Metrics (with Uncertainty) for Simulation Studies that Evaluate Statistical Methods.
simMetric
simMetric is an R package that provides metrics (and their Monte Carlo standard errors) for the assessment of statistical methods in simulation studies. This package includes metrics that are calculated as per this tutorial published by Tim Morris, Ian White and Michael Crowther. For an in-depth description on the calculation and interpretation, and how to perform a simulation study in general, refer to the tutorial.
Installation
You can install the development version of simMetric from GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("RWParsons/simMetric")
Or install from CRAN
install.packages("simMetric")
Included Metrics (taken from here).
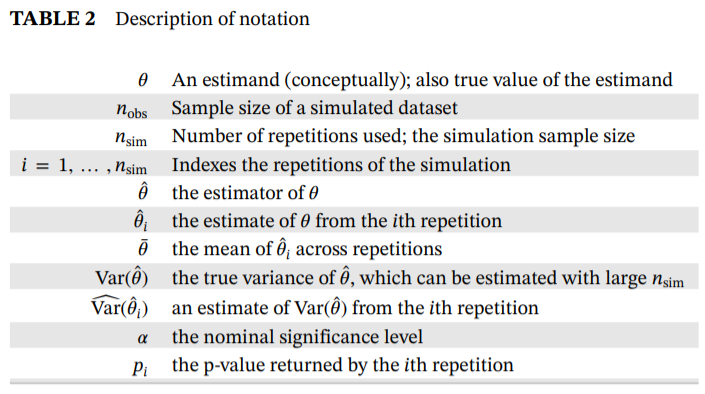
Notation
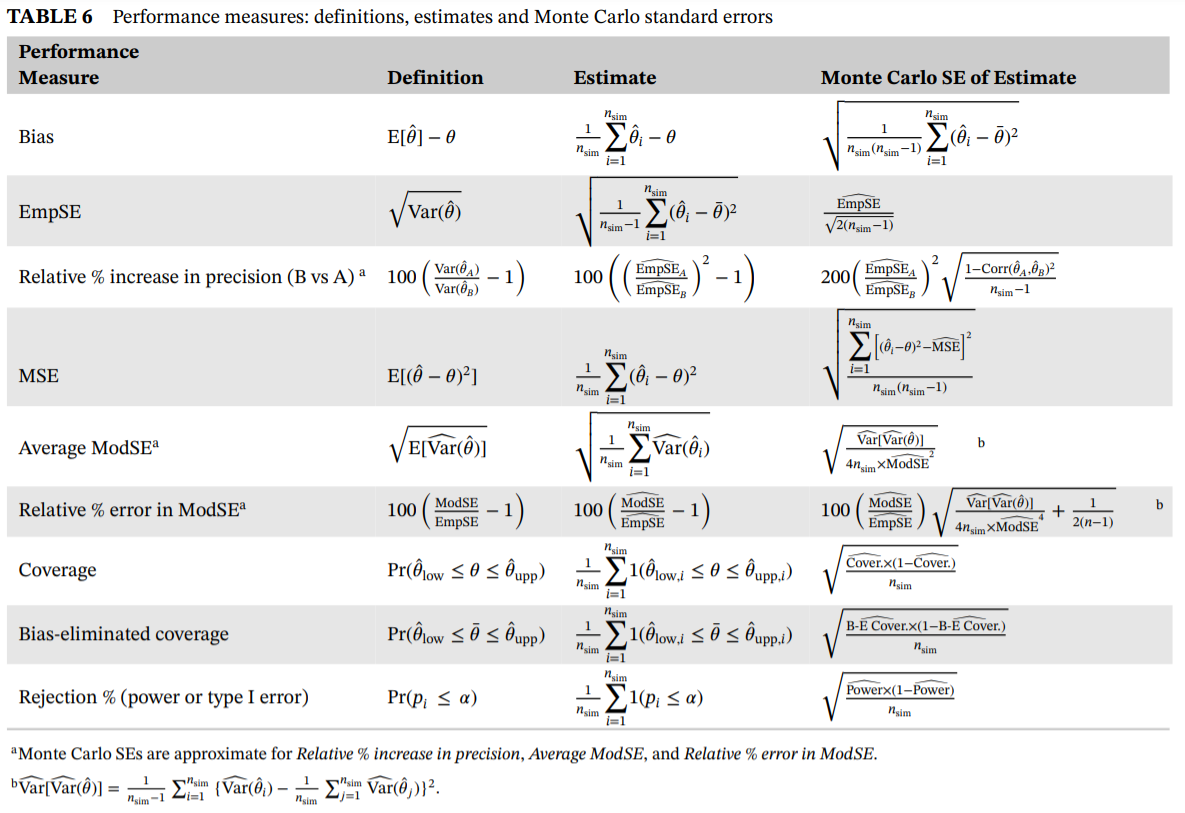
Metrics
Example
Here is a basic example that performs a simulation study, evaluates the metrics and plots the results:
library(simMetric)
library(tidyverse)
define a function to generate some data and another that fits a linear model and returns some useful outputs.
Here, we have two models that we want to compare. One of them includes an intercept term and the other doesn’t.
data_generator <- function(n_obs, noise = 1, effect = 0, s = 42) {
set.seed(s)
x <- rnorm(n = n_obs, mean = 0, sd = 1)
y <- x * effect + rnorm(n = n_obs, mean = 0, sd = noise)
data.frame(x = x, y = y)
}
assess_lm <- function(data) {
model <- lm(y ~ x, data = data)
model %>%
broom::tidy(., conf.int = T) %>%
filter(term == "x") %>%
select(-any_of(c("term", "statistic"))) %>%
add_column(model = "with_intercept")
}
assess_lm_no_intercept <- function(data) {
model <- lm(y ~ 0 + x, data = data)
model %>%
broom::tidy(., conf.int = T) %>%
filter(term == "x") %>%
select(-any_of(c("term", "statistic"))) %>%
add_column(model = "without_intercept")
}
assess_lm(data_generator(n_obs = 10, noise = 0.1, effect = 1))
#> # A tibble: 1 × 6
#> estimate std.error p.value conf.low conf.high model
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 0.927 0.0640 0.000000504 0.779 1.07 with_intercept
assess_lm_no_intercept(data_generator(n_obs = 10, noise = 0.1, effect = 1))
#> # A tibble: 1 × 6
#> estimate std.error p.value conf.low conf.high model
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
#> 1 0.941 0.0501 0.0000000158 0.828 1.05 without_intercept
define a grid of inputs to simulate many datasets
The number of unique seeds represents the number of simulations to be done (100 in this example)
g <- expand.grid(
seed = 1:100,
n_obs = seq(from = 10, to = 50, by = 10),
noise = 0.1,
effect = 0.5
)
define a function to take that grid and a (row) index, then generates the data and return the model outputs.
Since we want to simulate the multiple models, and we want to apply the same datasets to each set of models, we have one row returned per model that we are simulating. This way, fit_one_model is run once per simulated dataset, and the generated data is used for all included models.
fit_one_model <- function(grid, row) {
inputs <- grid[row, ]
d <- data_generator(
n_obs = inputs$n_obs,
noise = inputs$noise,
effect = inputs$effect,
s = inputs$seed
)
cbind(
rbind(assess_lm(d), assess_lm_no_intercept(d)),
inputs
)
}
fit_one_model(g, 1)
#> Warning in data.frame(..., check.names = FALSE): row names were found from a
#> short variable and have been discarded
#> estimate std.error p.value conf.low conf.high model seed
#> 1 0.4483862 0.04487337 8.537408e-06 0.3449081 0.5518644 with_intercept 1
#> 2 0.4557942 0.04388530 2.608370e-06 0.3565188 0.5550697 without_intercept 1
#> n_obs noise effect
#> 1 10 0.1 0.5
#> 2 10 0.1 0.5
run all simulations in parallel and collate all the results into a data.frame.
library(parallel)
cl <- parallelly::autoStopCluster(makeCluster(detectCores()))
clusterExport(cl, ls()[!ls() %in% "cl"]) # send the grid and functions to each node
x <- clusterEvalQ(cl, require(tidyverse, quietly = T)) # load the tidyverse on each node
start <- Sys.time()
ll <- parLapply(
cl,
1:nrow(g),
function(r) fit_one_model(grid = g, r)
)
par_res <- do.call("rbind", ll)
head(par_res)
#> estimate std.error p.value conf.low conf.high model seed
#> 1 0.4483862 0.04487337 8.537408e-06 0.3449081 0.5518644 with_intercept 1
#> 2 0.4557942 0.04388530 2.608370e-06 0.3565188 0.5550697 without_intercept 1
#> 3 0.5239730 0.04153620 1.463669e-06 0.4281904 0.6197557 with_intercept 2
#> 4 0.5269444 0.03844832 2.464367e-07 0.4399683 0.6139206 without_intercept 2
#> 5 0.4758010 0.02818650 1.537607e-07 0.4108028 0.5407992 with_intercept 3
#> 6 0.4786038 0.02884696 4.686118e-08 0.4133474 0.5438601 without_intercept 3
#> n_obs noise effect
#> 1 10 0.1 0.5
#> 2 10 0.1 0.5
#> 3 10 0.1 0.5
#> 4 10 0.1 0.5
#> 5 10 0.1 0.5
#> 6 10 0.1 0.5
Obtaining metrics using {simMetric}
Get metrics using simMetric::join_metrics()
df_metrics <- join_metrics(
par_res,
id_cols = c("n_obs", "model"),
metrics = c("coverage", "mse", "modSE", "empSE", "relativeErrorModSE"),
ll_col = "conf.low",
ul_col = "conf.high",
true_value = "effect",
estimates_col = "estimate",
se_col = "std.error"
)
head(df_metrics)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 12
#> n_obs model cover…¹ cover…² mse mse_m…³ modSE modSE…⁴ empSE empSE…⁵
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 10 with_inte… 0.97 0.0171 1.21e-3 1.93e-4 0.0370 1.55e-3 0.0349 0.00248
#> 2 10 without_i… 0.99 0.00995 9.88e-4 1.58e-4 0.0347 1.46e-3 0.0315 0.00224
#> 3 20 with_inte… 0.94 0.0237 6.13e-4 1.14e-4 0.0248 7.44e-4 0.0249 0.00177
#> 4 20 without_i… 0.92 0.0271 6.08e-4 1.13e-4 0.0241 7.35e-4 0.0248 0.00176
#> 5 30 with_inte… 0.95 0.0218 4.92e-4 6.65e-5 0.0193 4.08e-4 0.0223 0.00158
#> 6 30 without_i… 0.92 0.0271 4.61e-4 6.55e-5 0.0189 3.78e-4 0.0216 0.00153
#> # … with 2 more variables: relativeErrorModSE <dbl>,
#> # relativeErrorModSE_mcse <dbl>, and abbreviated variable names ¹coverage,
#> # ²coverage_mcse, ³mse_mcse, ⁴modSE_mcse, ⁵empSE_mcse
Get metrics within usual tidy workflow with group_by() and summarise()
df_metrics <-
par_res %>%
group_by(n_obs, model) %>%
summarise(
coverage_estimate = coverage(true_value = effect, ll = conf.low, ul = conf.high, get = "coverage"),
coverage_mcse = coverage(true_value = effect, ll = conf.low, ul = conf.high, get = "coverage_mcse"),
mean_squared_error_estimate = mse(true_value = effect, estimates = estimate, get = "mse"),
mean_squared_error_mcse = mse(true_value = effect, estimates = estimate, get = "mse_mcse")
)
#> `summarise()` has grouped output by 'n_obs'. You can override using the
#> `.groups` argument.
head(df_metrics)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 6
#> # Groups: n_obs [3]
#> n_obs model coverage_estimate coverage_mcse mean_squared…¹ mean_…²
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 10 with_intercept 0.97 0.0171 0.00121 1.93e-4
#> 2 10 without_intercept 0.99 0.00995 0.000988 1.58e-4
#> 3 20 with_intercept 0.94 0.0237 0.000613 1.14e-4
#> 4 20 without_intercept 0.92 0.0271 0.000608 1.13e-4
#> 5 30 with_intercept 0.95 0.0218 0.000492 6.65e-5
#> 6 30 without_intercept 0.92 0.0271 0.000461 6.55e-5
#> # … with abbreviated variable names ¹mean_squared_error_estimate,
#> # ²mean_squared_error_mcse
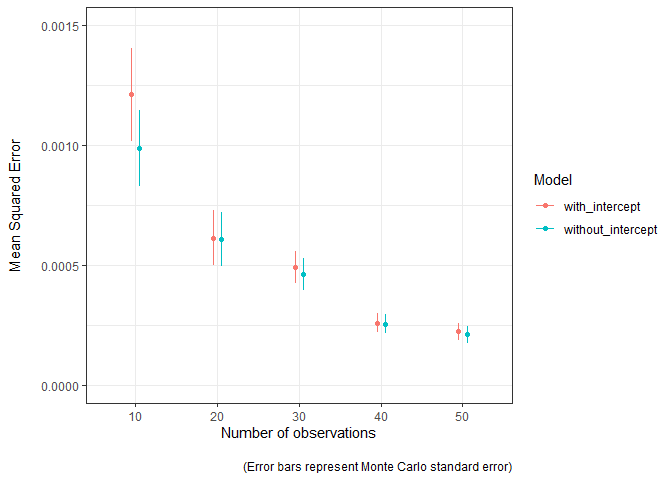
Plot the the Mean Squared Error (MSE) as the number of observations increases
The model estimates are closer to the truth (MSE is lower) as the sample used to fit the model increases in size. The Monte Carlo standard error can easily be visualised to convey the uncertainty in these estimates. The model without the intercept term seems to be a bit better, mostly when sample sizes are lower.
df_metrics %>%
ggplot(aes(as.factor(n_obs), mean_squared_error_estimate, group = model, colour = model)) +
geom_point(position = position_dodge(width = 0.2)) +
geom_errorbar(aes(
ymin = mean_squared_error_estimate - mean_squared_error_mcse,
ymax = mean_squared_error_estimate + mean_squared_error_mcse
),
width = 0, position = position_dodge(width = 0.2)
) +
theme_bw() +
labs(
x = "Number of observations",
y = "Mean Squared Error\n",
colour = "Model",
caption = "\n(Error bars represent Monte Carlo standard error)"
) +
scale_y_continuous(labels = scales::comma, limits = c(0, 0.0015))