Calculating Optimum Sampling Effort in Community Ecology.
ecocbo
Calculating Optimum Sampling Effort in Community Ecology
ecocbo is an R package that helps scientists calculate the optimum sampling effort for community ecology projects. The package is based on the principles developed in the SSP package, which simulates ecological communities by extracting and using parameters that control the simulation. The simulated communities are then compared with PERMANOVA to estimate their components of variation and consequently the optimal sampling effort.
ecocbo is a valuable tool for scientists who need to design efficient sampling plans. The package can help scientists to save time and money by ensuring that they collect the minimum amount of data necessary to achieve their research goals.
Installation
You can easilly obtain ‘ecocbo’ from CRAN:
install.packages("ecocbo")
Alternatively, you can install the development version of ecocbo from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("arturoSP/ecocbo")
Example
This is a basic example which shows you how to use the different functions in the package:
Prepare the data
# Load data and adjust it.
data(epiDat)
epiH0 <- epiDat
epiH0[,"site"] <- as.factor("T0")
epiHa <- epiDat
epiHa[,"site"] <- as.factor(epiHa[,"site"])
# Calculate simulation parameters.
parH0 <- SSP::assempar(data = epiH0, type = "counts", Sest.method = "average")
parHa <- SSP::assempar(data = epiHa, type = "counts", Sest.method = "average")
# Simulation.
simH0Dat <- SSP::simdata(parH0, cases = 3, N = 1000, sites = 1)
simHaDat <- SSP::simdata(parHa, cases = 3, N = 100, sites = 10)
Calculate statistical power
betaResult <- sim_beta(simH0Dat, simHaDat,
n = 5, m = 4, k = 30,
alpha = 0.05,
transformation = "square root", method = "bray",
dummy = FALSE,
useParallel = TRUE)
betaResult
#> Power at different sampling efforts (m x n):
#> n = 2 n = 3 n = 4 n = 5
#> m = 2 0.50 0.75 0.84 0.97
#> m = 3 0.44 0.96 0.97 1.00
#> m = 4 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.00
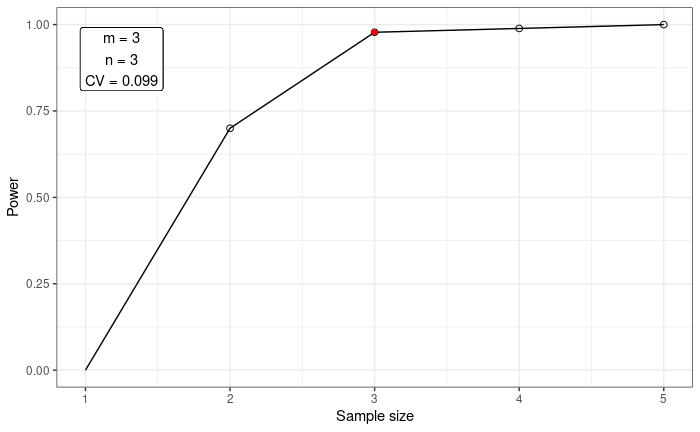
Plot the power progression as sampling increases.
plot_power(data = betaResult, n = NULL, m = 3, method = "power")
Calculate components of variation.
compVar <- scompvar(data = betaResult)
compVar
#> compVarA compVarR
#> 1 0.09943608 0.2626768
Determine optimal sampling effort
The sampling effort can be evaluated depending on an economic budget (ct) or desired precision level (multSE), depending on the proposed parameter, the function will calculate optimal values for number of treatments (bOpt) and replicates (nOpt).
cboCost <- sim_cbo(comp.var = compVar, ct = 20000, ck = 100, cj = 2500)
cboCost
#> nOpt mOpt
#> 1 8 6
cboPrecision <- sim_cbo(comp.var = compVar, multSE = 0.10, ck = 100, cj = 2500)
cboPrecision
#> nOpt mOpt
#> 1 8 13
R packages required for running ecocbo
- Required: ggplot2, ggpubr, sampling, stats, vegan
- Suggested: SSP, knitr, rmarkdown, testthat
Participating institutions.


