Calculating Optimal and D-Augmented Designs.
optedr
Overview
The package optedr is an optimal experimental design suite for calculating optimal designs, D-augmenting designs and efficiently rounding approximate design. Among its capabilities are:
- Calculating D-, Ds-, A- and I-optimal designs for non-linear models.
- D-augment designs controlling the loss of efficiency.
- Evaluate the efficiency of a given design against the optimum.
- Efficiently rounding approximate designs to exact designs.
Installation
You can install the released version of optedr from CRAN with:
install.packages("optedr")
You can install the latest version of the package from GitHub with:
devtools::install_github("kezrael/optedr")
Functions
The user available functions are:
opt_des()calculates optimal designs.design_efficiency()evaluates the efficiency of a design against the optimum.augment_design()augments designs, allowing the user to add points controlling the D-efficiency.efficient_round()efficiently round approximate designs.shiny_optimal()demo of optimal designs calculation with a graphical interface, applied to Antoine’s Equation.shiny_augment()demo of augmenting design with a graphical interface, usable for a handful of models.
The optdes object generated by opt_des() has its own implementation of print(), summary() and plot().
Usage
library(optedr)
The calculation of an optimal design requires a to specify the Criterion, the model, the parameters and their initial values and the design_space.
resArr.D <- opt_des(Criterion = "D-Optimality",
model = y ~ a*exp(-b/x),
parameters = c("a", "b"),
par_values = c(1, 1500),
design_space = c(212, 422))
#> i Stop condition not reached, max iterations performed
#> i The lower bound for efficiency is 99.9986396401789%
resArr.D$optdes
#> Point Weight
#> 1 329.2966 0.5000068
#> 2 422.0000 0.4999932
resArr.D$sens
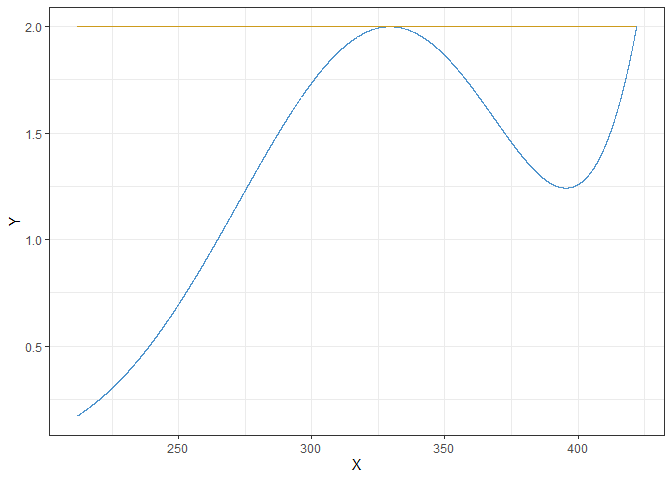
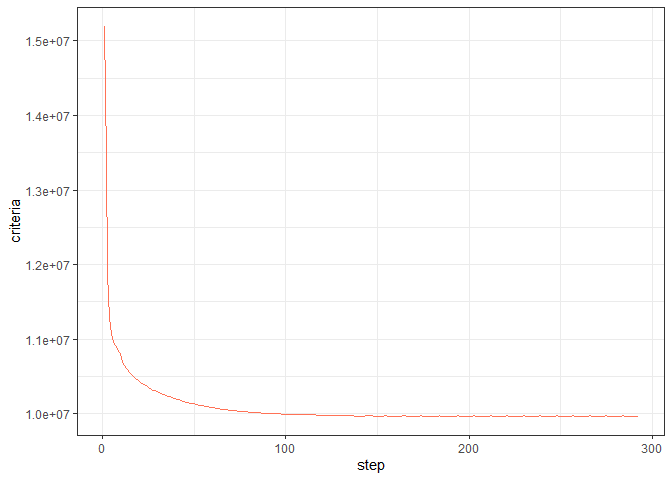
resArr.D$convergence
After calculating the D-optimal design, the user might want to add points to the design to fit their needs:
aug_arr <- augment_design(resArr.D$optdes, 0.3, y ~ a * exp(-b/x),
parameters = c("a", "b"),
par_values = c(1, 1500),
design_space = c(212, 422),
F)
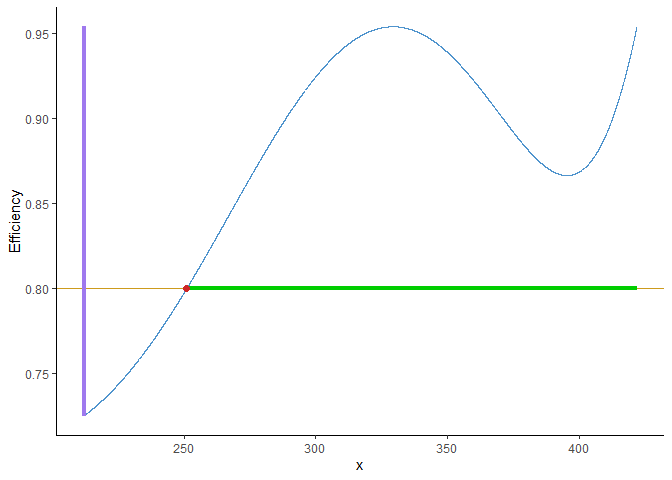
#> The region(s) are [250.98-422]The region(s) are [250.98-422]The region(s) are [250.98-422]
aug_arr
#> Point Weight
#> 1 329.2966 0.3500048
#> 2 422.0000 0.3499952
#> 3 260.0000 0.1500000
#> 4 380.0000 0.1500000
This new design can be rounded to the desired number of points:
(exact_design <- efficient_round(aug_arr, 20))
#> Point Weight
#> 1 329.2966 7
#> 2 422.0000 7
#> 3 260.0000 3
#> 4 380.0000 3
And its efficiency compared against the optimum:
aprox_design <- exact_design
aprox_design$Weight <- aprox_design$Weight /sum(aprox_design$Weight)
design_efficiency(resArr.D, aprox_design)
#> i The efficiency of the design is 86.0744365761564%
#> [1] 0.8607444
