Basic Pipe and Open Channel Hydraulics.
Description
The hydraulics R package solves basic pipe hydraulics for both pressure and gravity flow conditions, and open-channel hydraulics for trapezoidal channels, including triangular and rectangular. Pressure pipe solutions include functions to 1) describe properties of water, 2) solve the Darcy-Weisbach equation for friction loss through pipes, and 3) plot a Moody diagram. There are also functions for matching a pump characteristic curve to a system curve, and solving for flows in a pipe network using the Hardy-Cross method. Partially-filled pipe and other open-channel flow solutions are solved with the Manning equation. The format of functions and pressure pipe solutions are designed to be compatible with the iemisc package, and the open channel hydraulics solutions are modifications of code in that package.
Installation
#Install the stable CRAN version of this package
install.packages("hydraulics")
#Install the development version of this package
if (!requireNamespace("remotes", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("EdM44/hydraulics")
Examples (see more examples in the function descriptions)
library(hydraulics)
1) Type 1 problem (solve for friction loss): Eng (US) units
D <- 20/12 #20 inch converted to ft
L <- 10560 #ft
Q <- 4 #ft3/s
T <- 60 #F
ks <- 0.0005 #ft
#Optionally, use utility functions to find the Reynolds Number and friction factor, f:
reynolds_number(V = velocity(D, Q), D = D, nu = kvisc(T = T, units = "Eng"))
#> [1] 248624.7
colebrook(ks = ks, V = velocity(D, Q), D = D, nu = kvisc(T = T, units = "Eng"))
#> [1] 0.0173031
#Solve directly for the missing value of friction loss
ans1 <- darcyweisbach(Q = Q,D = D, L = L, ks = ks, nu = kvisc(T=T, units="Eng"), units = c("Eng"))
#> hf missing: solving a Type 1 problem
cat(sprintf("Reynolds no: %.0f\nFriction Fact: %.4f\nHead Loss: %.2f ft\n", ans1$Re, ans1$f, ans1$hf))
#> Reynolds no: 248625
#> Friction Fact: 0.0173
#> Head Loss: 5.72 ft
2) Type 2 (solving for flow rate, Q): SI Units
D <- .5 #m
L <- 10 #m
hf <- 0.006*L #m
T <- 20 #C
ks <- 0.000046 #m
ans2 <- darcyweisbach(D = D, hf = hf, L = L, ks = ks, nu = kvisc(T=T, units='SI'), units = c('SI'))
#> Q missing: solving a Type 2 problem
cat(sprintf("Reynolds no: %.0f\nFriction Fact: %.4f\nFlow: %.2f m3/s\n", ans2$Re, ans2$f, ans2$Q))
#> Reynolds no: 1010337
#> Friction Fact: 0.0133
#> Flow: 0.41 m3/s
Type 3 (solving for diameter, D): Eng (US) units
Q <- 37.5 #flow in ft^3/s
L <- 8000 #pipe length in ft
hf <- 215 #head loss due to friction, in ft
T <- 68 #water temperature, F
ks <- 0.0008 #pipe roughness, ft
ans3 <- darcyweisbach(Q = Q, hf = hf, L = L, ks = ks, nu = kvisc(T=T, units='Eng'), units = c('Eng'))
#> D missing: solving a Type 3 problem
cat(sprintf("Reynolds no: %.0f\nFriction Fact: %.4f\nDiameter: %.2f ft\n", ans3$Re, ans3$f, ans3$D))
#> Reynolds no: 2336974
#> Friction Fact: 0.0164
#> Diameter: 1.85 ft
Solving for roughness height (ks): Eng (US) units, print results as data frame
D <- 1.85 #diameter in ft
Q <- 37.5 #flow in ft^3/s
L <- 8000 #pipe length in ft
hf <- 215 #head loss due to friction, in ft
T <- 68 #water temperature, F
ans4 <- darcyweisbach(Q = Q, D = D, hf = hf, L = L, nu = kvisc(T=T, units='Eng'), units = c('Eng'))
#> ks missing: solving for missing roughness height
knitr::kable(setNames(as.data.frame(unlist(ans4)),c('value')), format = "html", padding=0)
value | |
|---|---|
Q | 3.750000e+01 |
V | 1.395076e+01 |
L | 8.000000e+03 |
D | 1.850000e+00 |
hf | 2.150000e+02 |
f | 1.649880e-02 |
ks | 8.176000e-04 |
Re | 2.335866e+06 |
Utility functions for water properties can be used independently as well:
Find kinematic viscosity for water temperature of 55 F
nu = kvisc(T = 55, units = 'Eng')
cat(sprintf("Kinematic viscosity: %.3e ft2/s\n", nu))
#> Kinematic viscosity: 1.318e-05 ft2/s
Find kinematic viscosity assuming default water temperature of 68 F
nu = kvisc(units = 'Eng')
#>
#> Temperature not given.
#> Assuming T = 68 F
cat(sprintf("Kinematic viscosity: %.3e ft2/s\n", nu))
#> Kinematic viscosity: 1.105e-05 ft2/s
Find water density for water temperature of 25 C
rho = dens(T = 25, units = 'SI')
cat(sprintf("Water density: %.3f kg/m3\n", rho))
#> Water density: 997.075 kg/m3
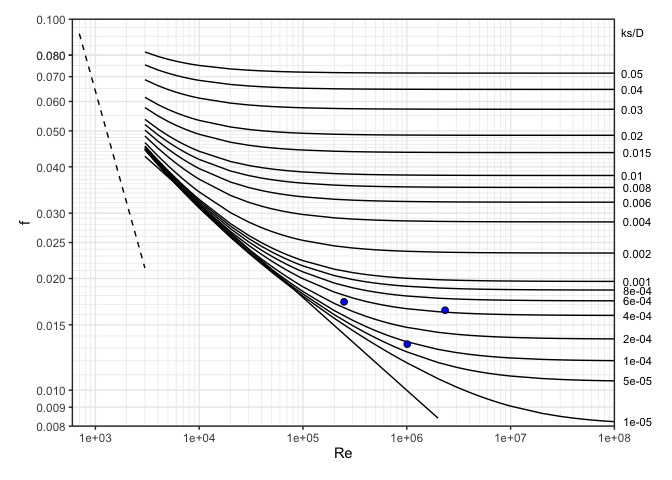
Plot a Moody diagram, with optional points added
moody(Re = c(ans1$Re, ans2$Re, ans3$Re), f = c(ans1$f, ans2$f, ans3$f))
Open Channel Flow in a Pipe: solving for Q: SI Units
oc1 <- manningc(d = 0.6, n = 0.013, Sf = 1./400., y = 0.24, units = "SI")
cat(sprintf("Flow rate, Q: %.2f m3/s\nFull pipe flow rate, Qf: %.2f\n", oc1$Q, oc1$Qf))
#> Flow rate, Q: 0.10 m3/s
#> Full pipe flow rate, Qf: 0.31
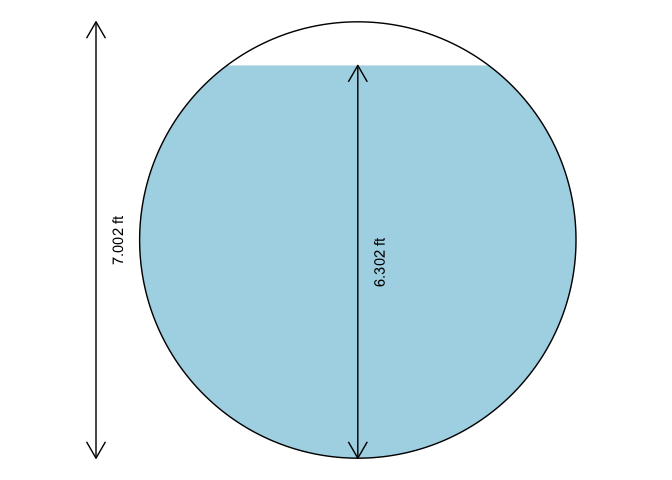
Open Channel Flow in a Pipe: solving for diameter, d when given y_d): Eng (US) units
oc2 <- manningc(Q = 83.5, n = 0.015, Sf = 0.0002, y_d = 0.9, units = "Eng")
cat(sprintf("Required diameter: %.2f ft\nFlow depth: %.2f\n", oc2$d, oc2$y))
#> Required diameter: 7.00 ft
#> Flow depth: 6.30
Plot the cross section for the last example
xc_circle( y = oc2$y ,d = oc2$d, units = "Eng" )
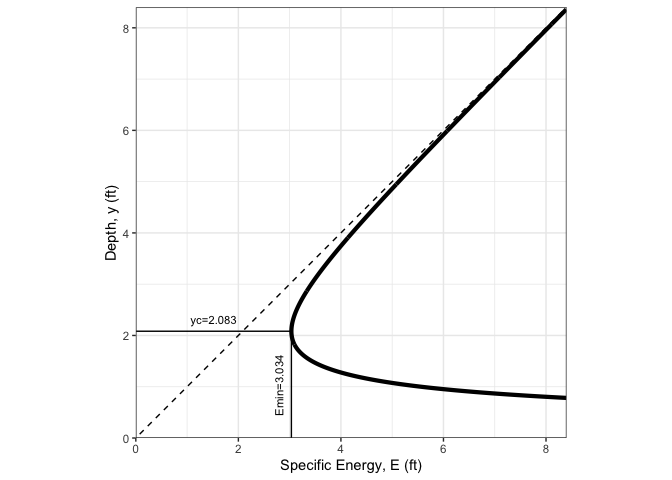
Open Channel Flow in a Channel: solving for slope: Eng (US) units
oc3 <- manningt(Q = 360., n = 0.015, m = 1, b = 20.0, y = 3.0, units = "Eng")
cat(sprintf("Slope: %.5f ft\nCritical depth: %.2f\n", oc3$Sf, oc3$yc))
#> Slope: 0.00088 ft
#> Critical depth: 2.08
Plot a specific energy diagram for the channel of last example
spec_energy_trap( Q = oc3$Q, b = oc3$b, m = oc3$m, scale = 4, units = "Eng" )
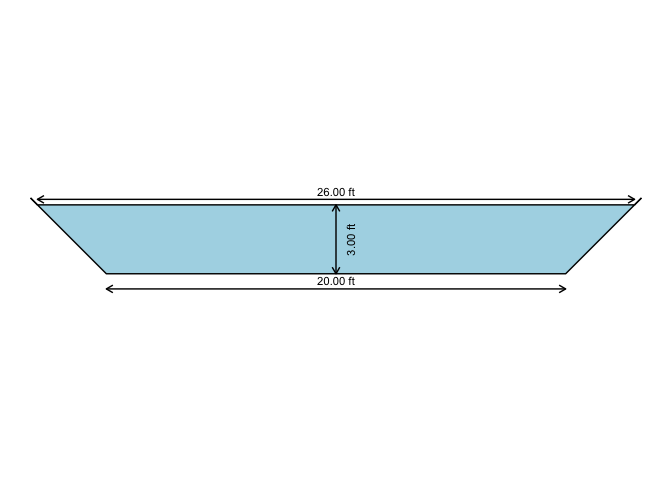
Plot the cross section for the last example
xc_trap( y = oc3$y, b = oc3$b, m = oc3$m, units = "Eng" )
#> Warning in ggplot2::geom_segment(data = seg1, ggplot2::aes(x = 0, xend = -0.1 * : All aesthetics have length 1, but the data has 2 rows.
#> ℹ Please consider using `annotate()` or provide this layer with data containing
#> a single row.
#> Warning in ggplot2::geom_segment(data = seg1, ggplot2::aes(x = B, xend = B + : All aesthetics have length 1, but the data has 2 rows.
#> ℹ Please consider using `annotate()` or provide this layer with data containing
#> a single row.
For other functions related to pump characteristic curves and operating point determination, and pipe network solutions, refer to the hydraulics vignette.