Analysis of Ecological Dynamic Regimes.
ecoregime
Analysis of Ecological Dynamic Regimes
ecoregime implements the EDR framework to characterize and compare groups of ecological trajectories in multidimensional spaces defined by ecosystem state variables. The EDR framework was introduced in:
- Sánchez-Pinillos, M., Kéfi, S., De Cáceres, M., Dakos, V. 2023. Ecological Dynamic Regimes: Identification, characterization, and comparison. Ecological Monographs. doi:10.1002/ecm.1589
ecoregime can be used to assess ecological resilience using ecological dynamic regimes as the system’s reference. This approach was introduced in:
- Sánchez-Pinillos M., Dakos, V., Kéfi, S. 2024. Ecological dynamic regimes: A key concept for assessing ecological resilience. Biological Conservation. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110409
Installation
You can install ecoregime via CRAN:
install.packages("ecoregime")
You can also install the development version of ecoregime with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("MSPinillos/ecoregime")
You can get an overview about its functionality and the workflow of the EDR framework in the package documentation and vignettes.
# Force the inclusion of the vignette in the installation
devtools::install_github("MSPinillos/ecoregime",
build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"),
build_vignettes = TRUE)
# Load the package after the installation
library(ecoregime)
# Access the documentation and vignette
?ecoregime
vignette("EDR_framework", package = "ecoregime")
vignette("Resilience", package = "ecoregime")
Usage
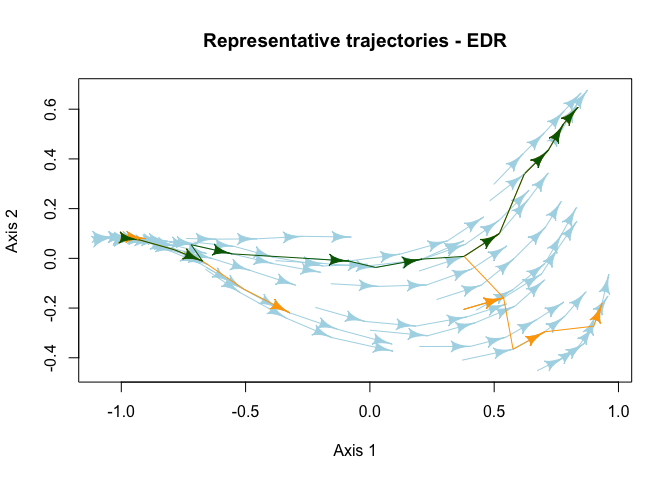
Identify and plot representative trajectories in ecological dynamic regimes.
library(ecoregime)
# Calculate state dissimilarities from a matrix of state variables (e.g., species abundances)
variables <- data.frame(EDR_data$EDR3$abundance)
d <- vegan::vegdist(variables[, -c(1:3)])
# Identify the trajectory (or site) and states in d
trajectories <- variables$traj
states <- as.integer(variables$state)
# Compute RETRA-EDR
RT <- retra_edr(d = d, trajectories = trajectories, states = states,
minSegs = 5)
# Plot representative trajectories of the EDR
plot(x = RT, d = d, trajectories = trajectories, states = states, select_RT = "T4",
traj.colors = "lightblue", RT.colors = "orange", sel.color = "darkgreen",
link.lty = 1, asp = 1, main = "Representative trajectories - EDR")
Characterize the internal structure of ecological dynamic regimes calculating the dispersion (dDis), beta diversity (dBD), and evenness (dEve) of the individual trajectories.
# Dynamic dispersion considering trajectory "1" as a reference
dDis(d = d, d.type = "dStates", trajectories = trajectories, states = states, reference = "1")
#> dDis (ref. 1)
#> 0.4083905
# Dynamic beta diversity
dBD(d = d, d.type = "dStates", trajectories = trajectories, states = states)
#> dBD
#> 0.07946371
# Dynamic evenness
dEve(d = d, d.type = "dStates", trajectories = trajectories, states = states)
#> dEve
#> 0.842375
Compare ecological dynamic regimes.
# Load species abundances and compile in a data frame
variables1 <- EDR_data$EDR1$abundance
variables2 <- EDR_data$EDR2$abundance
variables3 <- EDR_data$EDR3$abundance
all_variables <- data.frame(rbind(variables1, variables2, variables3))
# Calculate dissimilarities between every pair of states
d <- vegan::vegdist(all_variables[, -c(1:3)])
# Compute dissimilarities between EDRs:
dist_edr(d = d, d.type = "dStates",
trajectories = all_variables$traj, states = all_variables$state,
edr = all_variables$EDR, metric = "dDR", symmetrize = NULL)
#> 1 2 3
#> 1 0.0000000 0.5895458 0.6467200
#> 2 0.5700499 0.0000000 0.2768759
#> 3 0.6317846 0.5050273 0.0000000
Assess ecological resilience to pulse disturbances.
# Species abundances for disturbed communities
disturbed <- EDR_data$EDR3_disturbed$abundance[disturbed_states %in% c(0, 1, 14)]
# Species abundances for disturbed and reference communities
variables$disturbed_states <- 0
disturbed_ref <- rbind(variables, disturbed)
# Calculate dissimilarities between every pair of states
d <- vegan::vegdist(disturbed_ref[, -c(1:3, 16)])
# Use one or more representative trajectories as the reference
RT_ref <- define_retra(RT$T4$Segments)
# Resistance
resistance(d = d, trajectories = disturbed_ref$traj, states = disturbed_ref$state,
disturbed_trajectories = unique(disturbed$traj),
disturbed_states = disturbed[disturbed_states == 1]$state)
#> disturbed_trajectories Rt
#> 1 31 0.9578947
#> 2 32 0.8117647
#> 3 33 0.6928105
# Amplitude
amplitude(d = d, trajectories = disturbed_ref$traj, states = disturbed_ref$state,
disturbed_trajectories = unique(disturbed$traj),
disturbed_states = disturbed[disturbed_states == 1]$state,
reference = RT_ref)
#> disturbed_trajectories reference A_abs A_rel
#> 1 31 newT 0.0275000 0.6531250
#> 2 32 newT 0.1187553 0.6308877
#> 3 33 newT 0.2675325 0.8709036
# Recovery
recovery(d = d, trajectories = disturbed_ref$traj, states = disturbed_ref$state,
disturbed_trajectories = unique(disturbed$traj),
disturbed_states = disturbed[disturbed_states == 1]$state,
reference = RT_ref)
#> disturbed_trajectories states reference Rc_abs Rc_rel
#> 1 31 16 newT -0.46424129 -0.6288659
#> 2 32 17 newT 0.07232084 0.1065781
#> 3 33 19 newT 0.24753247 0.6885903
# Net change
net_change(d = d, trajectories = disturbed_ref$traj, states = disturbed_ref$state,
disturbed_trajectories = unique(disturbed$traj),
disturbed_states = disturbed[disturbed_states == 1]$state,
reference = RT_ref)
#> disturbed_trajectories states reference NC_abs NC_rel
#> 1 31 16 newT 0.49174129 0.7357633
#> 2 32 17 newT 0.04643449 0.1132549
#> 3 33 19 newT 0.02000000 0.5000000
Citation
To cite ecoregime in publications use:
Sánchez-Pinillos M, Kéfi S, De Cáceres M, Dakos V (2023). “Ecological dynamic regimes: Identification, characterization, and comparison.” Ecological Monographs, e1589. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1589.
Sánchez-Pinillos M, Dakos V, Kéfi S (2024). “Ecological dynamic regimes: A key concept for assessing ecological resilience.” Biological Conservation, 110409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110409.
Sánchez-Pinillos M (2023). ecoregime: Analysis of Ecological Dynamic Regimes. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7584943.
Acknowledgements
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 891477 (RESET project).