Write Events for 'TensorBoard'.
tfevents
tfevents allows logging data from machine learning experiments to a file format that can be later consumed by TensorBoard in order to generate visualizations.
Installation
You can install tfevents from CRAN with:
install.packages("tfevents")
You can install the development version of tfevents from GitHub with:
You need to have cmake on your path. See installation instructions in the cmake install webpage - or:
If you use brew on MacOS you can run:
brew install cmake
Or on linux install the cmake library, for example on Debian systems:
sudo apt install cmake
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("mlverse/tfevents")
Example
The main entrypoint in tfevents API is the log_event function. It can be used to log summaries like scalars, images, audio (Coming soon), histograms (Coming soon) and arbitrary tensors (soon) to a log directory, which we like to call logdir. You can later point TensorBoard to this logdir to visualize the results.
library(tfevents)
Summaries are always associated to a step in the TensorBoard API, and log_event automatically increases the step everytime it’s called, unless you provide the step argument.
Let’s start by logging some metrics:
epochs <- 10
for (i in seq_len(epochs)) {
# training code would go here
log_event(
train = list(loss = runif(1), acc = runif(1)),
valid = list(loss = runif(1), acc = runif(1))
)
}
By default this will create a logs directory in your working directory and write metrics to it - you can change the default logdir using context like with_logdir or globally with set_default_logdir().
Since we passed a nested list of metrics, log_event will create subdirectories under logs to write metrics for each group.
fs::dir_tree("logs")
#> logs
#> ├── train
#> │ └── events.out.tfevents.1719410709.v2
#> └── valid
#> └── events.out.tfevents.1719410709.v2
You can later point TensorBoard to that logdir using TensorBoard’s command line interface or tensorflow’s utility function tensorboard()
tensorflow::tensorboard(normalizePath("logs"), port = 6060)
#> Started TensorBoard at http://127.0.0.1:6060
TensorBoard will display the results in a dashbboard, similar to one you can see in the screenshot below:
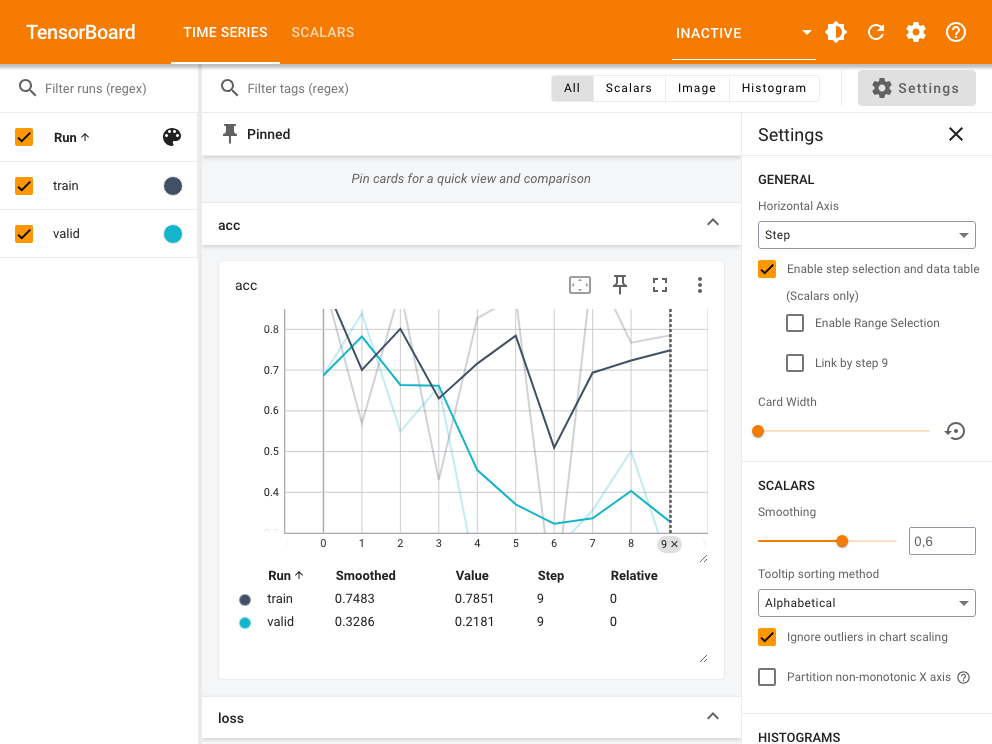
You can learn more in the tfevents website.