Combines 'data.table' and 'matrix' Classes.
tableMatrix package
tableMatrix package provides two classes extending data.table class. Simple tableList class wraps data.table and any additional structures together. More complex tableMatrix class combines data.table and matrix.
Installation
From CRAN:
install.packages("tableMatrix")
From github:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("InferenceTechnologies/tableMatrix")
tableList class
Motivation
Goal is to wrap data.table class and other structures together and preserve data.table behaviour.
Example
Combine data and linear model into one object.
data(chickwts)
# Bundle chickwts data.frame together with a linear model
TL <- tableList(chickwts, lm(weight~feed, chickwts))
# tableList behaves like a data.table
mean(TL[feed=="casein", weight])
#> [1] 323.5833
# Aid part of the tableList object carries the linear model
aid(TL)
#>
#> Call:
#> lm(formula = weight ~ feed, data = chickwts)
#>
#> Coefficients:
#> (Intercept) feedhorsebean feedlinseed feedmeatmeal feedsoybean
#> 323.583 -163.383 -104.833 -46.674 -77.155
#> feedsunflower
#> 5.333
tableMatrix class
Motivation
Let’s have a dataset with the following structure: first set of columns of varying types is intented as meta data, second set of columns of the same type is intended as main data. tableMatrix stores meta data as a data.table and main data as a matrix. It also keeps track of dimensions of main data, thus allowing to combine rows of varying lengths into one object. As in tableList, tableMatrix can carry any additional aid data.
Example
Working with bitmaps of different sizes. Datasets images8By8 and images10By10 contain 8x8 and 10x10 images in the form of vectors. For each row first three columns represent image meta data, remaining columns represent the image itself. For more information see ?images8By8.
# Load datasets
data(images8By8)
data(images10By10)
# Create a signle tableMatrix object from both datasets
# First 3 columns used as meta data, the rest as main data with corresponding dimensions
TM <- tableMatrix(list(images8By8, images10By10),
list(1:3, 1:3), list(c(4:ncol(images8By8)),c(4:ncol(images10By10))), list(c(8,8), c(10,10)))
# Default print displays the table (meta data) part
TM
#> direction dimX dimY
#> 1: down 8 8
#> 2: down 8 8
#> 3: down 8 8
#> 4: down 8 8
#> 5: down 8 8
#> ---
#> 176: both 10 10
#> 177: both 10 10
#> 178: both 10 10
#> 179: both 10 10
#> 180: both 10 10
# Number of matrices stored in the matrix (main data) part
length(mat(TM))
#> [1] 2
# Dimensions of the matrix part
matDim(TM)
#> tm.matN tm.matDim1 tm.matDim2
#> 1: 1 8 8
#> 2: 2 10 10
# Aid part is empty
aid(TM)
#> list()
# Image data for first row
img <- getRow(TM, 1)
# Restoring dimensions of the image
dim(img) <- getRowDim(TM, 1)
# Visualising the image
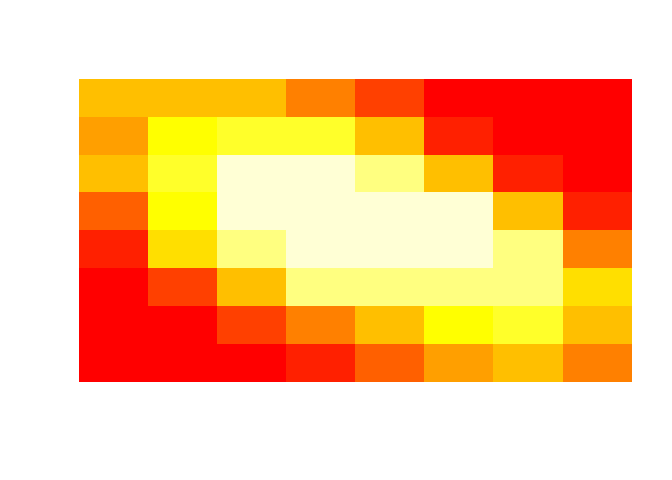
image(img, axes=F)
Let’s create a heat map
# Subsetting via bracket passed to the table (meta data) part
# We choose first matrix type, down direction
TM1down <- TM[.(1)][direction=="down"]
# One matrix in the matrix part of TM1down
length(mat(TM1down))
#> [1] 1
# One dimension row
matDim(TM1down)
#> tm.matN tm.matDim1 tm.matDim2
#> 1: 1 8 8
# Heatmap
imgHeat <- colMeans(mat(TM1down, 1))
# Restoring dimensions of the heatmap
dim(imgHeat) <- getRowDim(TM1down, 1)
# Visualising heatmap
image(imgHeat, axes=F)
