Compare Big Datasets to the Uniform Distribution.
gg_QQ_unif
ggbigQQ extends ggplot2 to allow the user to make a quantile-quantile plot with a big dataset. Specifically, geom_big_qq uses all the data provided to calculate quantiles, but drops points that would overplot before plotting. <!-- There's no use in having ten thousand points in a plot to define a line -- we can't even see most of them! --> In this way, the resultant figure maintains all the accuracy of a Q-Q plot made with a large dataset, but renders as fast as one from a smaller dataset and, when stored as a vector graphic, has the file size of a Q-Q plot from a smaller dataset.
Examples
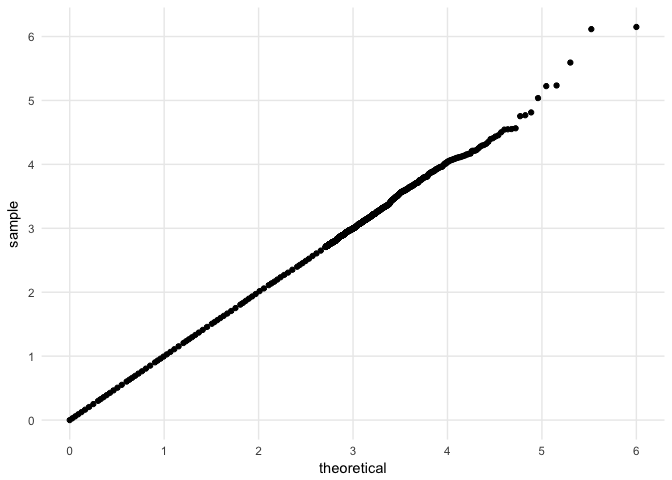
Here's an example where geom_qq takes 14 seconds to render the plot on my intel i5 and geom_big_qq takes 1 second to produce the same plot.
set.seed(27599)
d <- data.frame(s = runif(n = 5e5))
# # takes 14 seconds
# d %>%
# ggplot(mapping = aes(sample = s)) +
# geom_qq(distribution = qunif) +
# QQ_scale_x() +
# QQ_scale_y()
# takes 1 second
d %>%
ggplot(mapping = aes(sample = s)) +
geom_QQ_unif() +
scale_x_QQ() +
scale_y_QQ() +
theme_minimal()
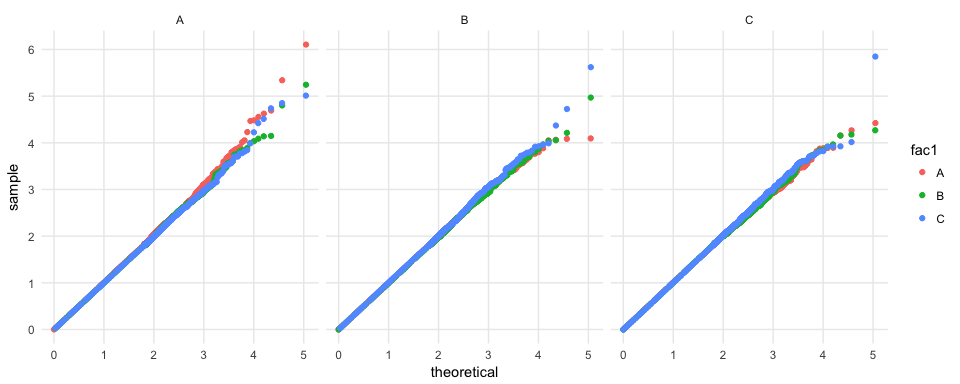
This geom works with other aesthetics, too.
set.seed(27599)
n <- 5e5
d <- data.frame(fac1 = sample(x = LETTERS[1:3], size = n, replace = TRUE),
fac2 = sample(x = LETTERS[1:3], size = n, replace = TRUE),
s = runif(n = n))
# takes 1 second
d %>%
ggplot(mapping = aes(sample = s, color = fac1)) +
geom_QQ_unif() +
facet_wrap(~ fac2) +
scale_x_QQ() +
scale_y_QQ() +
theme_minimal()