Description
Small Area Estimation with Cluster Information for Estimation of Non-Sampled Areas.
Description
Implementation of small area estimation (Fay-Herriot model) with EBLUP (Empirical Best Linear Unbiased Prediction) Approach for non-sampled area estimation by adding cluster information and assuming that there are similarities among particular areas. See also Rao & Molina (2015, ISBN:978-1-118-73578-7) and Anisa et al. (2013) <doi:10.9790/5728-10121519>.
README.md
saens
Author
Ridson Al Farizal P, Azka Ubaidillah
Maintainer
Ridson Al Farizal P [email protected]
Description
EBLUP Fay-Herriot Model for Estimation of Non-Sampled Areas with Cluster Information.
Installation
You can install the development version of saens from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("Alfrzlp/saens")
or you can install cran version
install.packages("saens")
Example
This is a basic example which shows you how to solve a common problem:
library(saens)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(ggplot2)
windowsFonts(
poppins = windowsFont('poppins')
)
Data
milk$var <- milk$SD^2
# glimpse(mys)
# glimpse(milk)
EBLUP Model
model1 <- eblupfh(yi ~ as.factor(MajorArea), data = milk, vardir = "var")
#> ✔ Convergence after 4 iterations
#> → Method : REML
#>
#> ── Coefficient ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> beta Std.Error z-value p-value
#> (Intercept) 0.968189 0.069362 13.9585 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> as.factor(MajorArea)2 0.132780 0.103001 1.2891 0.197357
#> as.factor(MajorArea)3 0.226946 0.092330 2.4580 0.013972 *
#> as.factor(MajorArea)4 -0.241301 0.081617 -2.9565 0.003111 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
AIC, BIC, and Loglikehood
AIC(model1)
#> AIC
#> -15.35496
BIC(model1)
#> BIC
#> -6.548956
logLik(model1)
#> loglike
#> 12.67748
Coef
coef(model1)
#> (Intercept) as.factor(MajorArea)2 as.factor(MajorArea)3
#> 0.9681890 0.1327801 0.2269462
#> as.factor(MajorArea)4
#> -0.2413011
Summary
summary(model1)
#> beta Std.Error z-value p-value
#> (Intercept) 0.968189 0.069362 13.9585 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> as.factor(MajorArea)2 0.132780 0.103001 1.2891 0.197357
#> as.factor(MajorArea)3 0.226946 0.092330 2.4580 0.013972 *
#> as.factor(MajorArea)4 -0.241301 0.081617 -2.9565 0.003111 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Autoplot
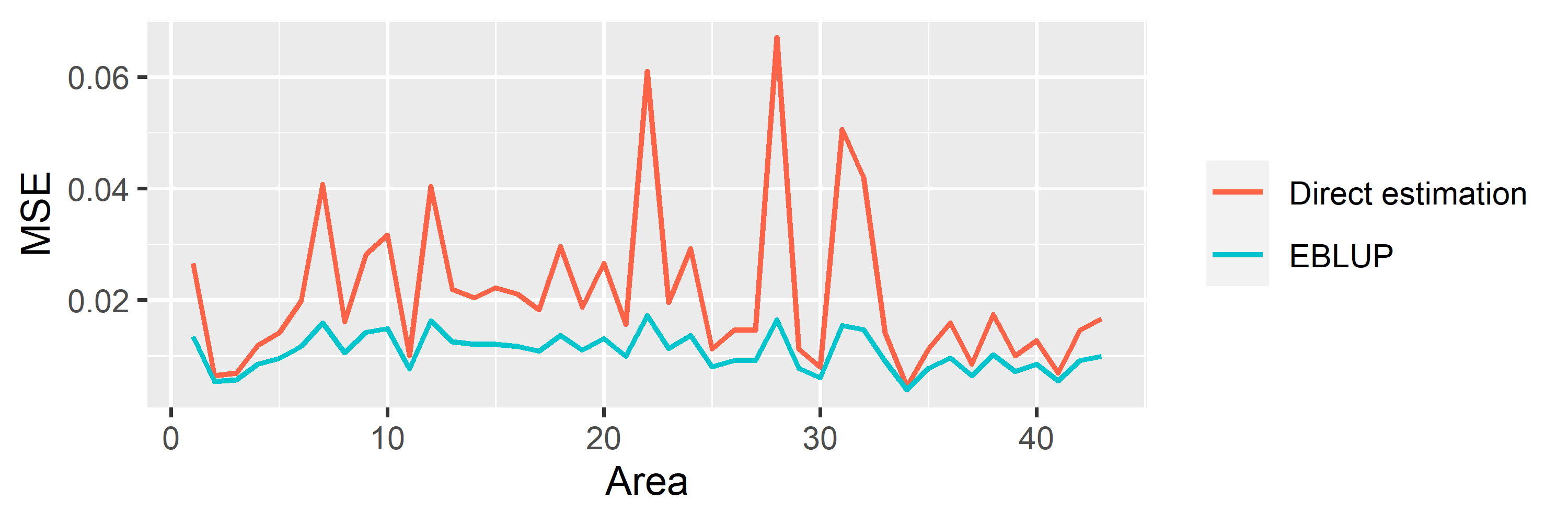
saens::autoplot(model1, variable = 'MSE')
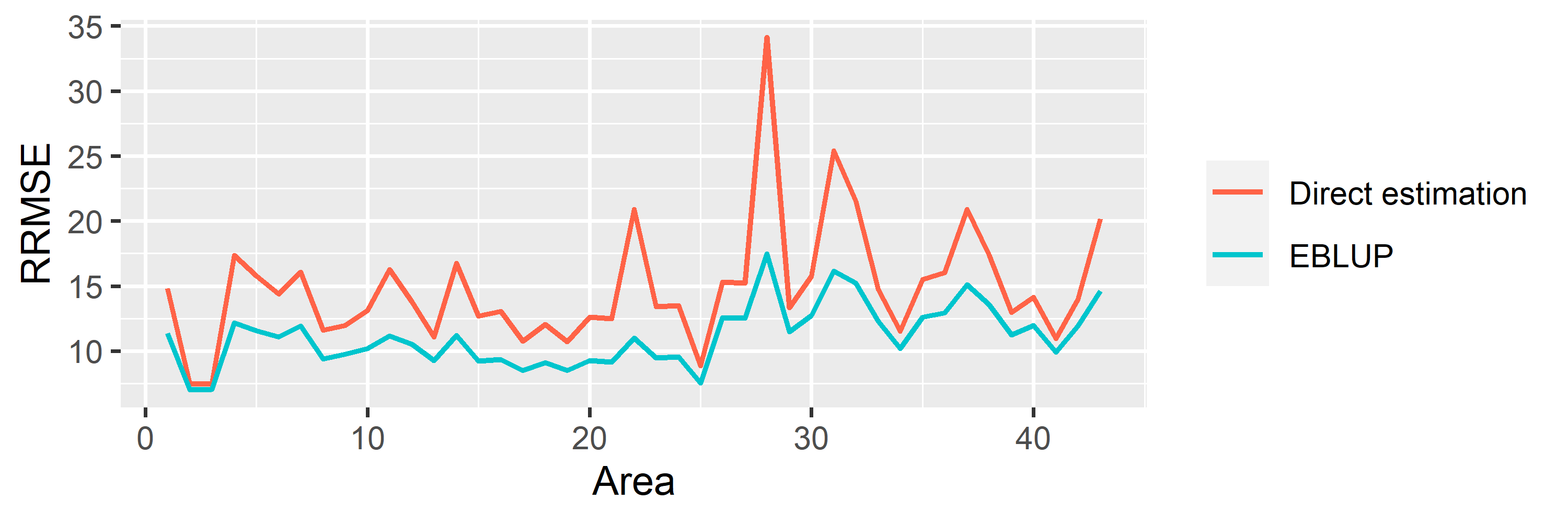
saens::autoplot(model1, variable = 'RRMSE')
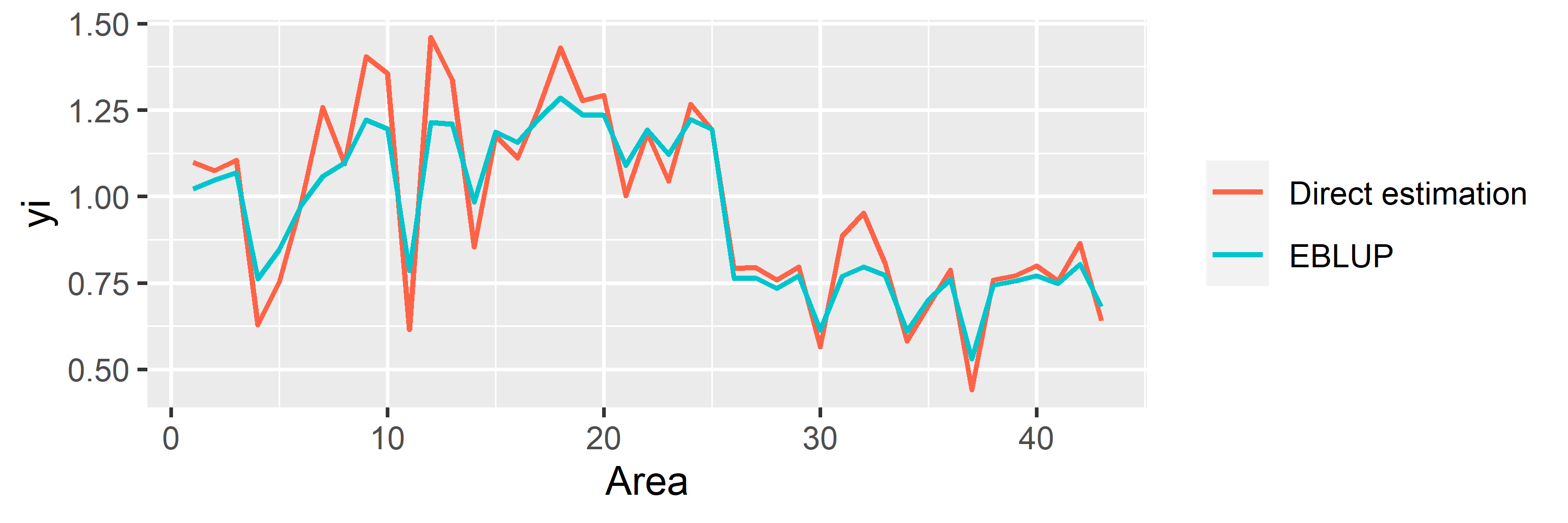
saens::autoplot(model1, variable = 'estimation')
EBLUP Model for Non-sampled Areas
model_ns <- eblupfh_cluster(y ~ x1 + x2 + x3, data = mys, vardir = "var", cluster = "clust")
#> ✔ Convergence after 6 iterations
#> → Method : REML
#>
#> ── Coefficient ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> beta Std.Error z-value p-value
#> (Intercept) 3.1077510 0.7697687 4.0373 5.408e-05 ***
#> x1 -0.0019323 0.0098886 -0.1954 0.8451
#> x2 0.0555184 0.0614129 0.9040 0.3660
#> x3 0.0335344 0.0580013 0.5782 0.5632
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
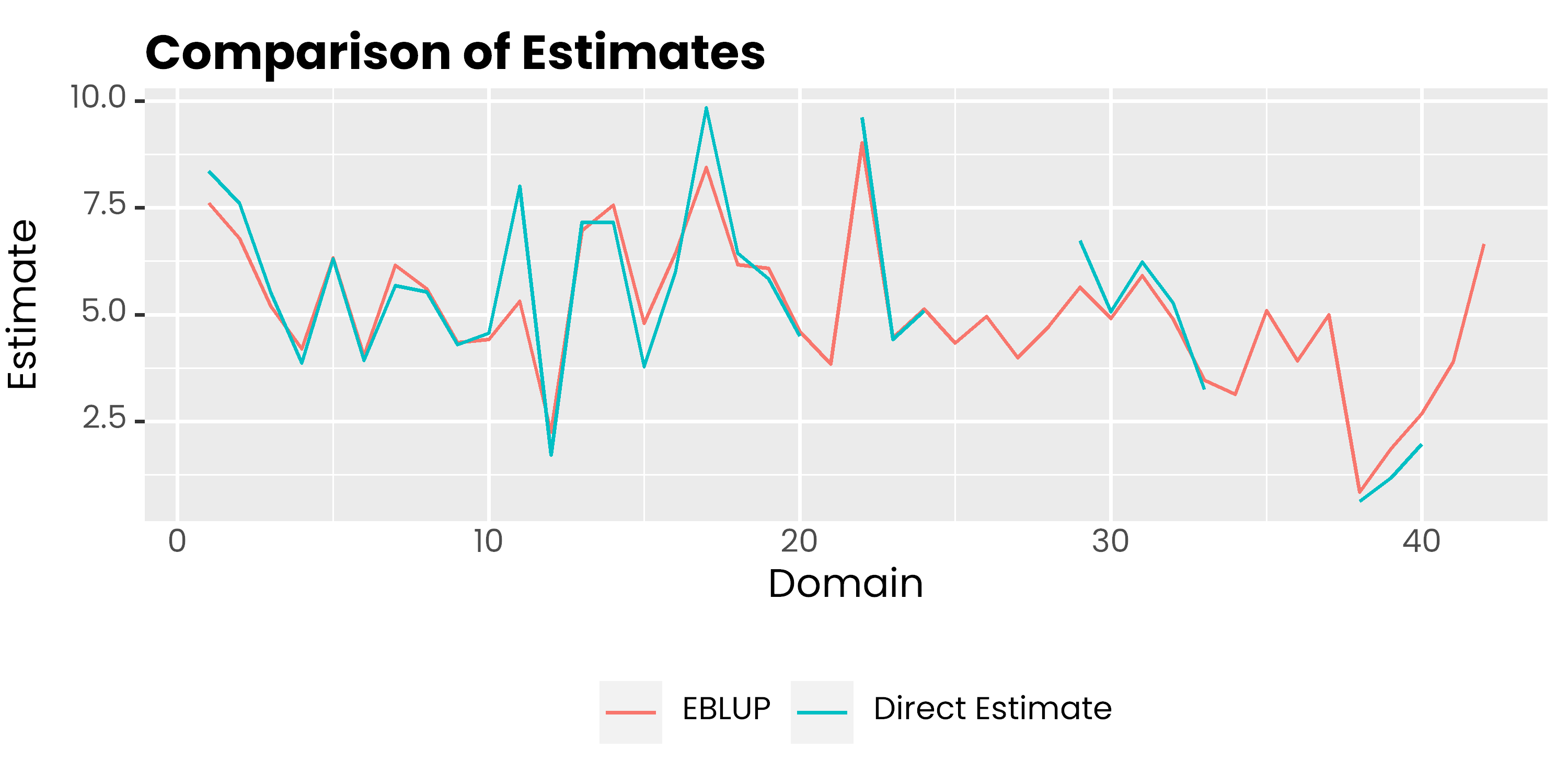
Comparison of estimates and RSE
mys$eblup_est <- model_ns$df_res$eblup
mys$eblup_rse <- model_ns$df_res$rse
glimpse(mys)
#> Rows: 42
#> Columns: 10
#> $ area <int> 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1…
#> $ y <dbl> 8.359527, 7.599650, 5.514137, 3.869326, 6.305063, 3.926807, …
#> $ var <dbl> 0.6618838, 0.8374691, 0.8822257, 0.6581716, 1.2788021, 0.387…
#> $ rse <dbl> 9.732158, 12.041783, 17.033831, 20.966899, 17.935449, 15.858…
#> $ x1 <dbl> 124, 89, 57, 88, 141, 96, 146, 110, 58, 63, 35, 56, 84, 240,…
#> $ x2 <dbl> 24, 18, 19, 35, 46, 29, 57, 41, 18, 13, 12, 14, 38, 71, 33, …
#> $ x3 <dbl> 14, 9, 5, 19, 29, 10, 34, 23, 11, 5, 9, 11, 35, 48, 29, 44, …
#> $ clust <dbl> 3, 3, 4, 4, 3, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 3, …
#> $ eblup_est <dbl> 7.612738, 6.782316, 5.187060, 4.201545, 6.323679, 4.048590, …
#> $ eblup_rse <dbl> 9.844182, 12.144869, 16.347620, 17.841554, 15.307573, 14.713…
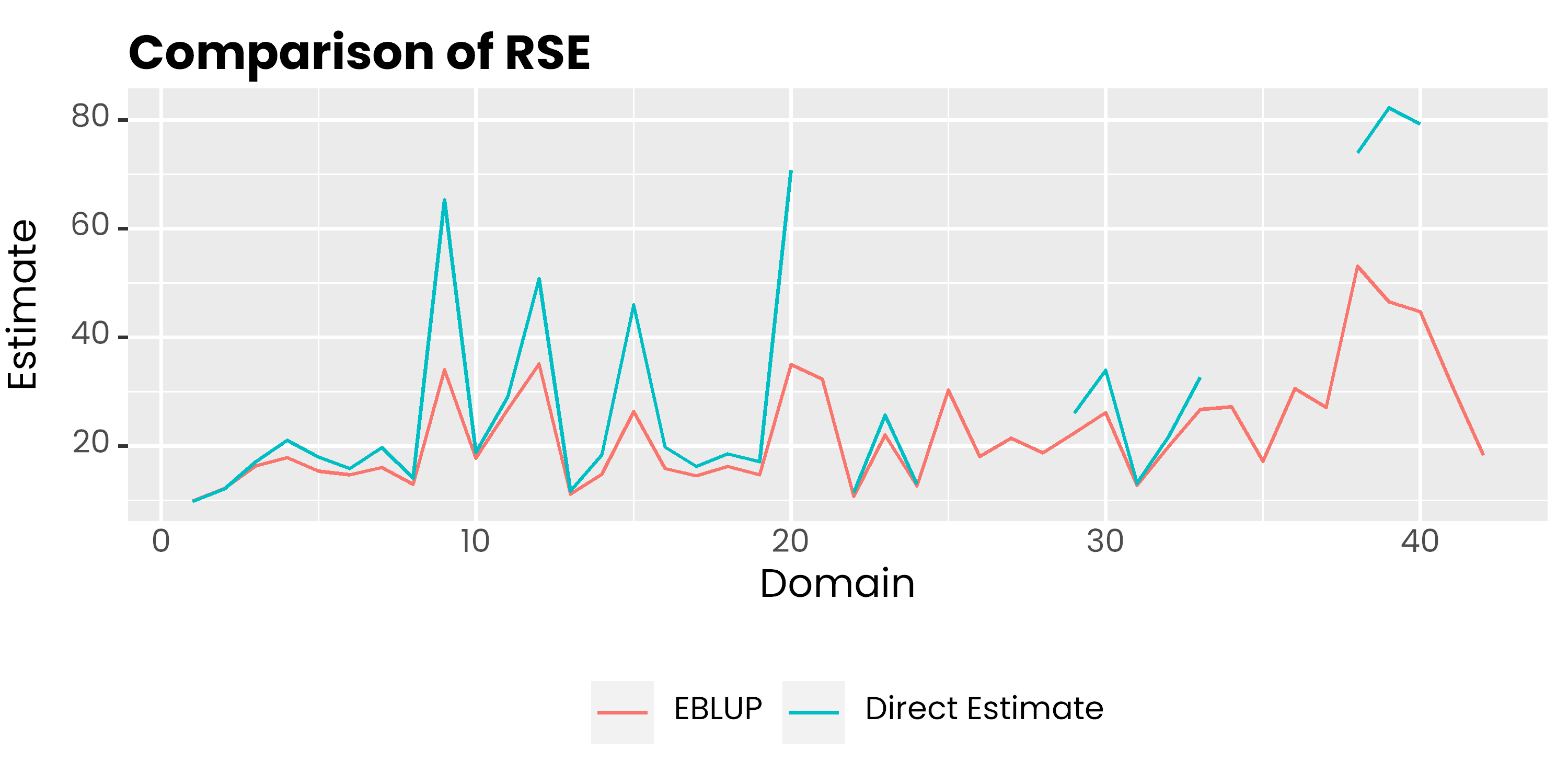
mys %>%
select(area, rse, eblup_rse) %>%
pivot_longer(-1, names_to = "metode", values_to = "rse") %>%
ggplot(aes(x = area, y = rse, col = metode)) +
geom_line() +
scale_color_discrete(
labels = c('EBLUP', 'Direct Estimate')
) +
labs(col = NULL, y = 'Estimate', x = 'Domain', title = 'Comparison of RSE') +
theme(
legend.position = 'bottom',
text = element_text(family = 'poppins'),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_text(face = 2, vjust = 0),
plot.subtitle = element_text(colour = 'gray30', vjust = 0)
)
mys %>%
select(area, y, eblup_est) %>%
pivot_longer(-1, names_to = "metode", values_to = "rse") %>%
ggplot(aes(x = area, y = rse, col = metode)) +
geom_line() +
scale_color_discrete(
labels = c('EBLUP', 'Direct Estimate')
) +
labs(col = NULL, y = 'Estimate', x = 'Domain', title = 'Comparison of Estimates') +
theme(
legend.position = 'bottom',
text = element_text(family = 'poppins'),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_text(face = 2, vjust = 0),
plot.subtitle = element_text(colour = 'gray30', vjust = 0)
)
References
- Rao, J. N., & Molina, I. (2015). Small area estimation. John Wiley & Sons.
- Anisa, R., Kurnia, A., & Indahwati, I. (2013). Cluster information of non-sampled area in small area estimation. E-Prosiding Internasional| Departemen Statistika FMIPA Universitas Padjadjaran, 1(1), 69-76.