Create Hillshade Relief Maps Using Ray-Tracing.
hillshader
The hillshader package is a wrapper around the rayshader and raster packages to create hillshade relief maps using ray-tracing, and write them to (spatial) files.
Installation
The stable version of hillshader can be installed from CRAN:
install.packages("hillshader")
Alternatively, if you feel brave, you can install the development version of hillshader with the remotes package:
remotes::install_github("pierreroudier/hillshader")
First steps
Below is a quick tutorial of the hillshader capabilities:
The hillshader function
The hillshader function is the main function of that package, and allows to create a hillshade map as a RasterLayer:
library(raster)
#> Loading required package: sp
library(rayshader)
library(hillshader)
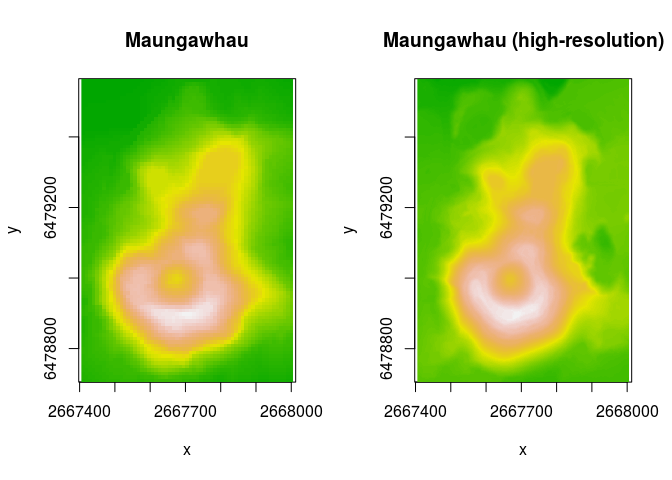
Note that the hillshader package includes the maungawhau and maungawhau_hr datasets. These are geo-referenced, raster datasets. maungawhau corresponds to the well-known volcano dataset. It is a 87 × 61 elevation matrix for Maungawhau, one of the circa 80 volcanoes in the Auckland volcano filed, in Aotearoa/New Zealand. The maungawhau_hr dataset is a “high-resolution” version of that dataset, and is a 1 m resolution, 860 × 600 elevation matrix derived from a LiDAR dataset recorded by NZ Aerial Mapping & Aerial Surveying Limited for Auckland Council, and distributed by Land Information New Zealand.
layout(matrix(c(1,2), nrow = 1, ncol = 2))
image(maungawhau, asp = 1, main = "Maungawhau", col = terrain.colors(100))
image(maungawhau_hr, asp = 1, main = "Maungawhau (high-resolution)", col = terrain.colors(100))
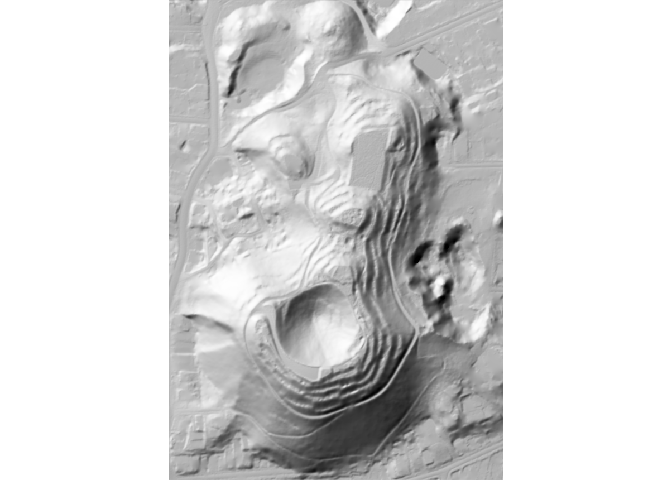
The hillshader function can be simply called on a elevation raster to generate a hillshade RasterLayer. By default, the shader used is rayshader::ray_shade, with its default values.
hs <- hillshader(maungawhau_hr)
plot_map(hs)

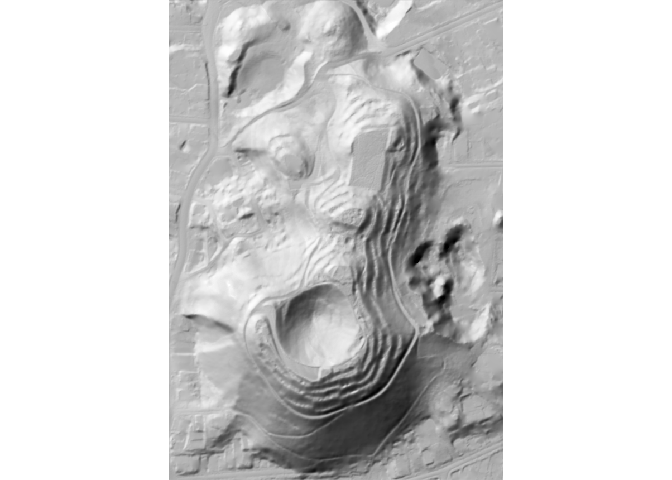
Add more shaders!
The hillshader function accept a shader option, with is a list of the successive shader functions to apply to create the hillshade layer. The accepted values must be rayshader shader functions (ray_shade, ambient_shade, lamb_shade), and the order is important.
hs <- hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade")
)
plot_map(hs)

Changing sun position
The hillshader function uses the rayshader options defaults, but other values can be specify and passed as arguments:
hs <- hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 180,
sunaltitude = 25
)
plot_map(hs)
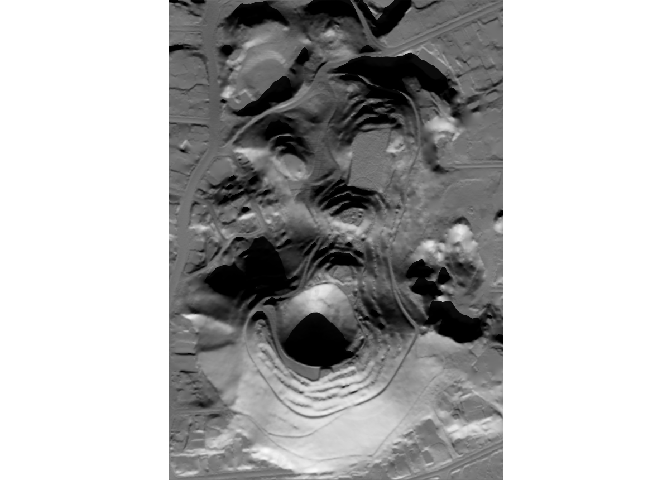

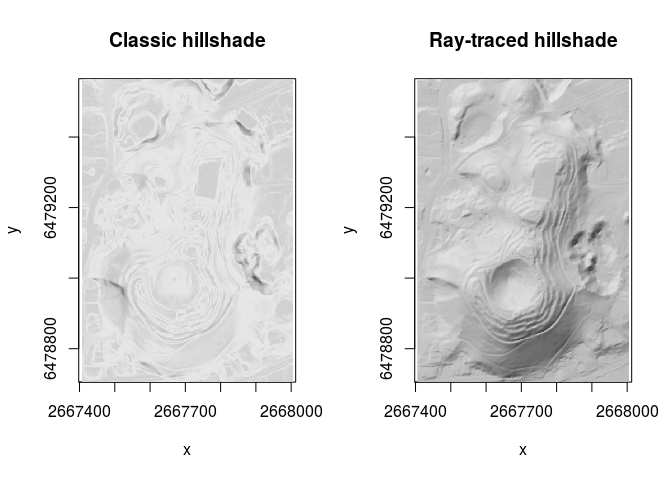
How does it compare to your usual hillshade method?
library(raster)
slope <- terrain(maungawhau_hr, out = "slope")
aspect <- terrain(maungawhau_hr, out = "aspect")
hs_raster <- hillShade(
slope,
aspect,
angle = 40,
direction = 325
)
hs_hillshader <- hillshader(
maungawhau_hr,
c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 325,
sunaltitude = 40
)
layout(matrix(c(1,2), nrow = 1, ncol = 2))
image(hs_raster, asp = 1, main = "Classic hillshade", col = grey.colors(100))
image(hs_hillshader, asp = 1, main = "Ray-traced hillshade", col = grey.colors(100))
Saving to file
If a filename is passed to hillshader, then the resulting hillshade layer is saved to file. This is a wrapper around raster::writeRaster, and options specific to the latter function can be used.
hillshader(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
shader = c("ray_shade", "ambient_shade"),
sunangle = 180,
sunaltitude = 25,
filename = "hillshade.tif"
)
Advanced use in the rayshader pipelines
The hillshader package provides three functions that can be used within the rayshader pipelines:
add_shadow_2d: a function that multiplies a shadow map by another shadow map, a corrected 2D version ofrayshader::add_shadow,matrix_to_raster: a function that converts a matrix (typically used by therayshaderfunctions) back to aRasterLayer, for input into a GIS workflow,write_raster: a function that a hillshade matrix to a raster file format.
library(rayshader)
library(hillshader)
# Create elevation matrix
el_mat <- raster_to_matrix(maungawhau_hr)
el_mat %>%
# Create hillshade layer using
# ray-tracing
ray_shade %>%
# Add ambient shading
add_shadow_2d(
ambient_shade(
heightmap = el_mat
)
) %>%
# Write to GIS file
write_raster(
elevation = maungawhau_hr,
filename = "hillshade.tif"
)
Code of Conduct
Please note that the hillshader project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.