Pretty Summaries of Generalized Linear Model Coefficients.
prettyglm 
One of the main advantages of using Generalised Linear Models is their interpretability. The goal of prettyglm is to provide a set of functions which easily create beautiful coefficient summaries which can readily be shared and explained.
Forword
prettyglm was created to solve some common faced when building Generalised Linear Models, such as displaying categorical base levels, and visualizing the number of records in each category on a duel axis. Since then a number of other functions which are useful when fitting glms have been added.
If you don’t find the function you are looking for here consider checking out some other great packages which help visualize the output from glms:tidycat, jtools or GGally
Installation
You can install the latest CRAN release with:
install.packages('prettyglm')
Documentation
Please see the website prettyglm for more detailed documentation and examples.
A Simple Example
To explore the functionality of prettyglm we will use a data set sourced from kaggle which contains information about a Portugal banks marketing campaigns results. The campaign was based mostly on direct phone calls, offering clients a term deposit. The target variable y indicates if the client agreed to place the deposit after the phone call.
Pre-processing
A critical step for this package to work well is to set all categorical predictors as factors.
library(prettyglm)
library(dplyr)
data("bank")
# Easiest way to convert multiple columns to a factor.
columns_to_factor <- c('job',
'marital',
'education',
'default',
'housing',
'loan')
bank_data <- bank_data %>%
dplyr::filter(loan != 'unknown') %>%
dplyr::filter(default != 'yes') %>%
dplyr::mutate(age = as.numeric(age)) %>%
dplyr::mutate_at(columns_to_factor, list(~factor(.))) %>% # multiple columns to factor
dplyr::mutate(T_DEPOSIT = as.factor(base::ifelse(y=='yes',1,0))) #convert target to 0 and 1 for performance plots
Building a glm
For this example we will build a glm using stats::glm(), however prettyglm is working to support parsnip and workflow model objects which use the glm model engine.
deposit_model <- stats::glm(T_DEPOSIT ~ marital +
default:loan +
loan +
age,
data = bank_data,
family = binomial)
Visualising Fitted Model Coefficients
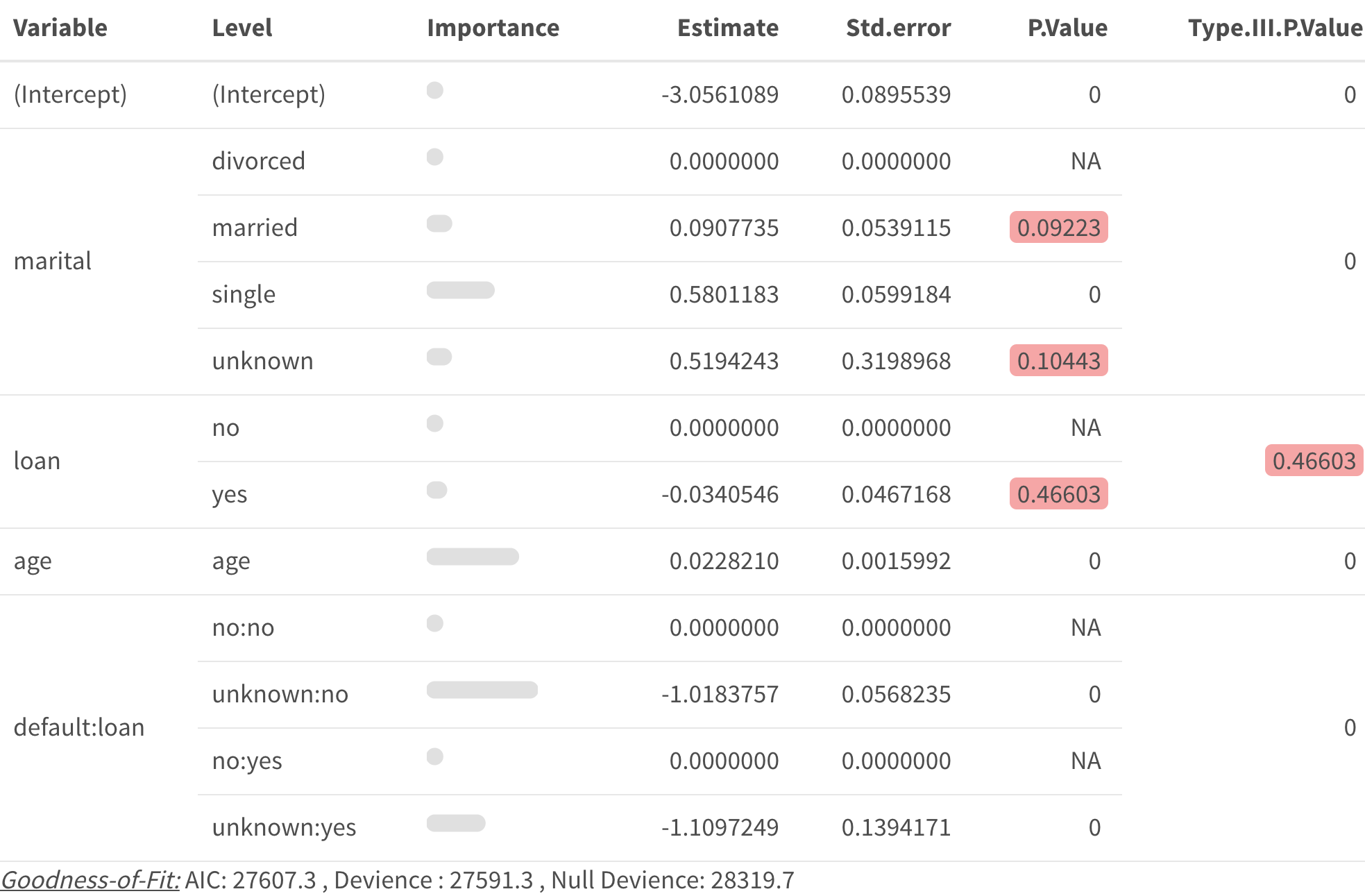
Create table of model coefficients with pretty_coefficients()
pretty_coefficients()automatically includes categorical variable base levels.You can complete a type III test on the coefficients by specifying a
type_iiiargument.You can include a “relativity” column in the output by including a
relativity_transforminput. (Note “relativity” is sometimes referred to as “likelihood” or “odds-ratio”, you can change the title of this column with therelativity_labelinput.)You can return the data set instead of
kablebut settingReturn_Data = TRUE
pretty_coefficients(deposit_model, type_iii = 'Wald')
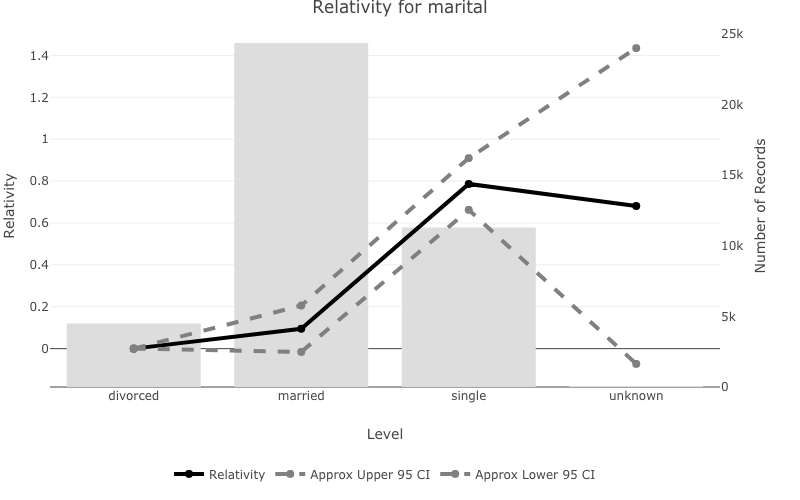
Create plots of the model relativities with pretty_relativities()
- A model relativity is a transform of the model estimate. By default
pretty_relativities()uses ‘exp(estimate)-1’ which is useful for GLM’s which use a log or logit link function. pretty_relativities()automatically extracts the training data from the model object and plots the number of records on the second y axis.
pretty_relativities(feature_to_plot = 'marital',
model_object = deposit_model)
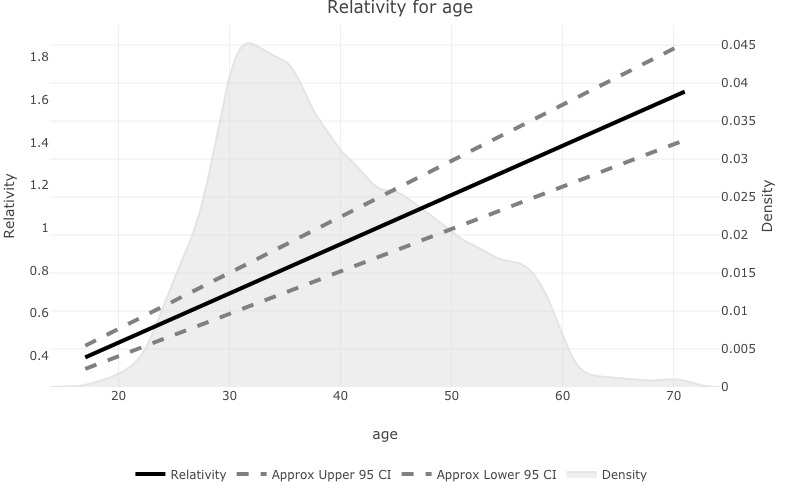
- If the variable you are plotting is a continuous variable
prettyglmwill plot the density on a second axis, and attempt to plot the fit with confidence intervals.
pretty_relativities(feature_to_plot = 'age',
model_object = deposit_model)
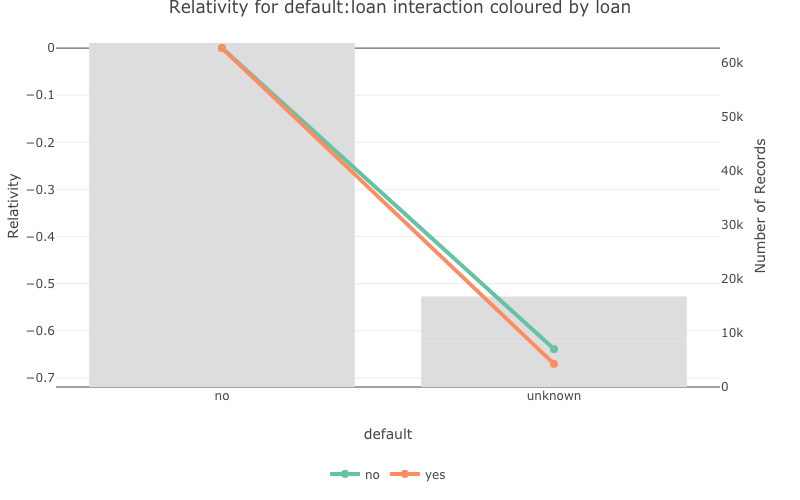
- For interactions you can colour or facet by one of the variables.
pretty_relativities(feature_to_plot = 'default:loan',
model_object = deposit_model,
iteractionplottype = 'colour',
facetorcolourby = 'loan')
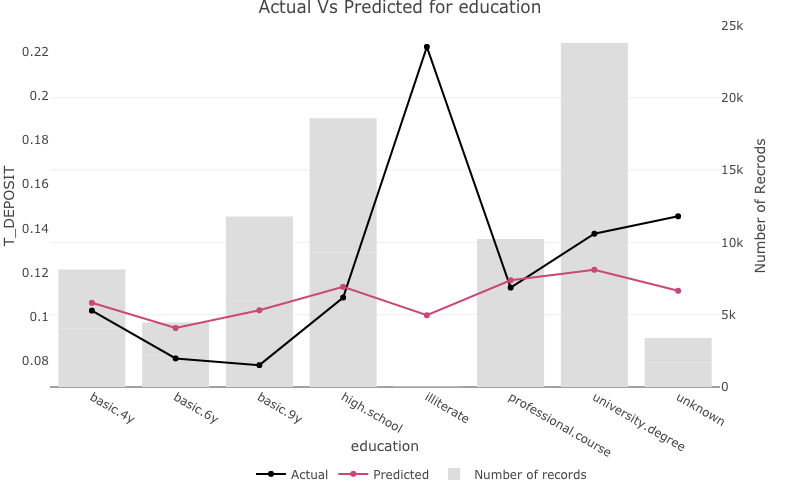
Visualising one-way model performance with one_way_ave()
one_way_ave() creates one-way model performance plots.
education
For discrete variables the number of records in each group will be plotted on a second axis.
one_way_ave(feature_to_plot = 'education',
model_object = deposit_model,
target_variable = 'T_DEPOSIT',
data_set = bank_data)
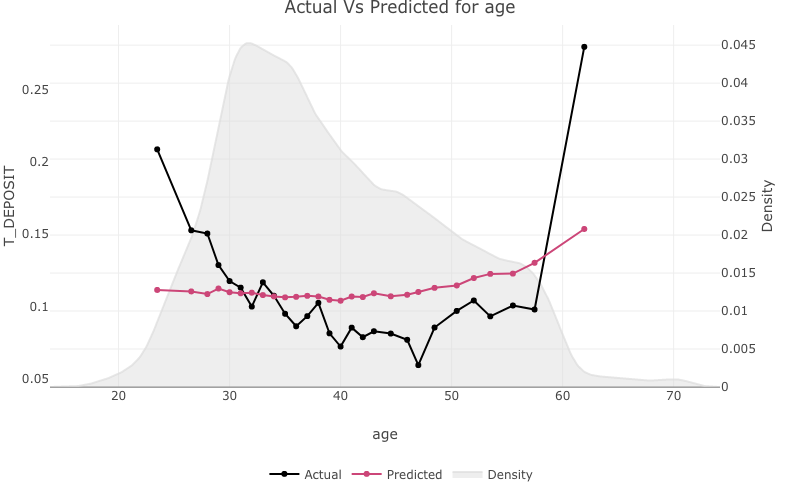
age
For continuous variables the stats::density() will be plotted on a second axis.
one_way_ave(feature_to_plot = 'age',
model_object = deposit_model,
target_variable = 'T_DEPOSIT',
data_set = bank_data)
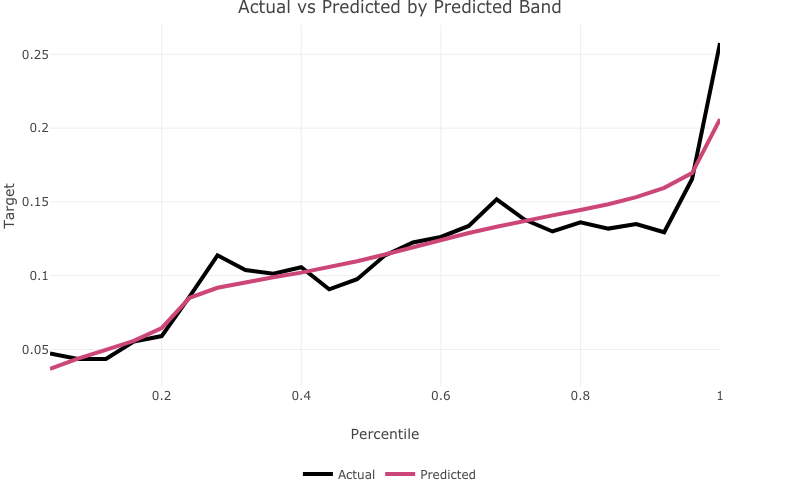
Plot actual vs expected by predicted band with actual_expected_bucketed()
actual_expected_bucketed() creates actual vs expected performance plots by predicted band.
actual_expected_bucketed(target_variable = 'T_DEPOSIT',
model_object = deposit_model,
data_set = bank_data)