Simulates Dice Rolls and Coin Flips.

tidydice
Simulates Dice Rolls and Coin Flips.
Introduction
A basic understanding of probability and statistics is crucial for data understanding. A great way to teach probability and statistics is to start with an experiment, like rolling a dice or flipping a coin.
This package simulates rolling a dice and flipping a coin. Each experiment generates a tibble. Dice rolls and coin flips are simulated using sample(). The properties of the dice can be changed, like the number of sides. A coin flip is simulated using a two sided dice. Experiments can be combined with the pipe-operator.
Installation
CRAN
install.packages("tidydice")
DEV version (github)
# install from github
if (!require(devtools)) install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("rolkra/tidydice")
if you are behind a firewall, you may want to:
- Download and unzip the tidydice package
- Then install it with devtools::install_local
# install local
if (!require(devtools)) install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_local(path = <path of local package>, force = TRUE)
Basic example
Let's roll 60 dice:
# load packages
library(tidydice)
# roll 60 dice (10 x 6 dice = 60)
data <- roll_dice(times = 10, rounds = 6)
data
We get tidy data, where each row is a dice. It is a success, if the result is a 6.
# A tibble: 60 × 5
experiment round nr result success
<int> <int> <int> <int> <lgl>
1 1 1 1 5 FALSE
2 1 1 2 6 TRUE
3 1 1 3 6 TRUE
4 1 1 4 1 FALSE
5 1 1 5 5 FALSE
6 1 1 6 1 FALSE
7 1 1 7 4 FALSE
8 1 1 8 5 FALSE
9 1 1 9 1 FALSE
10 1 1 10 2 FALSE
# … with 50 more rows
Now let's plot it:
data |> plot_dice()
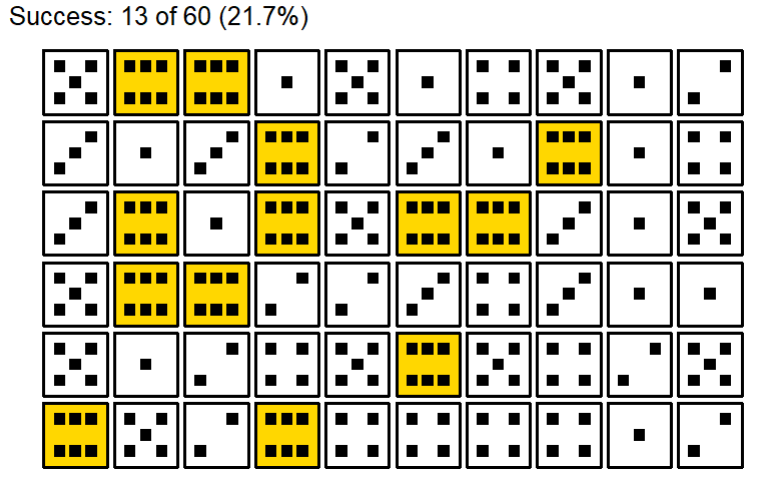
We got 13 six. Is this unlikely? The expected value is 10 (60 dice / 6 sides = 10). So 13 is more than expected, is it a sign of cheating? Let's check using the binomial ditribution:
# binomial distribution
binom_dice(times = 60) |>
plot_binom(highlight = c(13:60))
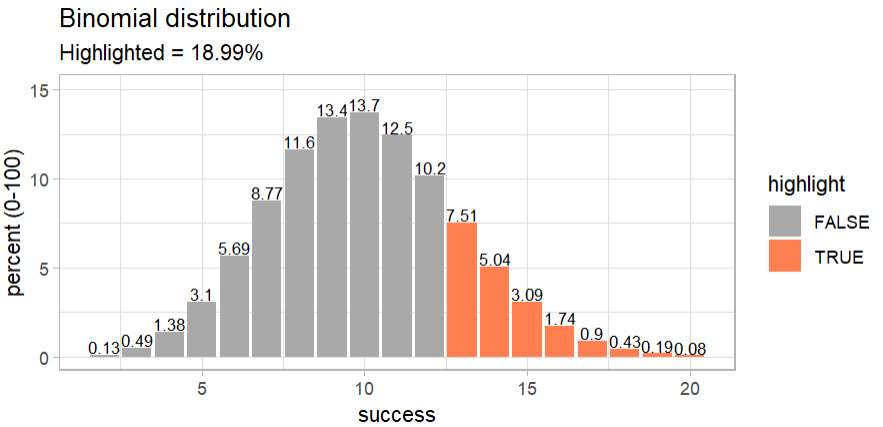
The binomial distribution shows, that there is a 19% chance that you can get 13 or more six using a fair dice.
Roll dice
# load packages
library(tidydice)
# roll a dice
roll_dice()
# roll a dice 6x
roll_dice(times = 6)
# roll a dice 6x and plot result
roll_dice(times = 6) |>
plot_dice()
# repeat 6x
roll_dice(times = 6, rounds = 6) |>
plot_dice()
# count success per round
roll_dice(times = 6, rounds = 6, agg = TRUE)
# Binomial distribution
binom_dice(times = 6)
# Binomial distribution + plot
binom_dice(times = 6) |>
plot_binom()
# Binomial distribution + plot
binom_dice(times = 6) |>
plot_binom(highlight = 0:2)
Roll dice (advanced)
To do more complex dice rolls use roll_dice_formula():
library(tidydice)
roll_dice_formula(
dice_formula = "4d6e3", # 4 dice with 6 sides, explode on a 3
rounds = 5, # repeat 5 times
success = 15:24, # success is defined as sum between 15 and 24
seed = 123 # random seed to make it reproducible
)
1d6= roll one 6-sided dice1d8= roll one 8-sided dice1d12= roll one 12-sided dice2d6= roll two 6-sided dice1d6e6= roll one 6-sided dice, explode dice on a 63d6kh2= roll three 6-sided dice, keep highest 2 rolls3d6kl2= roll three 6-sided dice, keep lowest 2 rolls4d6kh3e6= roll four 6-sided dice, keep highest 3 rolls, but explode on a 61d20+4= roll one 20-sided dice, and add 41d4+1d6= roll one 4-sided dice and one 6-sided dice, and sum the results
Flip coin
# load packages
library(tidydice)
# flip a coin
flip_coin()
# flip a coin 10x
flip_coin(times = 10)
# flip a coin 10x and plot result
flip_coin(times = 10) |>
plot_coin()
# repeat 10x and plot result
flip_coin(times = 10, rounds = 10) |>
plot_coin()
# count success per round
flip_coin(times = 10, rounds = 10, agg = TRUE)
# Binomial distribution
binom_coin(times = 10)
# Binomial distribution + plot
binom_coin(times = 10) |>
plot_binom()
# Binomial distribution + plot
binom_coin(times = 10) |>
plot_binom(highlight = 0:2)