Regression Analysis for Seed Germination as a Function of Temperature.
Package seedreg
Authors: Gabriel Danilo Shimizu; Hugo Roldi Guariz
Package: seedreg
Type: Package
Title: Regression for seeds
Version: 1.0.0
Author: Gabriel Danilo Shimizu
Maintainer: The package maintainer [email protected]
Description: The package is dedicated to regression analysis of common models in scientific works and others with potential for use in estimating the optimal, maximum and minimum temperature for the occurrence of seed germination
License: What license is it under?
import: drc, ggplot2, car, crayon, emmeans, multcomp
Encoding: UTF-8
LazyData: true
RoxygenNote: 7.1.1
The influence of temperature on plant seed germination is a very popular topic in agronomy. However, researchers have difficulty in estimating the optimal, maximum and minimum points for the occurrence of germination, often using inappropriate models. Thus, the present work has the purpose of presenting regression models common in scientific works and others with potential for use, implemented in the form of an R package called seedreg. Eight regression models were implemented: linear, quadratic, cubic, logistic of three or four parameters, Brain-Cousens logistic with four and five parameters, Cedergreen-Ritz-Streibig with four and five parameters, normal and loess. The package returns the estimate of the optimal, maximum and minimum points, in addition to statistical parameters, such as the criteria of AIC, BIC, R2, significance of the coefficients. Models can be accessed by the LL_model(), BC_model(),CD_model,normal_model, quali_model, loess_model and LL_model() functions.
Installation
The package can be installed by the following command:
devtools::install_github("https://github.com/AgronomiaR/seedreg", force=T)
Note: Current versions of R require the installation of Rtools software (https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/) to download packages that partially use the C++ language. The devtools package is one of those packages that depend on this software.
Usage
rm(list=ls())
library(seedreg)
data("aristolochia")
attach(aristolochia)
Linear regression
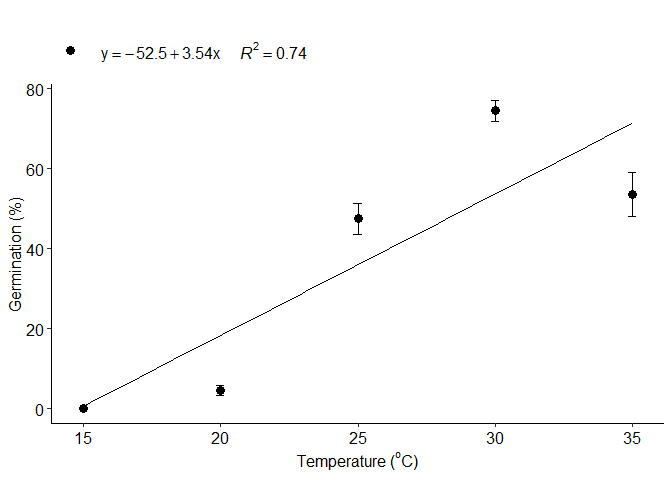
a=LM_model(trat,resp)
#> Scale for 'colour' is already present. Adding another scale for 'colour',
#> which will replace the existing scale.
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0"]): nenhum argumento não faltante para
#> max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models. VIF above 10 indicates variance inflation problem (Multicollinearity)
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) -52.50 8.0436071 -6.526922 6.166973e-09
#> trat 3.54 0.3095986 11.434161 2.398736e-18
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 35.0000000
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value -Inf
#> 4 AIC 706.9321172
#> 5 BIC 714.0781971
#> 6 r-squared 0.7443336
#>
#> $VIF
#> [1] NA
#>
#> [[3]]
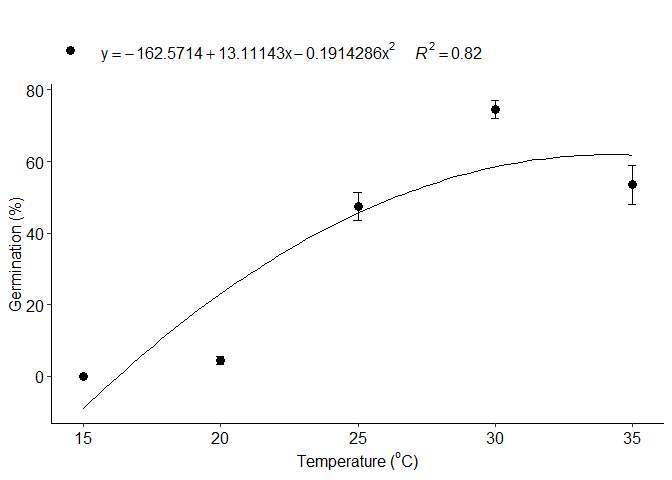
b=LM_model(trat,resp,grau = 2)
#> Scale for 'colour' is already present. Adding another scale for 'colour',
#> which will replace the existing scale.
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models. VIF above 10 indicates variance inflation problem (Multicollinearity)
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) -162.5714286 28.53350582 -5.697562 2.124445e-07
#> trat 13.1114286 2.41373278 5.432013 6.288396e-07
#> I(trat^2) -0.1914286 0.04794024 -3.993067 1.478864e-04
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 34.2459246
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 16.3301330
#> 4 AIC 693.8762781
#> 5 BIC 703.4043847
#> 6 r-squared 0.8205139
#>
#> $VIF
#> trat I(trat^2)
#> 72.42857 72.42857
#>
#> [[3]]
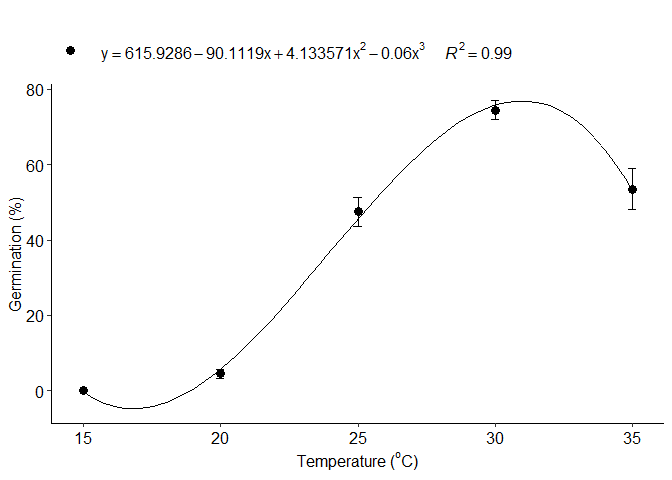
c=LM_model(trat,resp, grau=3)
#> Scale for 'colour' is already present. Adding another scale for 'colour',
#> which will replace the existing scale.
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models. VIF above 10 indicates variance inflation problem (Multicollinearity)
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 615.92857143 94.631279296 6.508721 7.284199e-09
#> trat -90.11190476 12.369050966 -7.285272 2.537032e-10
#> I(trat^2) 4.13357143 0.514234979 8.038293 9.299156e-12
#> I(trat^3) -0.05766667 0.006840848 -8.429754 1.653134e-12
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 30.9655966
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 19.0024002
#> 4 AIC 643.0672814
#> 5 BIC 654.9774146
#> 6 r-squared 0.9982817
#>
#> $VIF
#> trat I(trat^2) I(trat^3)
#> 3632.540 15916.179 4488.194
#>
#> [[3]]
Logistic regression
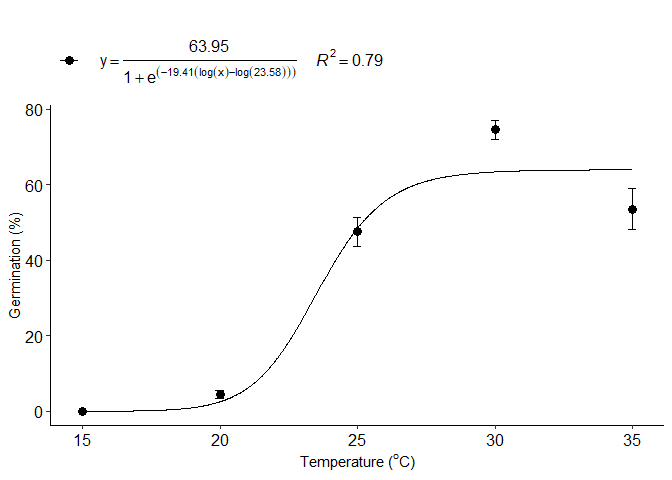
d=LL_model(trat,resp,npar = "LL.3")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) with lower limit at 0 (3 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -19.40819 7.22347 -2.6868 0.008834 **
#> d:(Intercept) 63.94663 2.65919 24.0474 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 23.57567 0.70284 33.5436 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.63286 (77 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) with lower limit at 0 (3 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -19.40819 7.22347 -2.6868 0.008834 **
#> d:(Intercept) 63.94663 2.65919 24.0474 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 23.57567 0.70284 33.5436 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.63286 (77 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 35.0000000
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 18.3683368
#> 4 AIC 661.2956178
#> 5 BIC 670.8237244
#> 6 r-squared 0.7943074
#>
#> [[2]]
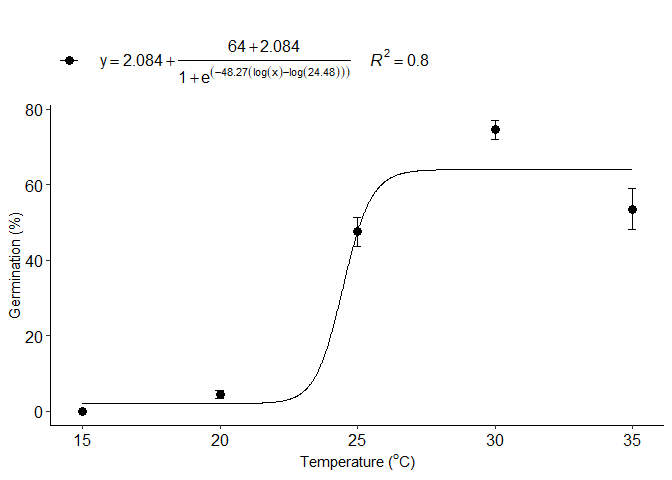
e=LL_model(trat,resp,npar = "LL.4")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 < maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (4 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -48.2686 121.7112 -0.3966 0.6928
#> c:(Intercept) 2.0836 2.5960 0.8026 0.4247
#> d:(Intercept) 63.9961 2.5954 24.6572 <2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 24.4808 1.3094 18.6960 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.6807 (76 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> Model fitted: Log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (4 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -48.2686 121.7112 -0.3966 0.6928
#> c:(Intercept) 2.0836 2.5960 0.8026 0.4247
#> d:(Intercept) 63.9961 2.5954 24.6572 <2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 24.4808 1.3094 18.6960 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.6807 (76 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 35.0000000
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value -Inf
#> 4 AIC 662.7721102
#> 5 BIC 674.6822433
#> 6 r-squared 0.7953455
#>
#> [[2]]
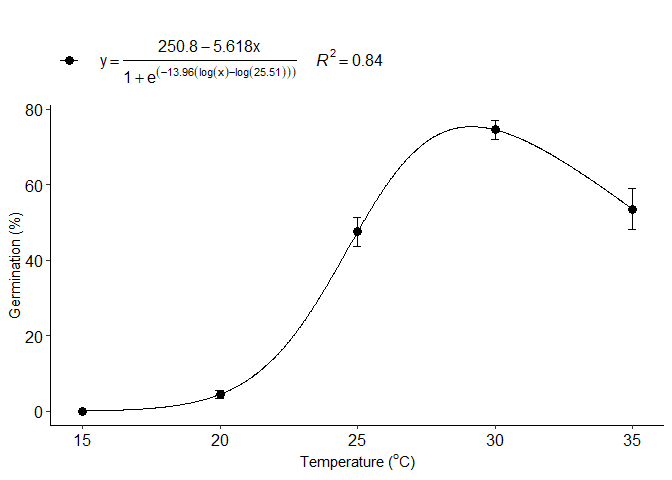
Logistic regression Brain-Cousens
f=BC_model(trat,resp, npar = "BC.4")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Brain-Cousens (hormesis) with lower limit fixed at 0 (4 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -13.95721 3.65564 -3.8180 0.0002727 ***
#> d:(Intercept) 250.77475 60.32596 4.1570 8.381e-05 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 25.50595 0.69513 36.6923 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> f:(Intercept) -5.61797 1.74018 -3.2284 0.0018389 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 12.92089 (76 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 29.1414141
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 16.9061906
#> 4 AIC 642.3420163
#> 5 BIC 654.2521495
#> 6 r-squared 0.8414623
#>
#> [[2]]
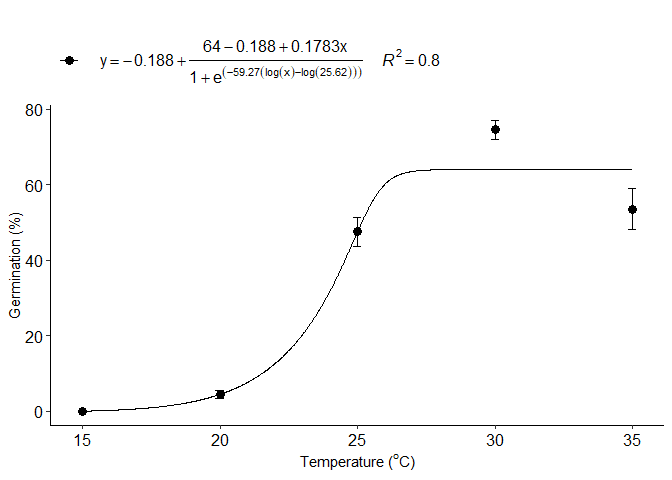
g=BC_model(trat,resp, npar = "BC.5")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Generalized log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (5 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -59.27493 215.42337 -0.2752 0.7840
#> c:(Intercept) -0.18797 4.13493 -0.0455 0.9639
#> d:(Intercept) 64.00006 2.59966 24.6186 <2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 25.62206 1.21891 21.0205 <2e-16 ***
#> f:(Intercept) 0.17829 0.68758 0.2593 0.7961
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.70436 (75 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 35.0000000
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 16.6801680
#> 4 AIC 663.9700837
#> 5 BIC 678.2622435
#> 6 r-squared 0.7973767
#>
#> [[2]]
Logistic regression Cedergreen-Ritz-Streibig
h=CD_model(trat,resp, npar = "CRS.4")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Cedergreen-Ritz-Streibig with lower limit 0 (alpha=1) (4 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -14.42145 3.53110 -4.0841 0.0001085 ***
#> d:(Intercept) 6110.38907 1944.20876 3.1429 0.0023858 **
#> e:(Intercept) 25.81624 0.75778 34.0682 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> f:(Intercept) -6231.70537 2001.17232 -3.1140 0.0026022 **
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 12.92096 (76 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 28.9633963
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 16.8361836
#> 4 AIC 642.3427825
#> 5 BIC 654.2529157
#> 6 r-squared 0.8414613
#>
#> [[2]]
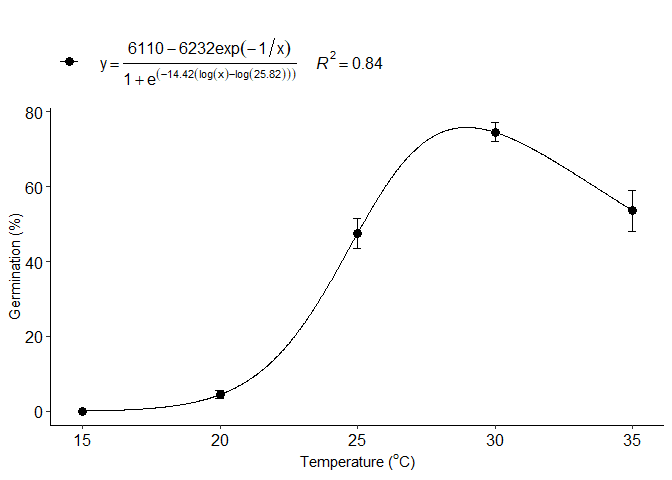
i=CD_model(trat,resp, npar = "CRS.5")
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Model fitted: Generalized log-logistic (ED50 as parameter) (5 parms)
#>
#> Parameter estimates:
#>
#> Estimate Std. Error t-value p-value
#> b:(Intercept) -59.27493 215.42337 -0.2752 0.7840
#> c:(Intercept) -0.18797 4.13493 -0.0455 0.9639
#> d:(Intercept) 64.00006 2.59966 24.6186 <2e-16 ***
#> e:(Intercept) 25.62206 1.21891 21.0205 <2e-16 ***
#> f:(Intercept) 0.17829 0.68758 0.2593 0.7961
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error:
#>
#> 14.70436 (75 degrees of freedom)
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 35.0000000
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 16.6801680
#> 4 AIC 663.9700837
#> 5 BIC 678.2622435
#> 6 r-squared 0.7973767
#>
#> [[2]]
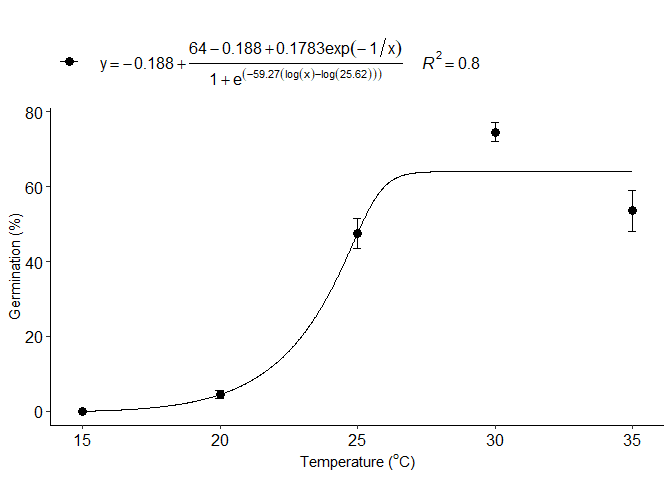
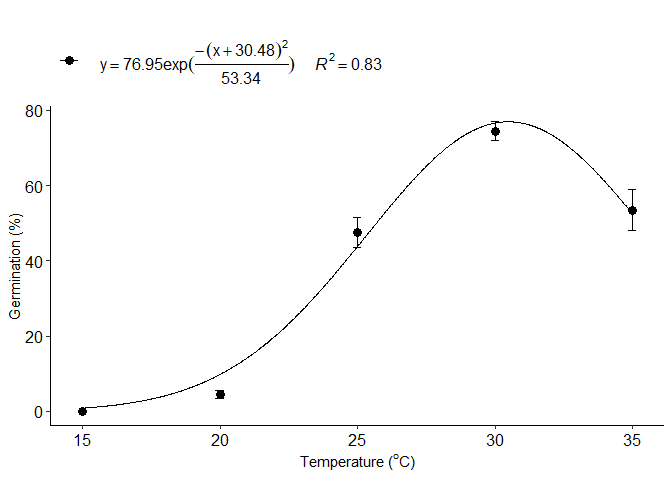
Normal model
j=normal_model(trat,resp)
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 < maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Formula: resp ~ a * exp(-1/2 * (trat - b)^2/c^2)
#>
#> Parameters:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> a 76.9526 3.1188 24.67 <2e-16 ***
#> b 30.4797 0.2581 118.09 <2e-16 ***
#> c 5.1641 0.2934 17.60 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 13.22 on 77 degrees of freedom
#>
#> Number of iterations to convergence: 10
#> Achieved convergence tolerance: 7.538e-06
#>
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 30.4795480
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value -Inf
#> 4 AIC 645.0511211
#> 5 BIC 654.5792276
#> 6 r-squared 0.8332529
#>
#> [[2]]
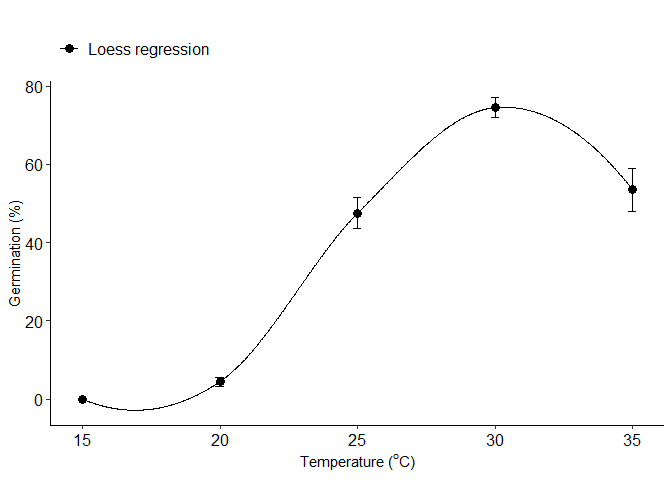
Loess model
k=loess_model(trat,resp)
#> Warning in max(temp1[round(result) == "0" & temp1 > maximo]): nenhum argumento
#> não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted maximum and minimum values
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 30.31153
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value 18.99240
#>
#> [[2]]
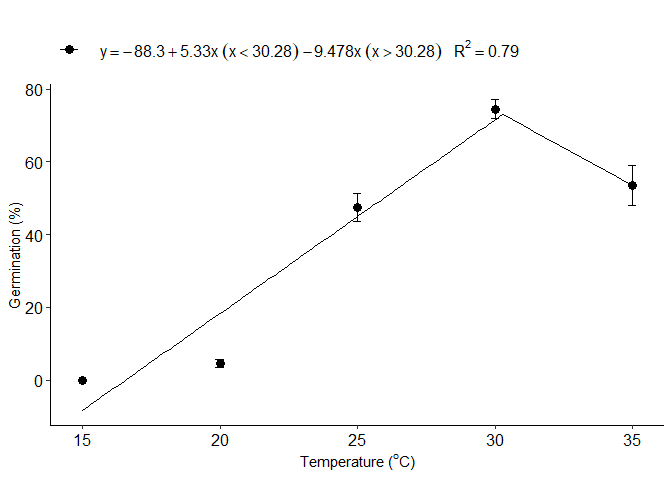
Piecewise linear-linear regression
l=piecewisel_model(trat,resp)
#> Warning in data.frame(x = temp2, y = predict(model, x = temp2)): row names were
#> found from a short variable and have been discarded
#> Warning in max(temp2[round(preditos1$y) == "0"]): nenhum argumento não faltante
#> para max; retornando -Inf
#> Warning in max(temp2[round(preditos1$y) == "0" && preditos1$y > breaks]): nenhum
#> argumento não faltante para max; retornando -Inf
#>
#> Call:
#> stats::lm(formula = y ~ x + w)
#>
#> Residuals:
#> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
#> -28.950 -11.600 2.775 8.350 46.500
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) -88.3000 7.7231 -11.433 < 2e-16 ***
#> x 5.3300 0.3331 16.000 < 2e-16 ***
#> w -9.4783 1.2473 -7.599 5.99e-11 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 14.9 on 77 degrees of freedom
#> Multiple R-squared: 0.7865, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7809
#> F-statistic: 141.8 on 2 and 77 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
#>
#>
#> ===================================
#> Predicted values and statistical parameters
#> ====================================
#> Note: if the maximum predicted value is equal to the maximum x, the curve does not have a maximum point within the studied range. If the minimum value is less than the lowest point studied, disregard the value.
#>
#> Note: Lower AIC and BIC values and higher R-squared values indicate better models.
#>
#>
#> ====================================
#> $teste
#> Parameter values
#> 1 optimum temperature 30.2787
#> 2 Predicted maximum value -Inf
#> 3 Predicted minimum value -Inf
#> 4 AIC 664.1642
#> 5 BIC 673.6923
#> 6 r-squared 0.7900
#>
#> [[2]]
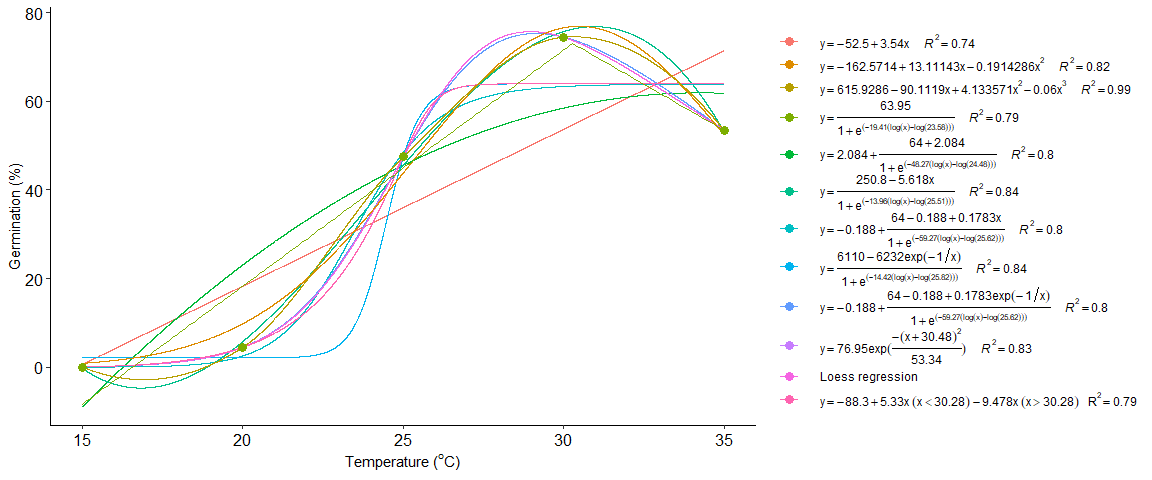
Merge multiple curves into a single graph
seedreg::multicurve(list(a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l),legend.position = "right")
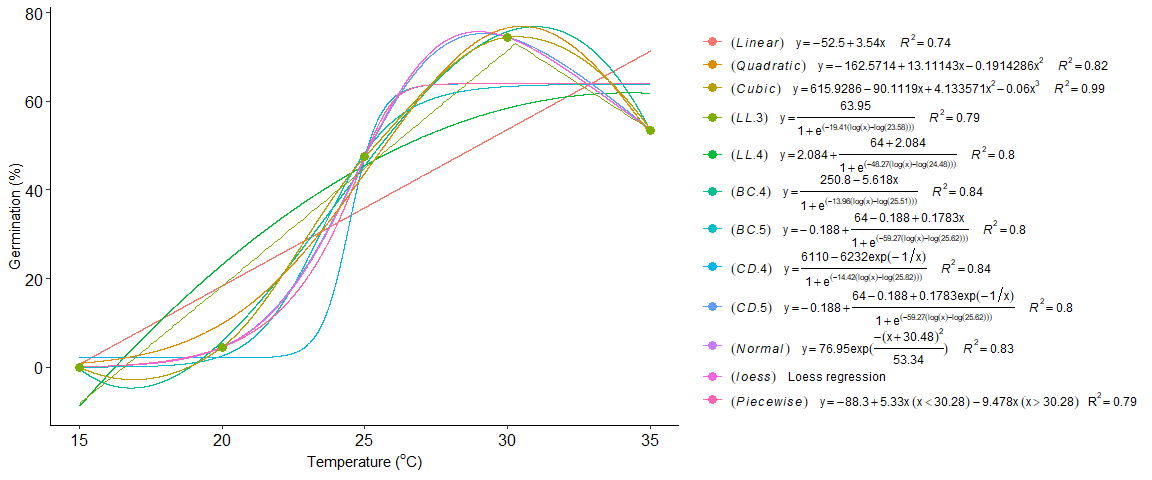
Add name in multicurve legend
seedreg::multicurve(list(a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l),
trat=c("(italic(Linear))",
"(italic(Quadratic))",
"(italic(Cubic))",
"(italic(LL.3))",
"(italic(LL.4))",
"(italic(BC.4))",
"(italic(BC.5))",
"(italic(CD.4))",
"(italic(CD.5))",
"(italic(Normal))",
"(italic(loess))",
"(italic(Piecewise))"),
legend.position = "right")
Qualitative analysis
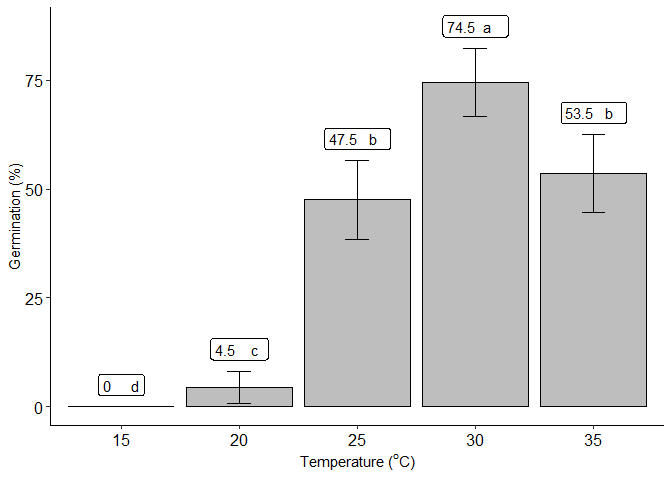
quali_model(trat, resp,family = "quasibinomial")
#> Quasi-binomial model
#> Note: adjust = "tukey" was changed to "sidak"
#> because "tukey" is only appropriate for one set of pairwise comparisons
#>
#> =======================================================
#> Analysis of Deviance Table (Type II tests)
#>
#> Response: cbind(nseeds, n - nseeds)
#> LR Chisq Df Pr(>Chisq)
#> trat 460.7 4 < 2.2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> =======================================================
#> trat prob SE df asymp.LCL asymp.UCL .group
#> 15 0.000 1.41e-06 Inf -3.60e-06 3.60e-06 d
#> 20 0.045 1.45e-02 Inf 7.65e-03 8.24e-02 c
#> 25 0.475 3.50e-02 Inf 3.85e-01 5.65e-01 b
#> 30 0.745 3.06e-02 Inf 6.66e-01 8.24e-01 a
#> 35 0.535 3.50e-02 Inf 4.45e-01 6.25e-01 b
#>
#> Confidence level used: 0.95
#> Conf-level adjustment: sidak method for 5 estimates
#> P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 5 estimates
#> significance level used: alpha = 0.05
#>
#> =======================================================