Description
Analyze and Create Elegant Directed Acyclic Graphs.
Description
Tidy, analyze, and plot directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). 'ggdag' is built on top of 'dagitty', an R package that uses the 'DAGitty' web tool (<https://dagitty.net/>) for creating and analyzing DAGs. 'ggdag' makes it easy to tidy and plot 'dagitty' objects using 'ggplot2' and 'ggraph', as well as common analytic and graphical functions, such as determining adjustment sets and node relationships.
README.md
ggdag: An R Package for visualizing and analyzing causal directed acyclic graphs 
Tidy, analyze, and plot causal directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). ggdag uses the powerful dagitty package to create and analyze structural causal models and plot them using ggplot2 and ggraph in a consistent and easy manner.
Installation
You can install ggdag with:
install.packages("ggdag")
Or you can install the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("r-causal/ggdag")
Example
ggdag makes it easy to use dagitty in the context of the tidyverse. You can directly tidy dagitty objects or use convenience functions to create DAGs using a more R-like syntax:
library(ggdag)
library(ggplot2)
# example from the dagitty package
dag <- dagitty::dagitty("dag {
y <- x <- z1 <- v -> z2 -> y
z1 <- w1 <-> w2 -> z2
x <- w1 -> y
x <- w2 -> y
x [exposure]
y [outcome]
}")
tidy_dag <- tidy_dagitty(dag)
tidy_dag
#> # A DAG with 7 nodes and 12 edges
#> #
#> # Exposure: x
#> # Outcome: y
#> #
#> # A tibble: 13 × 8
#> name x y direction to xend yend circular
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl>
#> 1 v 0.496 -3.40 -> z1 1.83 -2.92 FALSE
#> 2 v 0.496 -3.40 -> z2 0.0188 -2.08 FALSE
#> 3 w1 1.73 -1.94 -> x 2.07 -1.42 FALSE
#> 4 w1 1.73 -1.94 -> y 1.00 -0.944 FALSE
#> 5 w1 1.73 -1.94 -> z1 1.83 -2.92 FALSE
#> 6 w1 1.73 -1.94 <-> w2 0.873 -1.56 FALSE
#> 7 w2 0.873 -1.56 -> x 2.07 -1.42 FALSE
#> 8 w2 0.873 -1.56 -> y 1.00 -0.944 FALSE
#> 9 w2 0.873 -1.56 -> z2 0.0188 -2.08 FALSE
#> 10 x 2.07 -1.42 -> y 1.00 -0.944 FALSE
#> 11 y 1.00 -0.944 <NA> <NA> NA NA FALSE
#> 12 z1 1.83 -2.92 -> x 2.07 -1.42 FALSE
#> 13 z2 0.0188 -2.08 -> y 1.00 -0.944 FALSE
# using more R-like syntax to create the same DAG
tidy_ggdag <- dagify(
y ~ x + z2 + w2 + w1,
x ~ z1 + w1 + w2,
z1 ~ w1 + v,
z2 ~ w2 + v,
w1 ~ ~w2, # bidirected path
exposure = "x",
outcome = "y"
) %>%
tidy_dagitty()
tidy_ggdag
#> # A DAG with 7 nodes and 12 edges
#> #
#> # Exposure: x
#> # Outcome: y
#> #
#> # A tibble: 13 × 8
#> name x y direction to xend yend circular
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <lgl>
#> 1 v -3.58 3.30 -> z1 -4.05 4.63 FALSE
#> 2 v -3.58 3.30 -> z2 -2.23 3.74 FALSE
#> 3 w1 -3.03 5.74 -> x -3.20 5.14 FALSE
#> 4 w1 -3.03 5.74 -> y -1.98 5.22 FALSE
#> 5 w1 -3.03 5.74 -> z1 -4.05 4.63 FALSE
#> 6 w1 -3.03 5.74 <-> w2 -2.35 4.72 FALSE
#> 7 w2 -2.35 4.72 -> x -3.20 5.14 FALSE
#> 8 w2 -2.35 4.72 -> y -1.98 5.22 FALSE
#> 9 w2 -2.35 4.72 -> z2 -2.23 3.74 FALSE
#> 10 x -3.20 5.14 -> y -1.98 5.22 FALSE
#> 11 y -1.98 5.22 <NA> <NA> NA NA FALSE
#> 12 z1 -4.05 4.63 -> x -3.20 5.14 FALSE
#> 13 z2 -2.23 3.74 -> y -1.98 5.22 FALSE
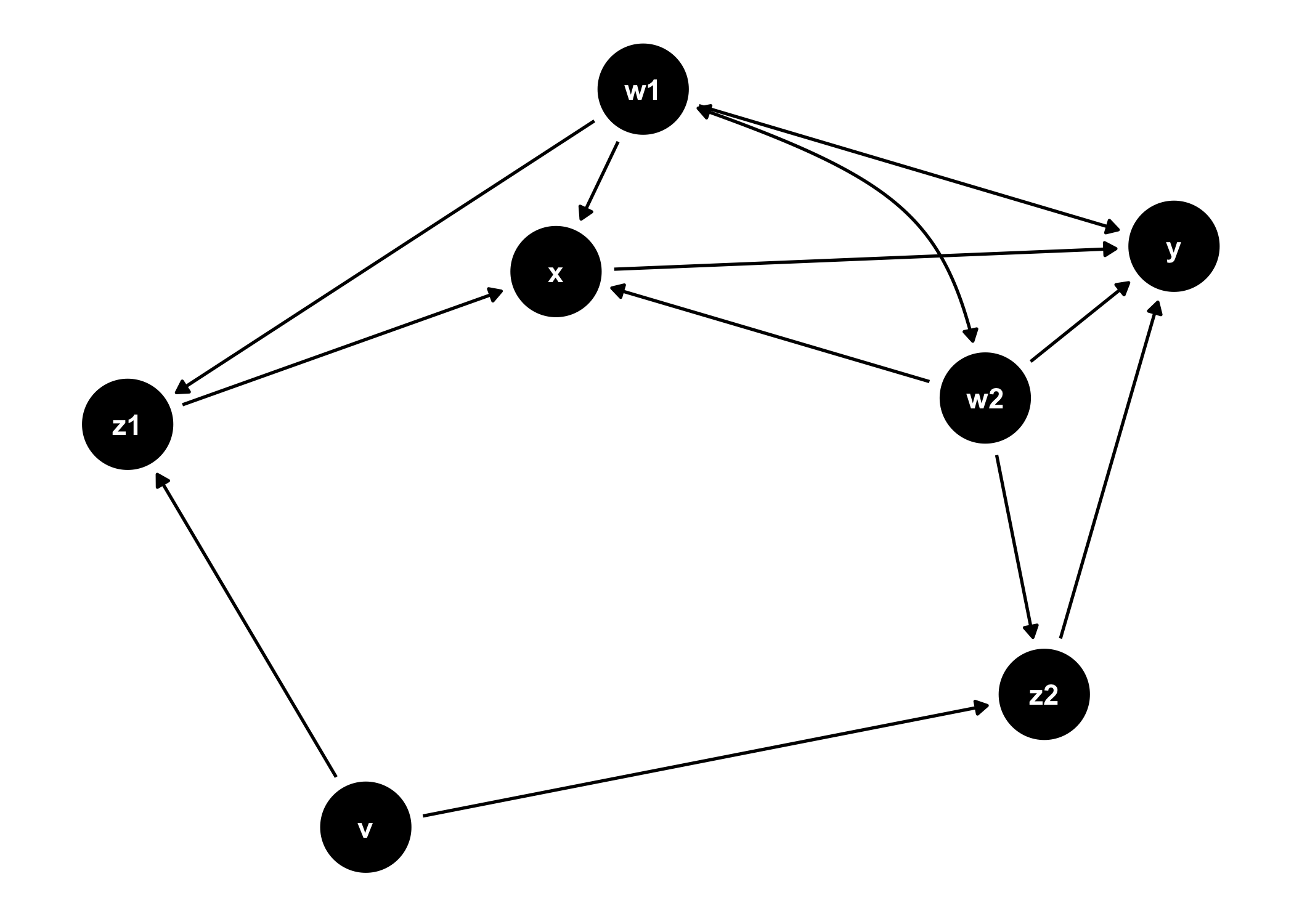
ggdag also provides functionality for analyzing DAGs and plotting them in ggplot2:
ggdag(tidy_ggdag) +
theme_dag()
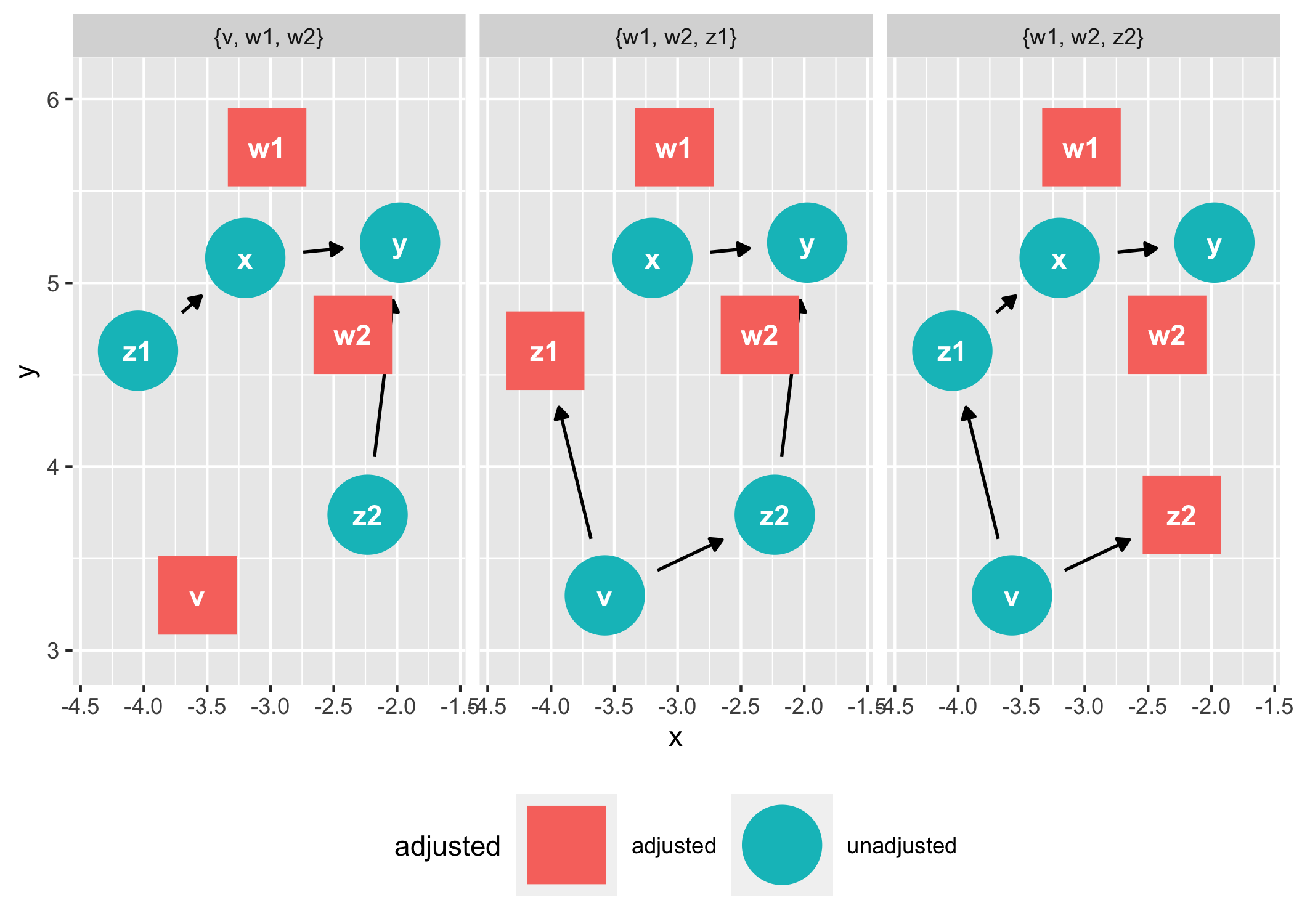
ggdag_adjustment_set(tidy_ggdag, node_size = 14) +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
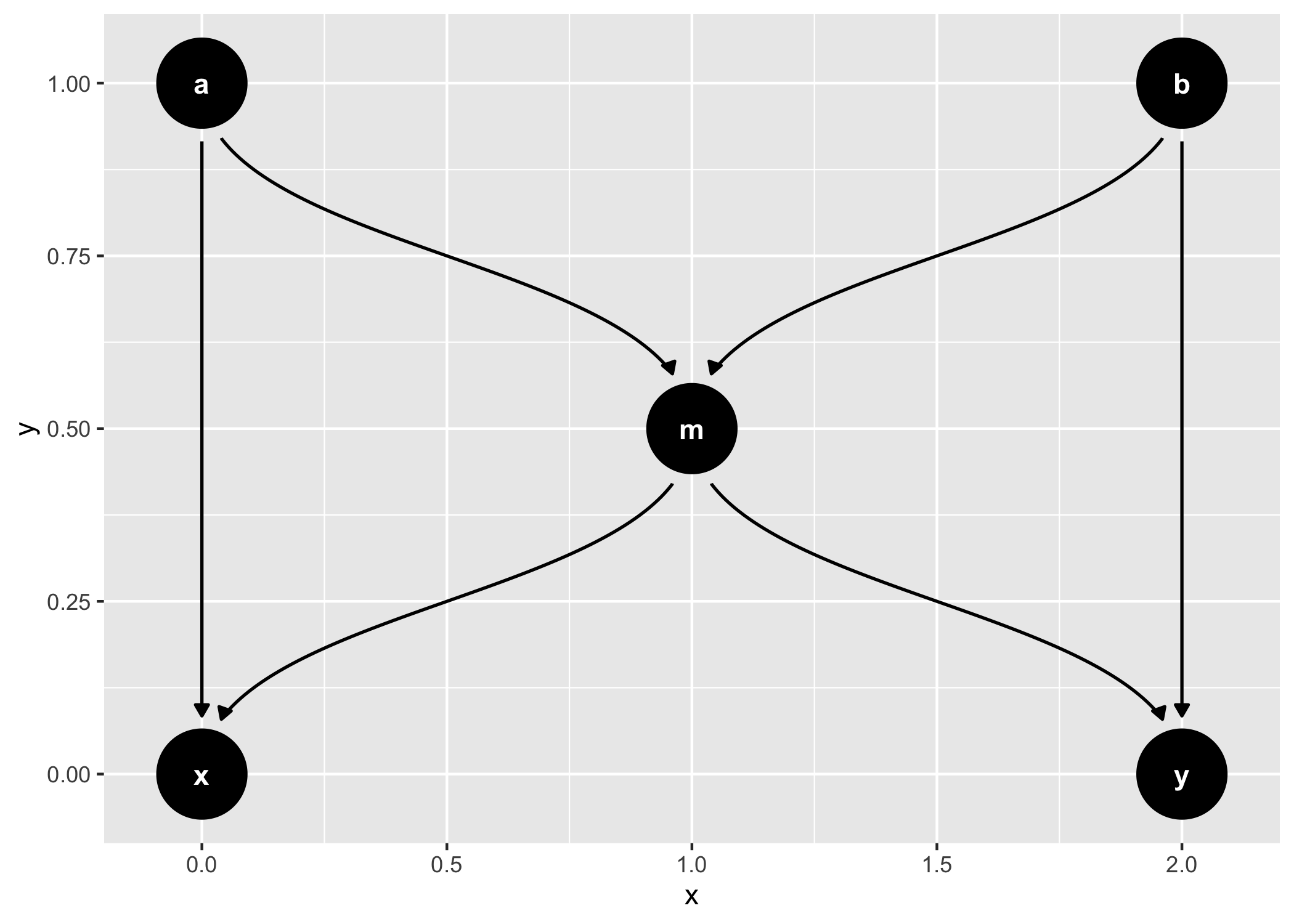
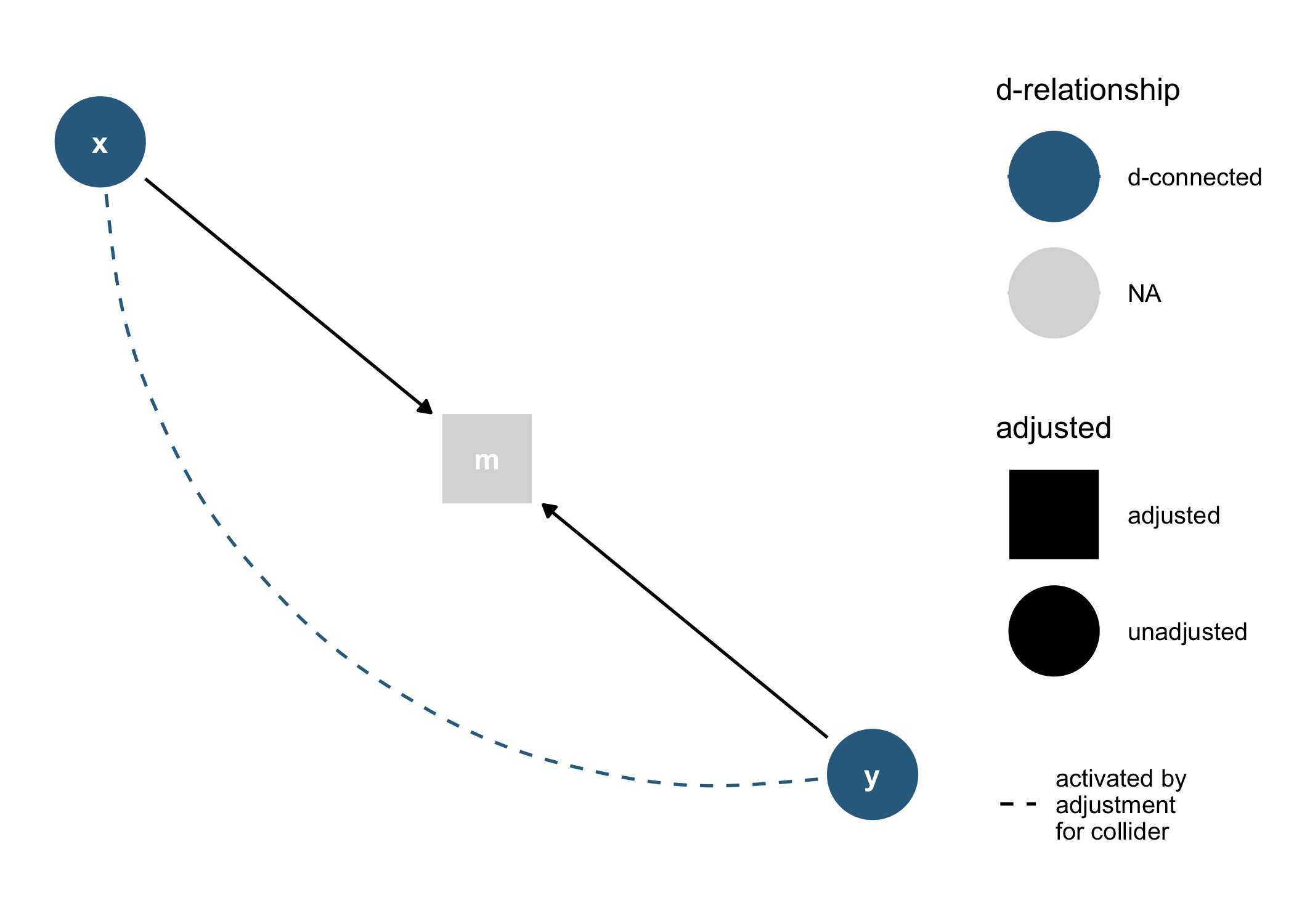
As well as geoms and other functions for plotting them directly in ggplot2:
dagify(m ~ x + y) %>%
tidy_dagitty() %>%
node_dconnected("x", "y", controlling_for = "m") %>%
ggplot(aes(
x = x,
y = y,
xend = xend,
yend = yend,
shape = adjusted,
col = d_relationship
)) +
geom_dag_edges(end_cap = ggraph::circle(10, "mm")) +
geom_dag_collider_edges() +
geom_dag_point() +
geom_dag_text(col = "white") +
theme_dag() +
scale_adjusted() +
expand_plot(expand_y = expansion(c(0.2, 0.2))) +
scale_color_viridis_d(
name = "d-relationship",
na.value = "grey85",
begin = .35
)
And common structures of bias:
ggdag_equivalent_dags(confounder_triangle())
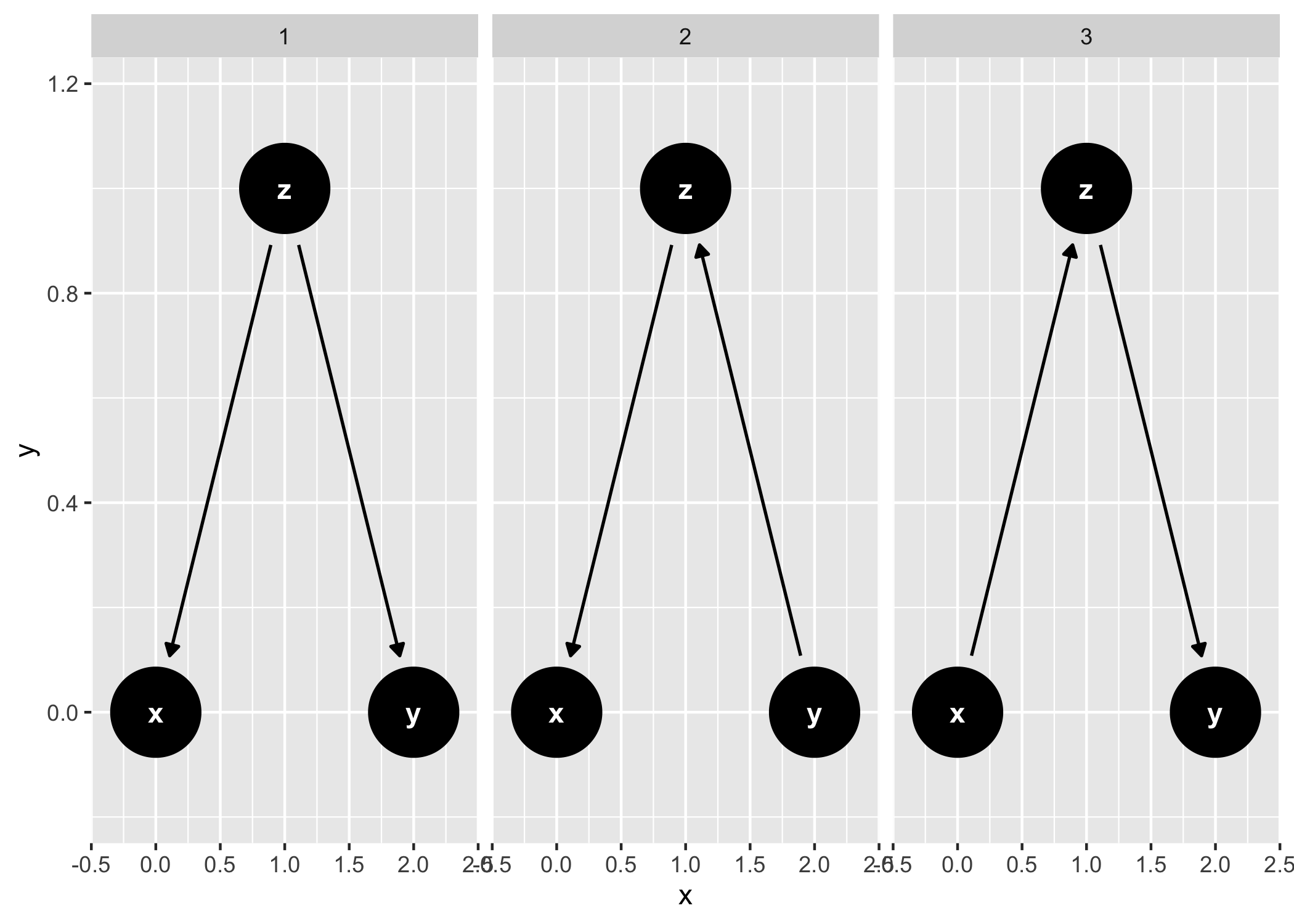
ggdag_butterfly_bias(edge_type = "diagonal")