Soil Food Web Analysis.
soilfoodwebs
The purpose of the soilfoodwebs package is to help analyze and simulate soil food webs. The following five functions are the core of the package:
- Calculate the fluxes through a food web given biomass, parameters, and food web structure.
- Calculate the direct and indirect contribution of each trophic species (i.e., node) to carbon and nitrogen mineralization.
- Calculate food web stability and
smin. - Simulate the food web away from equilibrium.
- Conduct a detritus decomposition simulation and calculate the decomposition constant.
The package also can complete the following tasks using functions built to work with the communities that are input:
- Modify the fluxes to balance carbon and nitrogen demands.
- Modify the structure of the food web.
Installation
You can install the released version of soilfoodwebs from GitHub with:
# Install devtools if not available:
if (!require("devtools")) install.packages("devtools")
# Install soilfoodwebs
devtools::install_github("robertwbuchkowski/soilfoodwebs")
# Install soilfoodwebs with the vignette
devtools::install_github("robertwbuchkowski/soilfoodwebs", build_vignettes = T, build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"))
Example
The core of the soilfoodwebs package allows you to calculate the fluxes of carbon and nitrogen through a food web at equilibrium using basic properties about each trophic species or node.
For example, here is a plot of the carbon flow through the introductory community after corrections are made to balance nitrogen demand.
library(soilfoodwebs)
intro_comm_temp = corrstoich(intro_comm)
ana1 <- comana(intro_comm_temp, mkplot = T, whattoplot = "web")
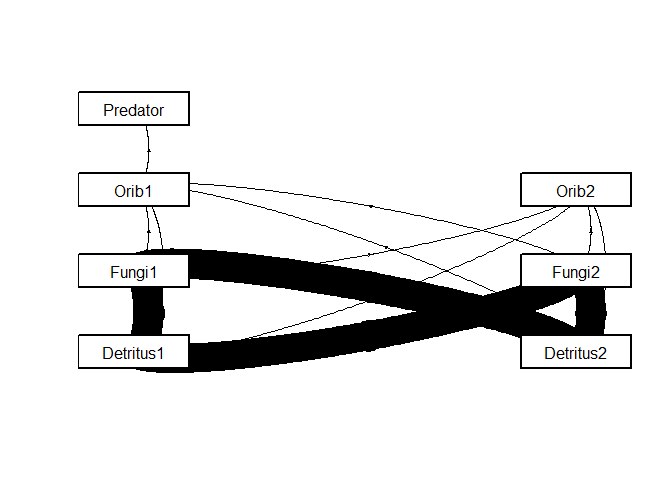
Here are the rates of carbon and nitrogen mineralization predicted for each species.
# Carbon mineralization:
ana1$Cmin
#> Predator Orib2 Orib1 Fungi1 Fungi2 Detritus1 Detritus2
#> 2.8704 9.5250 40.5350 20081.9528 19970.4067 0.0000 0.0000
# Nitrogen mineralization:
ana1$Nmin
#> Predator Orib2 Orib1 Fungi1 Fungi2
#> 5.510821e-01 5.941428e-17 -3.174544e-16 1.195354e+02 4.754859e+02
#> Detritus1 Detritus2
#> 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00