Random Effects Meta-Analysis for Correlated Test Statistics.
Random effects meta-analysis
for correlated test statistics
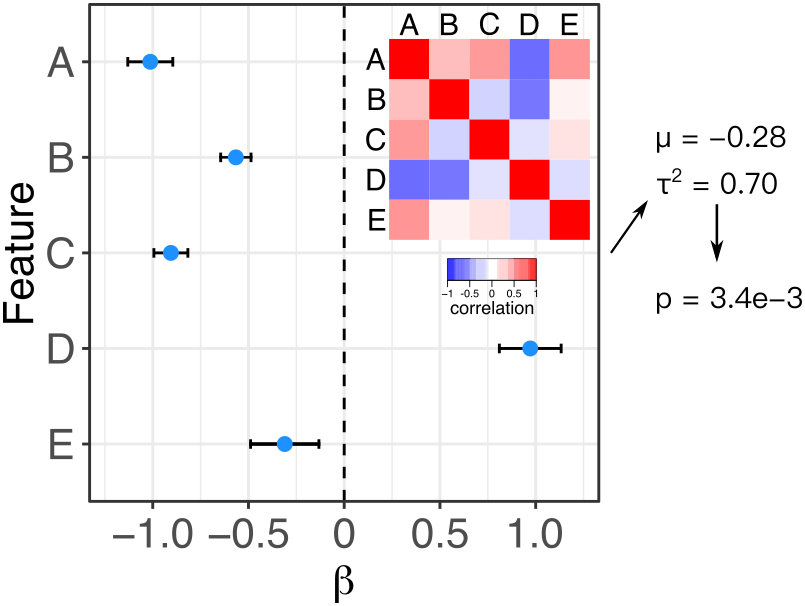
Meta-analysis is widely used to summarize estimated effects sizes across multiple statistical tests. Standard fixed and random effect meta-analysis methods assume that the estimated of the effect sizes are statistically independent. Here we relax this assumption and enable meta-analysis when the correlation matrix between effect size estimates is known. Fixed effect meta-analysis uses the method of [Lin and Sullivan (2009)](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.11.001), and random effects meta-analysis uses the method of [Han, et al. 2016](https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw049). An exentsion of the Lin-Sullivan method for finite sample size is described in [Hoffman and Roussos (2025)](https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.01.29.635498).
Usage
# Run fixed effects meta-analysis,
# accounting for correlation
LS( beta, stders, Sigma)
# Run fixed effects meta-analysis,
# accounting for correlation,
# and finite sample size using residual degrees of freedom
LS.empirical( beta, stders, Sigma, nu=rdf)
# Run random effects meta-analysis,
# accounting for correlation
RE2C( beta, stders, Sigma)
Install from GitHub
devtools::install_github("DiseaseNeurogenomics/remaCor")