Creating and Working with Pedigrees and Marker Data.
pedtools 
Introduction
The goal of pedtools is to provide a lightweight, but comprehensive tool set for creating, manipulating and visualizing pedigrees with or without marker data. Common pedigree structures are quickly produced with tailor-made functions, while a range of utilities enable modifications like adding or removing individuals, extracting subsets, loop breaking, and merging pedigrees. The plotting feature imports machinery from the kinship2 package.
pedtools is the hub of the pedsuite, a collection of R packages for pedigree analysis, including applications in forensic and medical genetics. The pedsuite has its own GitHub repository and a dedicated website offering more information.
Citation
If you use pedtools in a publication, please cite the book Pedigree Analysis in R (Vigeland, 2021. Academic Press. ISBN:9780128244302).
Online app
Try the online app QuickPed for building and analysing pedigrees here: https://magnusdv.shinyapps.io/quickped/
Installation
To get pedtools, install from CRAN as follows:
install.packages("pedtools")
Alternatively, fetch the latest development version from GitHub:
devtools::install_github("magnusdv/pedtools")
Example
The following example illustrates a step-by-step creation of a pedigree with a marker object.
library(pedtools)
# Start with two half brothers
x = halfSibPed(type = "paternal")
# Make 5 female
x = swapSex(x, 5)
# Add a sister to 5 (parents are 2 and 3)
x = addDaughter(x, parents = 2:3)
# Add inbred child
x = addSon(x, parents = 4:5)
# Create marker
x = addMarker(x, "7" = "a/b")
# Plot pedigree with genotypes
plot(x, marker = 1, hatched = 7)
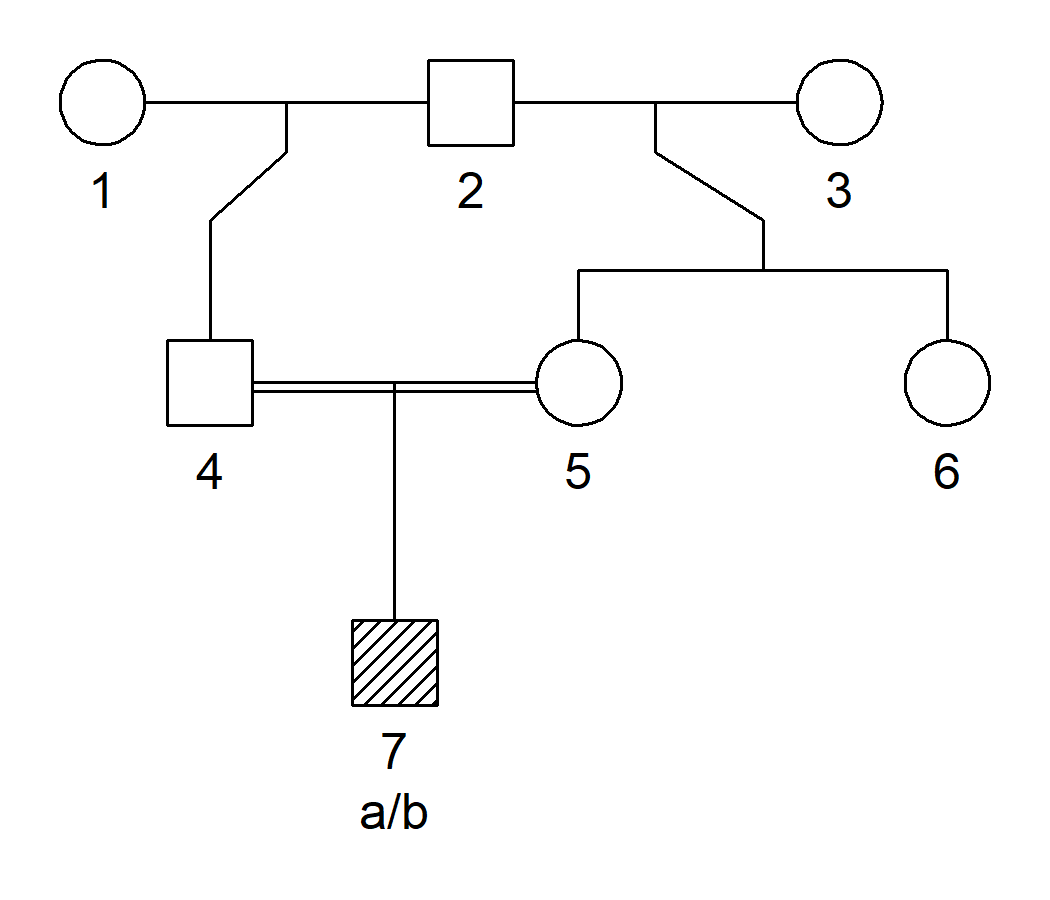
The process of building pedigrees is perfectly suited for R’s pipe operator |>. For example, the above pedigree could have been created as follows:
x = halfSibPed(type = "paternal") |>
swapSex(5) |>
addDaughter(parents = 2:3) |>
addSon(parents = 4:5) |>
addMarker("7" = "a/b")
For details about what pedtools can do, and many other examples, the vignette is a good place to start.