Dynamic and Interactive EEG Graphics.
diegr
Overview
The name diegr comes from Dynamic and Interactive EEG Graphics using R. The diegr package enables researchers to visualize high-density electroencephalography (HD-EEG) data with animated and interactive graphics, supporting both exploratory and confirmatory analyses of sensor-level brain signals.
The package diegr includes:
- interactive boxplots (
boxplot_epoch,boxplot_subject,boxplot_rt) - interactive epoch waveforms (
interactive_waveforms) - topographic maps in 2D (
topo_plot) - scalp plots in 3D (
scalp_plot) - functions for computing baseline correction, pointwise and jackknife mean (
baseline_correction,compute_mean) - functions for plotting the mean with pointwise confidence interval (
plot_time_mean,plot_topo_mean) - animations of time course of the raw signal or the average in 2D and 3D (
animate_topo,animate_topo_mean,animate_scalp)
Installation
You can install the development version of MyPackage from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("gerslovaz/diegr")
Data
Because of large volumes of data obtained from HD-EEG measurements, the package allows users to work directly with database tables (in addition to common formats such as data frames or tibbles). Such a procedure is more efficient in terms of memory usage.
The database you want to use as input to diegr functions must contain columns with the following structure::
subject- ID of subjects,epoch- epoch numberstime- numbers of time points (as sampling points, not in ms),sensor- sensor labels,signal- the EEG signal amplitude in microvolts (in some functions it is possible to set the name of the column containing the amplitude arbitrarily).
The package contains some included training datasets:
epochdata: epoched HD-EEG data (anonymized short slice from big HD-EEG study presented in Madetko-Alster, 2025) arranged as mentioned above,HCGSN256: a list with Cartesian coordinates of HD-EEG sensor positions in 3D space on the scalp surface and their projection into 2D spacertdata: response times (time between stimulus presentation and pressing the button) from the experiment involving a simple visual motor task (anonymized short slice from big HD-EEG study presented in Madetko-Alster, 2025).
For more information about the structure of built-in data see the package vignette vignette("diegr", package = "diegr").
Quick examples
Interactive boxplot
This is a basic example which shows how to plot interactive epoch boxplots from chosen electrode in different time points for one subject:
library(diegr)
data("epochdata")
boxplot_epoch(epochdata, amplitude = "signal", subject = 1, channel = "E65", time_lim = c(10:20))
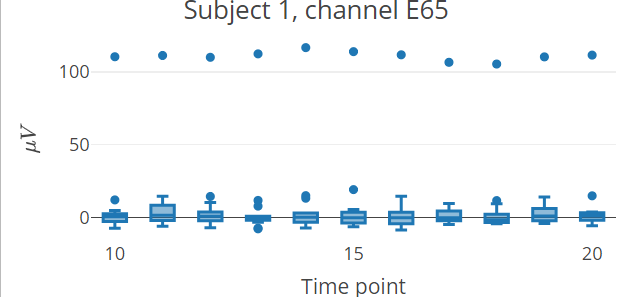
Note: The README format does not allow the inclusion of plotly interactive elements, only the static preview of the result is shown.
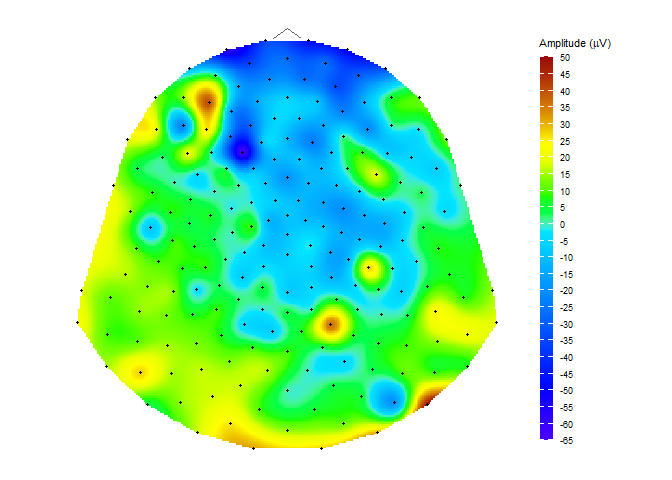
Topographic map
data("HCGSN256")
# creating a mesh
M1 <- point_mesh(dimension = 2, n = 30000, type = "polygon", sensor_select = unique(epochdata$sensor))
# filtering a subset of data to display
data_short <- epochdata |>
dplyr::filter(subject == 1 & epoch == 10 & time == 15)
# function for displaying a topographic map of the chosen signal on the created mesh M1
topo_plot(data_short, amplitude = "signal", mesh = M1)
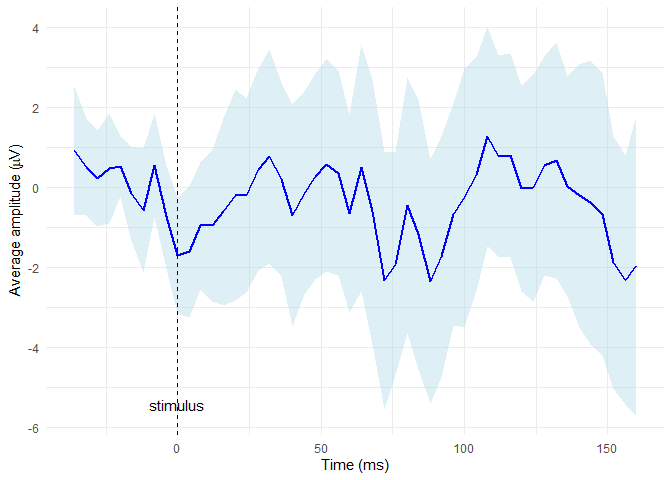
Computing and displaying the average
Compute the average signal for subject 2 from the channel E65 (exclude the oulier epochs 14 and 15) and then display it along with CI bounds
# extract required data
edata <- epochdata |>
dplyr::filter(subject == 2 & sensor == "E65" & epoch %in% 1:13)
# baseline correction
data_base <- baseline_correction(edata, baseline_range = 1:10)
# compute average
data_mean <- compute_mean(data_base, amplitude = "signal_base", subject = 2,
channel = "E65", type = "point")
# plot the average line with CI in blue colors
plot_time_mean(data = data_mean, t0 = 10, color = "blue", fill = "lightblue")
For detailed examples and usage explanation, please see the package vignette: vignette("diegr", package = "diegr").
References Madetko-Alster N., Alster P., Lamoš M., Šmahovská L., Boušek T., Rektor I. and Bočková M. The role of the somatosensory cortex in self-paced movement impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2025, vol. 171, 11-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2025.01.001
License This package is distributed under the MIT license. See LICENSE file for details.
Citation Use citation("diegr") to cite this package.