HMM Toolkit for Inferring IBD Segments from SNP Genotypes.
ibdfindr
The goal of ibdfindr is to detect genomic regions shared identical by descent (IBD) between two individuals, using SNP genotypes. It does so by fitting a continuous-time hidden Markov model (HMM) to the data.
Installation
Until ibdfindr becomes available on CRAN, you may install the development version from GitHub:
remotes::install_github("magnusdv/ibdfindr")
Example
library(ibdfindr)
As an example we consider the built-in dataset cousinsDemo, which contains almost 4000 SNP genotypes for two related individuals (in fact, a pair of cousins).
head(cousinsDemo)
#> CHROM MARKER MB CM A1 A2 FREQ1 ID1 ID2
#> 1 1 rs9442372 1.083324 0.0000000 A G 0.3890 A/G G/G
#> 2 1 rs4648727 1.844830 0.1803812 A C 0.3628 A/C A/C
#> 3 1 rs10910082 2.487496 1.2670505 C T 0.3740 C/T C/T
#> 4 1 rs6695131 3.084360 1.9782286 C T 0.5719 C/T C/T
#> 5 1 rs3765703 3.675872 4.8403127 G T 0.4058 G/G T/T
#> 6 1 rs7367066 3.887191 5.7748481 C T 0.6739 C/C C/C
The function findIBD() conveniently wraps the key steps of the package:
- Fit a continuous-time HMM to the data (
fitHMM()) - Find the most likely set of IBD segments (
findSegments()) - Calculate the posterior IBD probability at each marker (
ibdPosteriors())
ibd = findIBD(cousinsDemo)
#> Individuals: ID1, ID2
#> Chromosome type: autosomal
#> Fitting HMM parameters...
#> Optimising `k1` and `a` jointly; method: L-BFGS-B
#> k1 = 0.185, a = 7.430
#> Finding IBD segments...
#> 14 segments (total length: 597.21 cM)
#> Calculating IBD posteriors...
#> Analysis complete in 0.937 secs
For details of the different steps, see the documentation of the individual functions: fitHMM(), findSegments(), and ibdPosteriors().
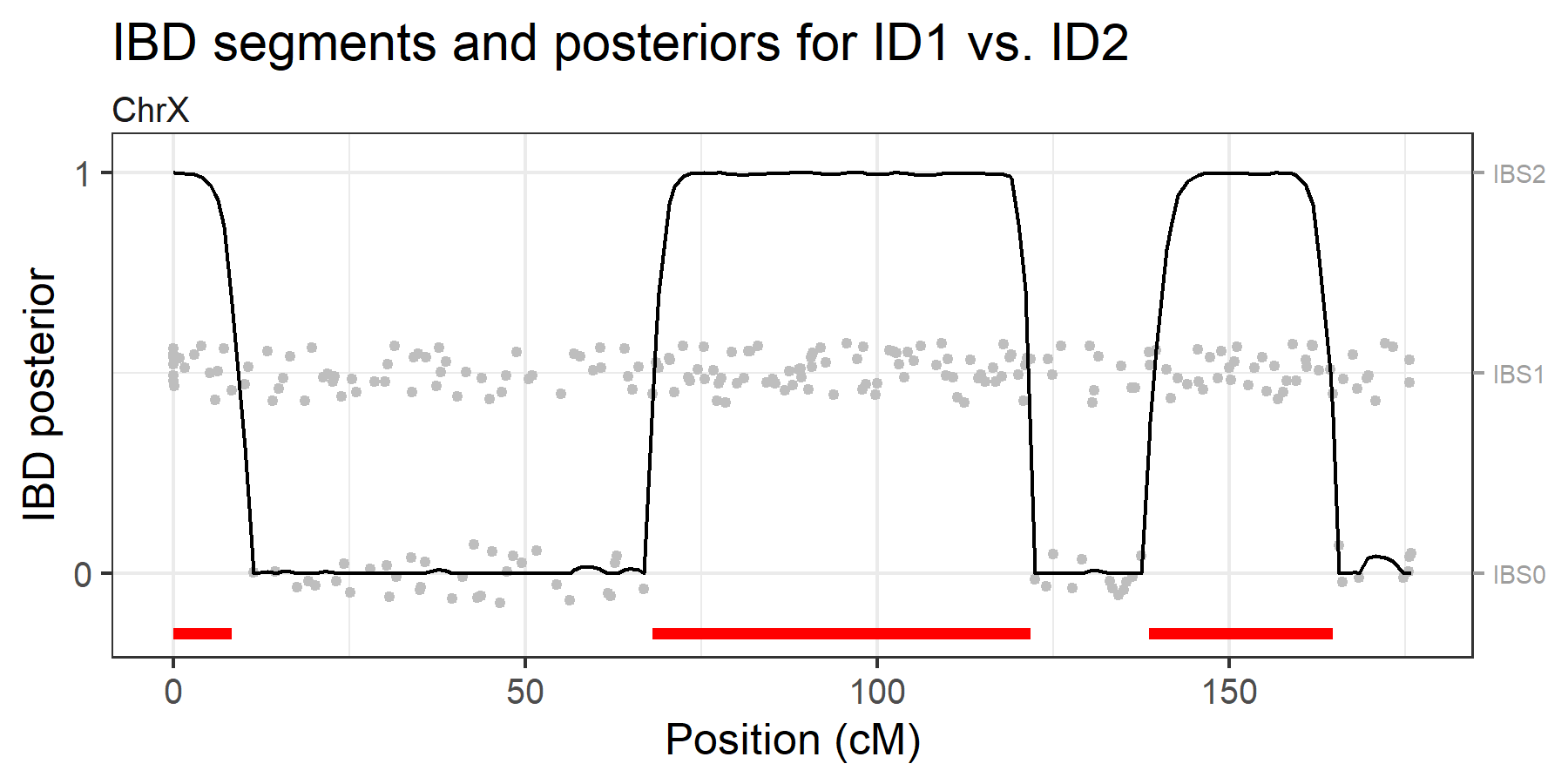
To visualise the results we pass the output to plotIBD(). This plots the posterior probabilities on a background (grey points) showing the identity-by-state (IBS) status at each marker, i.e. whether the individuals have 0, 1 or 2 alleles in common. Inferred IBD regions are shown as red segments at the bottom of each chromosome panel.
plotIBD(ibd)
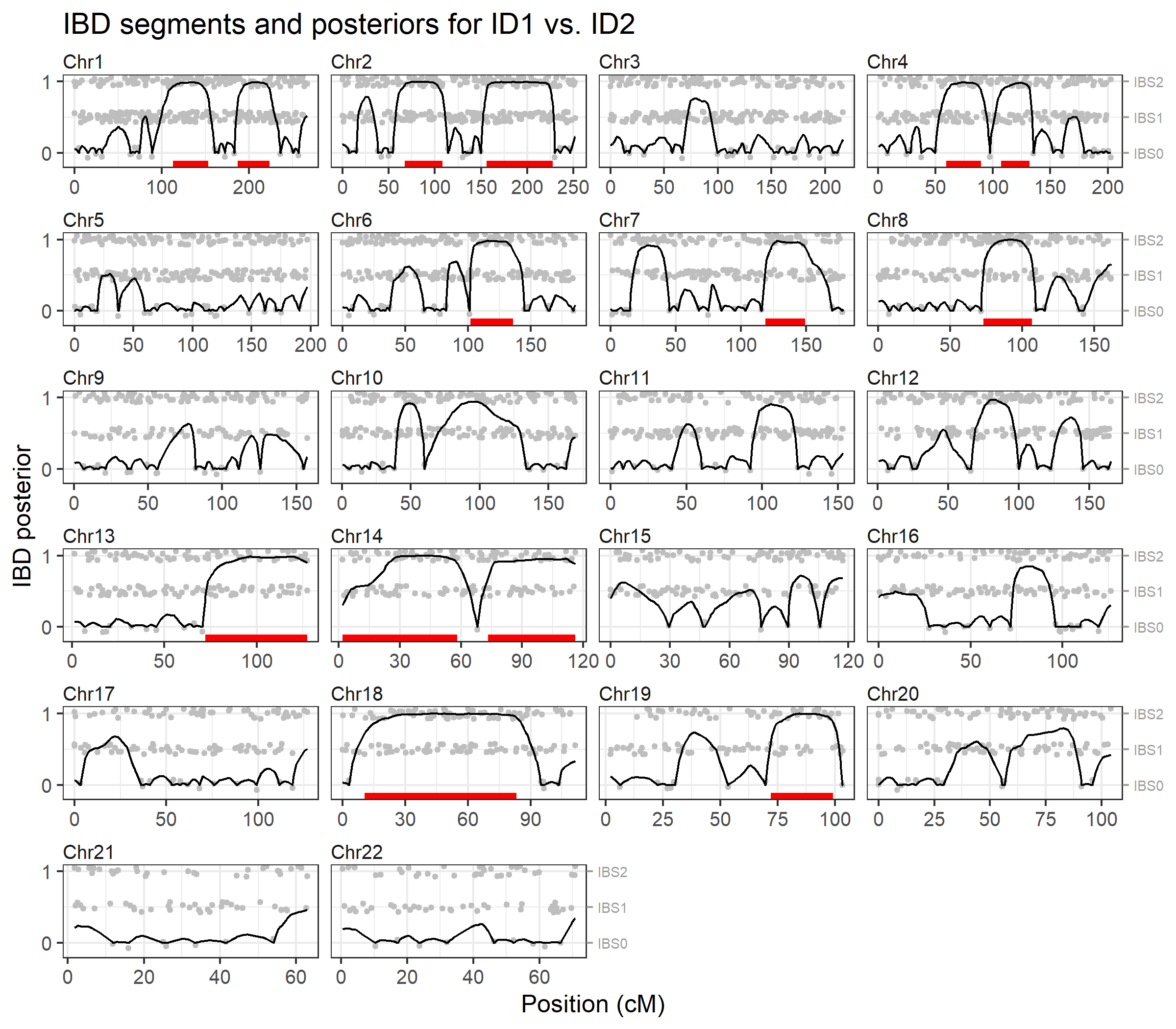
We may also inspect the identified segments as a data frame, showing the start and end positions, and the number of markers in each segment:
ibd$segments
#> chrom startCM endCM n
#> 1 1 113.000492 153.08623 54
#> 2 1 186.630319 223.39542 46
#> 3 2 67.118524 108.35905 50
#> 4 2 156.120361 227.62362 90
#> 5 4 59.474215 89.85522 41
#> 6 4 106.931772 131.69280 35
#> 7 6 102.041153 136.17734 43
#> 8 7 118.702115 149.11283 38
#> 9 8 72.976430 106.82971 55
#> 10 13 72.049460 127.22724 63
#> 11 14 1.808552 58.07117 67
#> 12 14 73.201009 116.00254 49
#> 13 18 10.592411 83.28443 101
#> 14 19 72.014020 99.15558 34
X-chromosome example
The brothersX dataset contains genotypes for two brothers typed with 246 X-chromosomal SNPs. The analysis below indicates that they share 3 IBD segments on the X chromosome.
ibdX = findIBD(brothersX)
#> Individuals: ID1, ID2
#> Chromosome type: X (male/male)
#> Fitting HMM parameters...
#> Optimising `k1` and `a` jointly; method: L-BFGS-B
#> k1 = 0.649, a = 6.635
#> Finding IBD segments...
#> 3 segments (total length: 88.05 cM)
#> Calculating IBD posteriors...
#> Analysis complete in 0.1 secs
plotIBD(ibdX)