Penalized Poisson Pseudo Maximum Likelihood Regression.
penppml
The penppml package is a set of tools that enables efficient estimation of penalized Poisson Pseudo Maximum Likelihood (PPML) regressions, using lasso or ridge penalties, for models that feature one or more sets of high-dimensional fixed effects (HDFE). The methodology is based on Breinlich, Corradi, Rocha, Ruta, Santos Silva, and Zylkin (2021) and takes advantage of the method of alternating projections of Gaure (2013) for dealing with HDFE, as well as the coordinate descent algorithm of Friedman, Hastie and Tibshirani (2010) for fitting lasso regressions. The package is also able to carry out cross-validation and to implement the plugin lasso of Belloni, Chernozhukov, Hansen and Kozbur (2016).
Installation
You can install the released version of penppml from CRAN with:
install.packages("penppml")
And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("diegoferrerasg/penppml")
Example
This is a basic example which demonstrate how to estimate a gravity model of international trade with three sets of HDFE using the package:
# Setup:
library(penppml)
selected <- countries$iso[countries$region %in% c("Americas")]
trade2 <- trade[(trade$exp %in% selected) & (trade$imp %in% selected), -(5:6)]
lambdas <- c(0.05, 0.025, 0.01, 0.0075, 0.005, 0.0025, 0.001, 0.00075, 0.0005, 0.00025, 0.0001, 0)
# Main command:
reg <- mlfitppml(data = trade2,
dep = "export",
fixed = list(c("exp", "time"),
c("imp", "time"),
c("exp", "imp")),
penalty = "lasso",
lambdas = lambdas)
We can plot the resulting regularization path as follows:
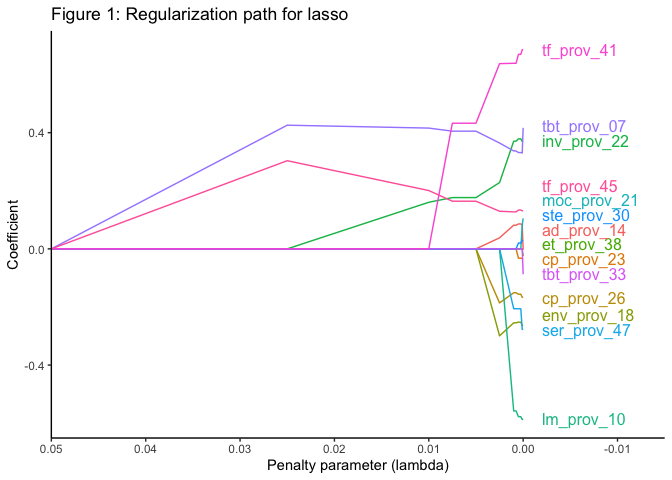
For more examples and details on how to use the package, see the vignette.
References
Breinlich, H., Corradi, V., Rocha, N., Ruta, M., Santos Silva, J.M.C. and T. Zylkin, T. (2021). “Machine Learning in International Trade Research: Evaluating the Impact of Trade Agreements”, Policy Research Working Paper; No. 9629. World Bank, Washington, DC.
Correia, S., P. Guimaraes and T. Zylkin (2020). “Fast Poisson estimation with high dimensional fixed effects”, STATA Journal, 20, 90-115.
Gaure, S (2013). “OLS with multiple high dimensional category variables”, Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 66, 8-18.
Friedman, J., T. Hastie, and R. Tibshirani (2010). “Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent”, Journal of Statistical Software, 33, 1-22.
Belloni, A., V. Chernozhukov, C. Hansen and D. Kozbur (2016). “Inference in high dimensional panel models with an application to gun control”, Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 34, 590-605.