean | DIANA_Euclidean | 53.647400 | 0.3348103 | -1.9749903 | 0.1589442 | 2.824201 | 3.450173 | 1.809561 | 0.0564065 | 21.93396 | 241.66310 |
| kmodes | kmodes | 55.138600 | 0.3396909 | -1.8704101 | 0.1453599 | 2.006752 | 3.986950 | 1.967467 | 0.1369288 | 21.91494 | 201.42540 |
| majority | majority | 19.373248 | 0.3544371 | 0.6529653 | 0.2102487 | 1.622799 | 4.039708 | 1.982210 | 0.1504666 | 23.85408 | 64.04921 |
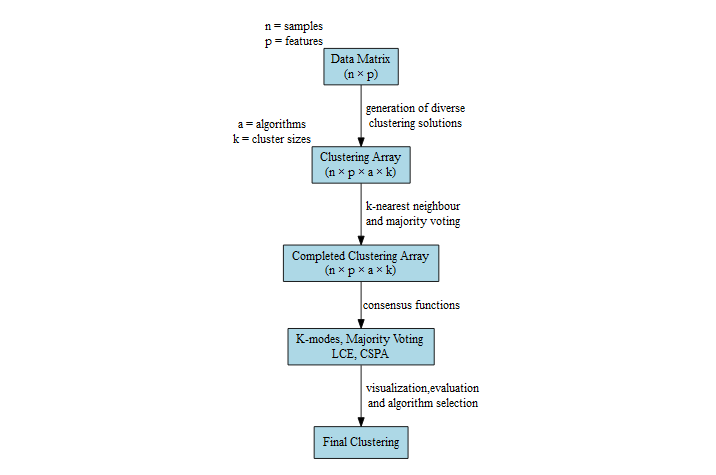
Pipeline
This figure is a visual schematic of the pipeline that dice() implements.
Please visit the overview page for more detail.