Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization.
rnnmf
Implements regularized non-negative matrix factorization by a method similar to Lee & Seung, "Algorithms for Non-negative Matrix Factorization," 2001.
-- Steven E. Pav, [email protected]
Installation
This package may be installed from CRAN; the latest version may be found on github via devtools, or installed via drat:
# CRAN
install.packages(c("rnnmf"))
# devtools
if (require(devtools)) {
# latest greatest
install_github("shabbychef/rnnmf")
}
# via drat:
if (require(drat)) {
drat:::add("shabbychef")
# not yet: install.packages('rnnmf')
}
What is it?
Non-negative matrix factorization is a tool for decomposing a non-negative matrix $Y$ approximately as $Y \approx L R$ for non-negative matrices $L, R$ of pre-specified rank. This package provides code for non-negative matrix factorization with penalty terms for the $\ell_1$ and $\ell_2$ norms of the two factors, as well as for non-orthogonality of the factors. The code is based on the conceptually simple multiplicative update of Lee & Seung. An additive update based on the same ideas is also given.
This code is provided mostly for research purposes, and no warranty is given regarding speed, or convergence.
Basic Usage
We demonstrate the usage of the multiplicative and additive updates in factoring a small matrix which we constructed to be the product of two reduced rank non-negative matrices.
library(dplyr)
library(rnnmf)
library(ggplot2)
frobenius_norm_err <- function(Y, L, R) {
sqrt(sum(abs(Y - L %*% R)^2))
}
runifmat <- function(nr, nc, ...) {
matrix(pmax(0, runif(nr * nc, ...)), nrow = nr)
}
test_a_bunch <- function(Y_t, L_0, R_0, niter = 10000L) {
iter_hist <- new.env()
iter_hist[["history"]] <- rep(NA_real_, niter)
on_iteration_end <- function(iteration, Y, L, R,
...) {
iter_hist[["history"]][iteration] <<- frobenius_norm_err(Y,
L, R)
}
wuz <- aurnmf(Y_t, L_0, R_0, max_iterations = niter,
on_iteration_end = on_iteration_end)
df1 <- tibble(x = seq_along(iter_hist[["history"]]),
y = iter_hist[["history"]]) %>%
mutate(method = "additive, optimal step")
iter_hist[["history"]] <- rep(NA_real_, niter)
wuz <- murnmf(Y_t, L_0, R_0, max_iterations = niter,
on_iteration_end = on_iteration_end)
df2 <- tibble(x = seq_along(iter_hist[["history"]]),
y = iter_hist[["history"]]) %>%
mutate(method = "multiplicative")
retv <- bind_rows(df1, df2) %>%
mutate(nr = nrow(Y_t), nc = ncol(Y_t), nd = ncol(L_0),
max_iter = niter)
return(retv)
}
nr <- 30
nc <- 8
nd <- 3
set.seed(1234)
L_t <- runifmat(nr, nd)
R_t <- runifmat(nd, nc)
Y_t <- L_t %*% R_t
L_0 <- runifmat(nrow(Y_t), nd + 1)
R_0 <- runifmat(ncol(L_0), ncol(Y_t))
test_a_bunch(Y_t, L_0, R_0, niter = 10000L) %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, color = method)) + geom_line() +
scale_x_log10(labels = scales::comma) + scale_y_log10() +
labs(x = "Step", y = expression(L[2] ~ ~Error),
title = "Frobenius Norm of Error vs Step",
color = "Method", caption = paste0("Factoring ",
nr, " x ", nc, " matrix down to ", nd,
" dimensions."))
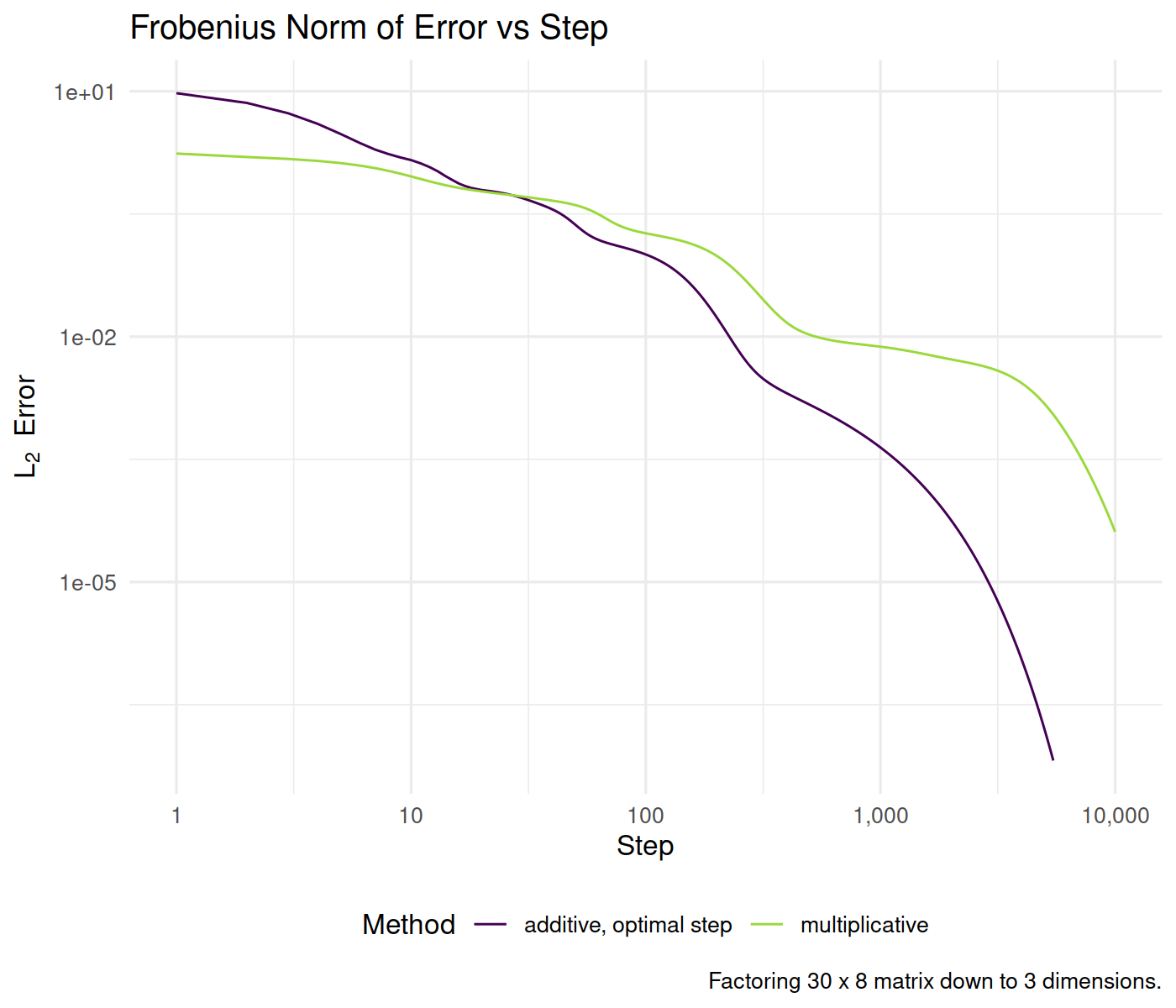
plot of chunk basic_simulations
See also
- Lee, Daniel D. and Seung, H. Sebastian. Algorithms for Non-negative Matrix Factorization, 2001.
- Pav, Steven E. System and method for unmixing spectroscopic observations with nonnegative matrix factorization, 2012.