A Generalized Multiclass Support Vector Machine.
GenSVM R Package
This package implements the GenSVM Multiclass Support Vector Machine classifier in R.
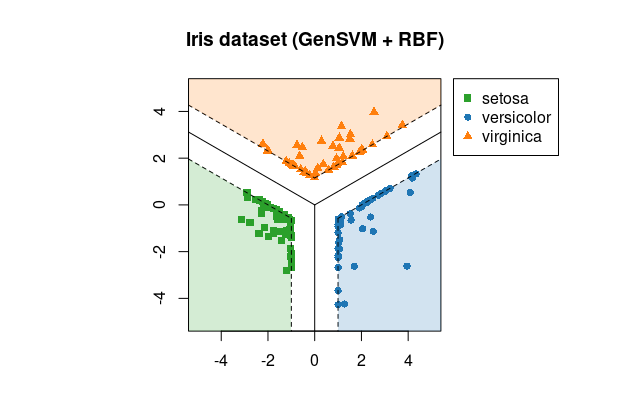
# Plot created with:
> library(gensvm)
> x <- iris[, -5]
> y <- iris[, 5]
> fit <- gensvm(x, y, kernel='rbf', gamma=10, max.iter=5000, verbose=1, random.seed=123)
> plot(fit, xlim=c(-5, 5), ylim=c(-5, 5))
> title("Iris dataset (GenSVM + RBF)")
Introduction
The GenSVM classifier is a generalized multiclass support vector machine (SVM). This classifier aims to find decision boundaries that separate the classes with as wide a margin as possible. In GenSVM, the loss functions that measures how misclassifications are counted is very flexible. This allows the user to tune the classifier to the dataset at hand and potentially obtain higher classification accuracy. Moreover, this flexibility means that GenSVM has a number of alternative multiclass SVMs as special cases. One of the other advantages of GenSVM is that it is trained in the primal space, allowing the use of warm starts during optimization. This means that for common tasks such as cross validation or repeated model fitting, GenSVM can be trained very quickly.
For more information about GenSVM, see the paper: GenSVM: A Generalized Multiclass Support Vector Machine by G.J.J. van den Burg and P.J.F. Groenen (Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016).
Installation
This package can be installed from CRAN:
> install.packages('gensvm')
Usage
The package is extensively documented with many examples. See ?gensvm-package, ?gensvm and ?gensvm.grid in R.
The main GenSVM functions are:
gensvm: Fit a GenSVM model for specific model parameters.gensvm.grid: Run a cross-validated grid search for GenSVM.
Both these functions return S3 objects for which plot and predict functions are available. For the GenSVMGrid object the function is applied to the best model found during training. For both of these objects a coef function is also available.
The following utility functions are also included in the package:
gensvm.accuracy: Compute the accuracy score between true and predicted class labelsgensvm.maxabs.scale: Scale each column of the dataset by its maximum absolute value, preserving sparsity and mapping the data to [-1, 1]gensvm.train.test.split: Split a dataset into a training and testing samplegensvm.refit: Refit a fitted GenSVM model with slightly different parameters or on a different dataset
Citing
If you use GenSVM in your work, please cite the paper using the information available through the following R command:
> citation('gensvm')
Alternatively, you can use the following BibTeX code directly:
@article{JMLR:v17:14-526,
author = {Gerrit J.J. {van den Burg} and Patrick J.F. Groenen},
title = {{GenSVM}: A Generalized Multiclass Support Vector Machine},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2016},
volume = {17},
number = {225},
pages = {1-42},
url = {https://jmlr.org/papers/v17/14-526.html}
}
License
Copyright 2018, G.J.J. van den Burg.
RGenSVM is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
RGenSVM is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with RGenSVM. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
For more information please contact:
G.J.J. van den Burg
email: [email protected]