Power Analysis for IRT Models Using the Wald, LR, Score, and Gradient Statistics.
irtpwr
This package offers implementation of analytical and sampling-based power analyses for the Wald, LR, score, and gradient tests in the frameworks of linear hypotheses and marginal maximum likelihood estimation. The methods are described in our paper (Zimmer et al. (2022), https://doi.org/10.1007/s11336-022-09883-5).
Installation
You can install the CRAN version using:
install.packages("irtpwr")
Or, you can install the development version of irtpwr from GitHub with:
# install.packages('devtools')
devtools::install_github("flxzimmer/irtpwr", build_vignettes = TRUE)
Toy example
We can load the irtpwr package using:
library(irtpwr)
library(mirt)
#> Loading required package: stats4
#> Loading required package: lattice
We want to know the power and the required sample size for a test of the Rasch vs 2PL model. We use the LSAT 7 data set which is included the mirt package.
As a first step, we load the data set and fit a 2PL model.
dat <- expand.table(LSAT7)
mirtfit <- mirt(dat, 1, verbose = FALSE)
The 2PL parameters are then used as parameters for the alternative hypothesis in our hypothesis definition.
hyp <- setup.hypothesis(type = "1PLvs2PL", altpars = mirtfit)
We can now perform the power analysis. We want to determine the sample size necessary for a power of .8 while using an alpha level of .05.
res <- irtpwr(hyp = hyp, power = 0.8, alpha = 0.05)
summary(res)
#>
#> Sample sizes for power = 0.8 (alpha = 0.05):
#>
#> Statistic N
#> Wald 1134
#> LR 887
#> Score 932
#> Gradient 778
#>
#> Method: Analytical
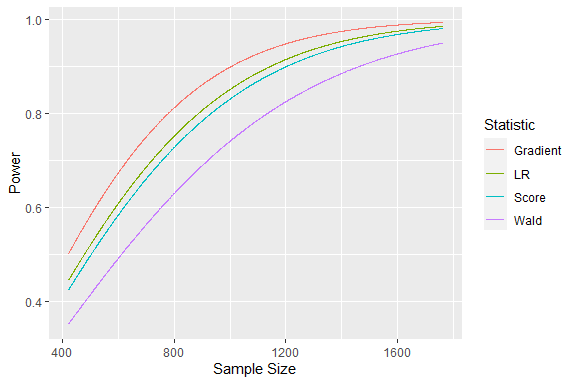
Here we see that the gradient statistic would be the most efficient to test our hypothesis: We would need a sample size of 778 to reach our desired power.
We can also plot the power curves to get a more detailed look on the relationships between sample size and power:
plot(res)
Further documentation
Further documentation on how to use the package is found in the package vignettes:
- The vignette “demo” gives a short introduction of basic features,
- “power_analysis” gives a more thorough walkthrough of power analysis with irtpwr,
- “adding_hypotheses” gives a tutorial on setting up custom hypotheses,
- “hypothesis_templates” includes some templates for hypothesis objects that can be altered for your specific use case.
If the vignettes were included during installation (for example using the methods above), they can be accessed via:
browsevignettes("irtpwr")