Deconvolution of Bulk RNA-Seq Data Based on Deep Learning.
digitalDLSorteR
An R package to deconvolute bulk RNA-Seq from scRNA-Seq data based on Deep Learning
The digitalDLSorteR R package provides a set of tools to deconvolute and infer cell type proportions of bulk RNA-Seq data through the development of context-specific deconvolution models based on Deep Learning and single-cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) data. These models are able to accurately enumerate and quantify cell proportions of bulk RNA-Seq samples from specific biological environments. For more details about the algorithm and the functionalities implemented in this package, see Torroja and Sanchez-Cabo, 2019 and https://diegommcc.github.io/digitalDLSorteR/.
Installation
digitalDLSorteR is available on CRAN and can be installed as follows:
install.packages("digitalDLSorteR")
The development version is available on GitHub and can be also installed in R:
if (!requireNamespace("devtools", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("diegommcc/digitalDLSorteR")
The package depends on the tensorflow R package, so a working Python interpreter with the Tensorflow Python library installed is needed. The installTFpython function provides an easy way to install a conda environment called digitaldlsorter-env with all necessary dependencies covered. We recommend installing the TensorFlow Python library in this way, although a custom installation is possible. See the Keras/TensorFlow installation and configuration article of the package website for more details.
library("digitalDLSorteR")
installTFpython(install.conda = TRUE)
Rationale of digitalDLSorteR
The algorithm consists of training Deep Neural Network (DNN) models with simulated bulk RNA-Seq samples whose cell composition is known. These pseudo-bulk RNA-Seq samples are generated by aggregating pre-characterized scRNA-Seq data from specific biological environments. These models are able to accurately deconvolute new bulk RNA-Seq samples from the same environment, as they are able to account for possible environmental-dependent transcriptional changes of specific cells, such as immune cells in complex diseases (e.g., specific subtypes of cancer or atherosclerosis). This aspect overcomes this limitation present in other methods. For instance, in the case of immune cells, published methods often rely on purified transcriptional profiles from peripheral blood mononuclear cells despite the fact these cells are highly variable depending on enviromental conditions. Therefore, considering this feature together with the use of powerful DNN models and the fact that the improvement of scRNA-Seq datasets over time will lead to build more accurate models, digitalDLSorteR offers a good alternative to classical methods based on linear models with pre-defined markers and unreliable transcriptional references.
Usage
The package has two main ways of usage:
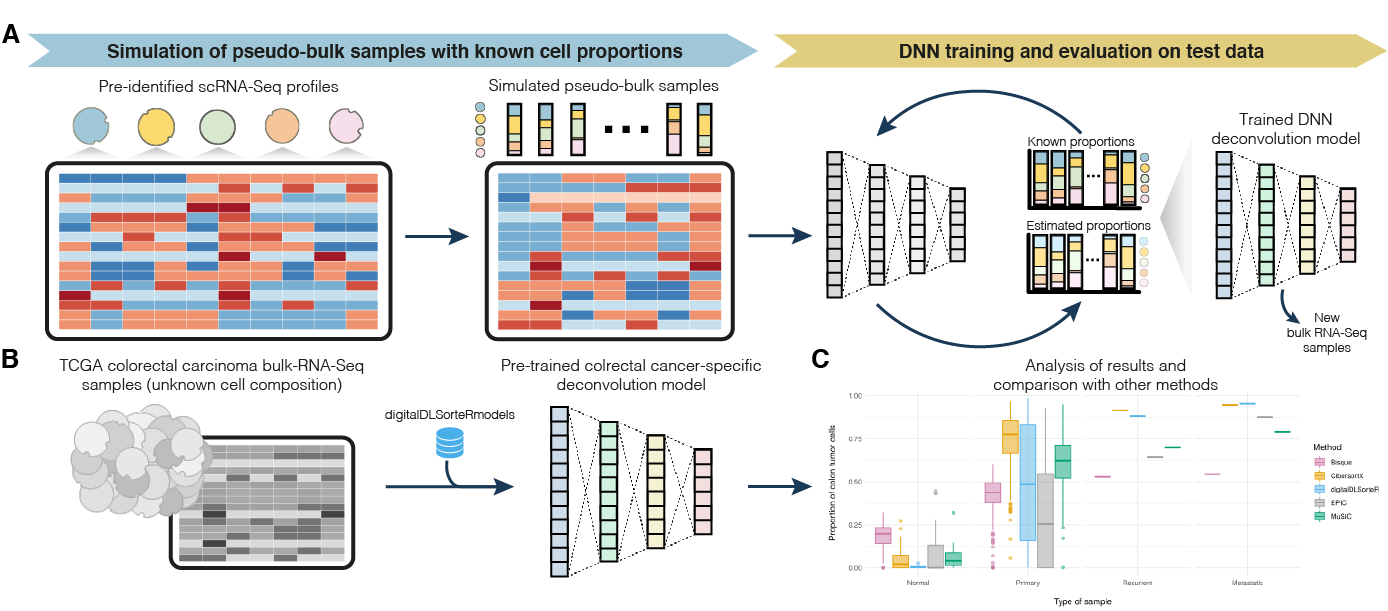
- Using pre-trained models included in the digitalLDSorteRmodels (https://github.com/diegommcc/digitalDLSorteRmodels) R package to deconvolute new bulk RNA-Seq samples from the same environment. So far, the available models allow to deconvolute samples from human breast cancer (GSE75688 data from Chung et al., 2017 used as reference), and colorectal cancer (GSE81861 data from Li et al., 2017 used as reference). For more details about this workflow, please see the Using pre-trained context-specific deconvolution models article. Moreover, it is summarized in the panel A of the figure below.
- Building new deconvolution models from pre-characterized scRNA-Seq datasets. This workflow involves some computational resource requirements, although digitalDLSorteR has been developed to provide all possible facilities to make the process easier, such as batch processing of data and the use of the HDF5Array and DelayedArray R packages to use HDF5 files as back-end. The main steps are summarized in panel B of the figure below, but for more information on the workflow, see the article Building new deconvolution models.
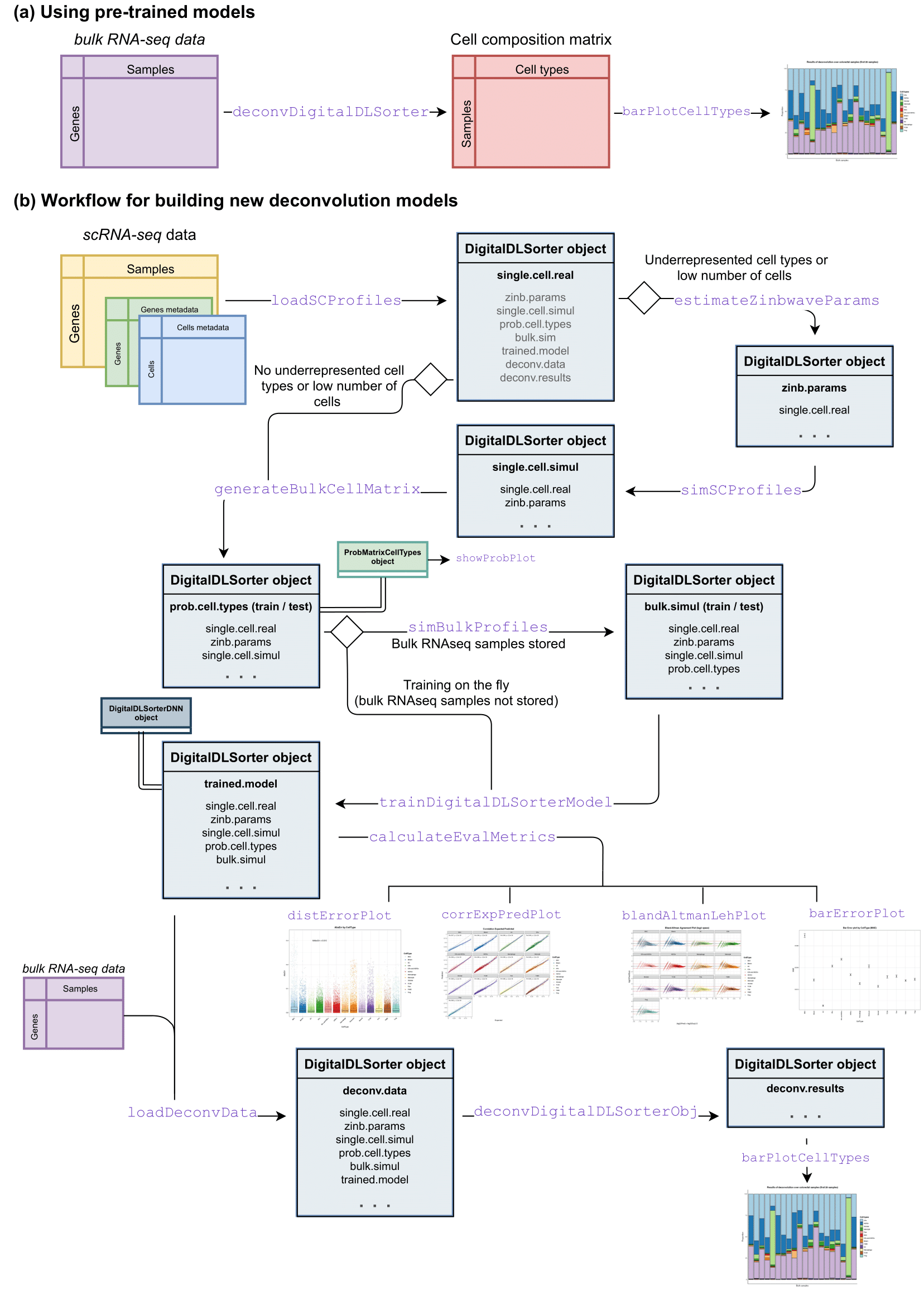
To use pre-trained context specific deconvolution models, digitalDLSorteR depends on digitalDLSorteRmodels data package as it makes them available. Therefore, it should be installed together with digitalDLSorteR if this functionality wants to be used. To do so, it can be installed from GitHub using devtools:
devtools::install_github("diegommcc/digitalDLSorteRmodels")
Once digitalDLSorteRmodels is loaded, the pre-trained models are available. See the article Using pre-trained context-specific deconvolution models for some examples.
In addition, some examples and the vignettes of digitalDLSorteR make use of pre-computed datasets from the digitalDLSorteRdata R package. If you want to inspect these pre-computed DigitalDLSorter objects, you can install it from GitHub using devtools as follows. See Performance of a real model: deconvolution of colorectal cancer samples for an example.
devtools::install_github("diegommcc/digitalDLSorteRdata")
Final remarks
- Regarding available pre-trained models, new models coming soon! Of course, you can build your own models and even contribute to digitalDLSorteR making them available. Contact us to incude them in the package.
- Pre-trained context-specific deconvolution models are available in the digitalDLSorteRmodels R package (https://github.com/diegommcc/digitalDLSorteRmodels)
- Data used for examples and vignettes are available in the digitalDLSorteRdata R package (https://github.com/diegommcc/digitalDLSorteRdata)
- Report bugs at https://github.com/diegommcc/digitalDLSorteR/issues
- Contributions and suggestions are welcome!
References
| Chung, W., Eum, H. H., Lee, H. O., Lee, K. M., Lee, H. B., Kim, K. T., et al. (2017). Single-cell RNA-Seq enables comprehensive tumour and immune cell profiling in primary breast cancer. Nat. Commun.8 (1) 15081 doi:10.1038/ncomms15081 |
| Li, H., Courtois, E. T., Sengupta, D., Tan, Y., Chen, K. H., Goh, J. J. L., et al. (2017). Reference component analysis of single-cell transcriptomes elucidates cellular heterogeneity in human colorectal tumors. Nat. Genet.49 (5), 708-718 doi:10.1038/ng.3818 |
| Torroja, C. and Sánchez-Cabo, F. (2019). digitalDLSorter: A Deep Learning algorithm to quantify immune cell populations based on scRNA-Seq data. Frontiers in Genetics10 978 doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.00978 |