Allocate Samples Among Strata.
optimall
optimall offers a collection of functions that are designed to streamline the process of optimum sample allocation, specifically under an adaptive, multi-wave approach. Its main functions allow users to:
Define, split, and merge strata based on values or quantiles of other variables.
Calculate the optimum number of samples to allocate to each stratum in a given study in order to minimize the variance of an estimate of interest.
Select specific ids to sample based on a stratified sampling design.
Optimally allocate a fixed number of samples to an ancillary sampling wave based on results from a prior wave.
When used together, these functions can automate most of the sampling workflow.
Installation
You can install optimall from CRAN with:
# install.packages("optimall")
Or, you can install the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("yangjasp/optimall")
Example
Given a dataframe where each row represents one unit, optimall can define the stratum each unit belongs to:
library(optimall)
data <- split_strata(data = data, strata = "old_strata",
split_var = "variable_to_split_on",
type = "value", split_at = c(1,2))
If the strata or values to split at are not obvious, it may be useful to try a few different splits and observe the effects that each has on sample allocation. optimall makes this process quick and easy with a Shiny app that can be launched with optimall_shiny. This app allows users to adjust inputs to the split_strata function and view the results in real time. Once the parameters are satisfactory, the user can confirm the split and move on to further ones if desired. The app prints the code required to replicate the splits in optimall, so making the changes inside of R becomes as easy as a copy and paste!
Screenshot:
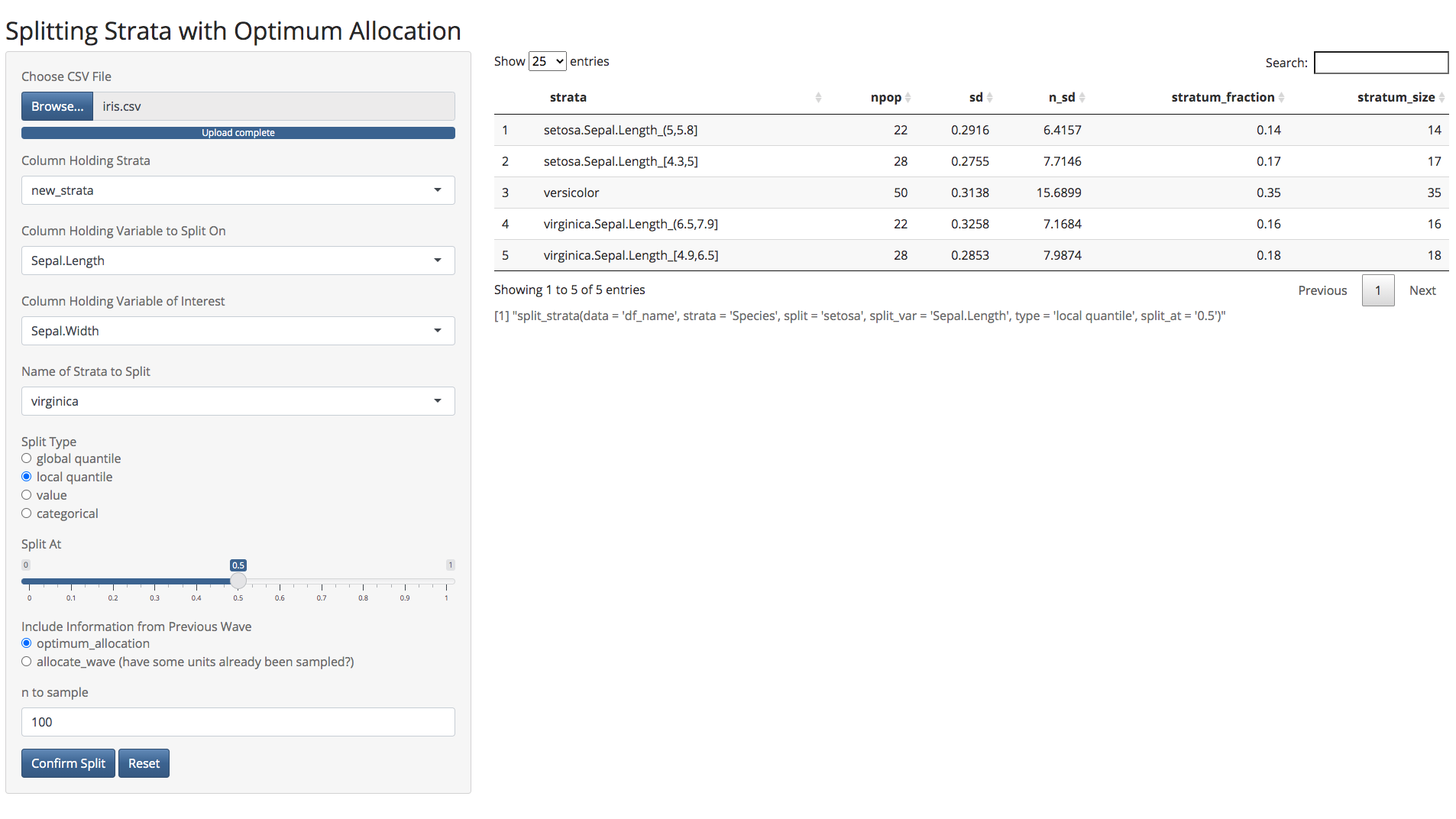
We can then use optimum_allocation to calculate the optimum allocation a fixed number of samples to our strata in order to minimize the variance of a variable of interest.
optimum_allocation(data = data, strata = "new_strata",
y = "var_of_interest", nsample = 100)
optimall offers more functions that streamline adaptive, multi-wave sampling workflows. For a more detailed description, see package vignettes.
References
McIsaac MA, Cook RJ. Adaptive sampling in two‐phase designs: a biomarker study for progression in arthritis. Statistics in Medicine. 2015 Sep 20;34(21):2899-912.
Wright, T. (2014). A simple method of exact optimal sample allocation under stratification with any mixed constraint patterns. Statistics, 07.