Transform Microplate Data into Tibbles.
tidyplate 
Microtiter plates or microplates have become a standard tool in analytical research and clinical diagnostic testing laboratories. They are convenient, high-throughput tools for organizing tissue culture, PCR tests (such as HIV/ COVID screening), or immunological assays such as ELISA, RIA and FIA. They offer many advantages over traditional assay formats including reduced sample and reagent volumes, increased throughput, and ease of automation. The goal of tidyplate is to help researchers convert different types of microplates into tibbles which can be used in data analysis. tidyplate accepts xlsx and csv files formatted in a specific way as input. tidyplate supports all types of standard microplate formats namely: 6-well, 12-well, 24-well, 48-well, 96-well, 384-well, and 1536-well plates.
tidyplate has five functions:
tidy_plate: Transforms the input file (excel or csv) into a tibble.generate_plate: Exports a tibble into plate-shaped csv or xlsx file.check_plate: Checks whether the input file is valid for use withtidy_plate().view_plate_names: Returns names/ id(s) of each plate in the input file.build_plate: Generates a empty csv or xlsx template for each plate type.
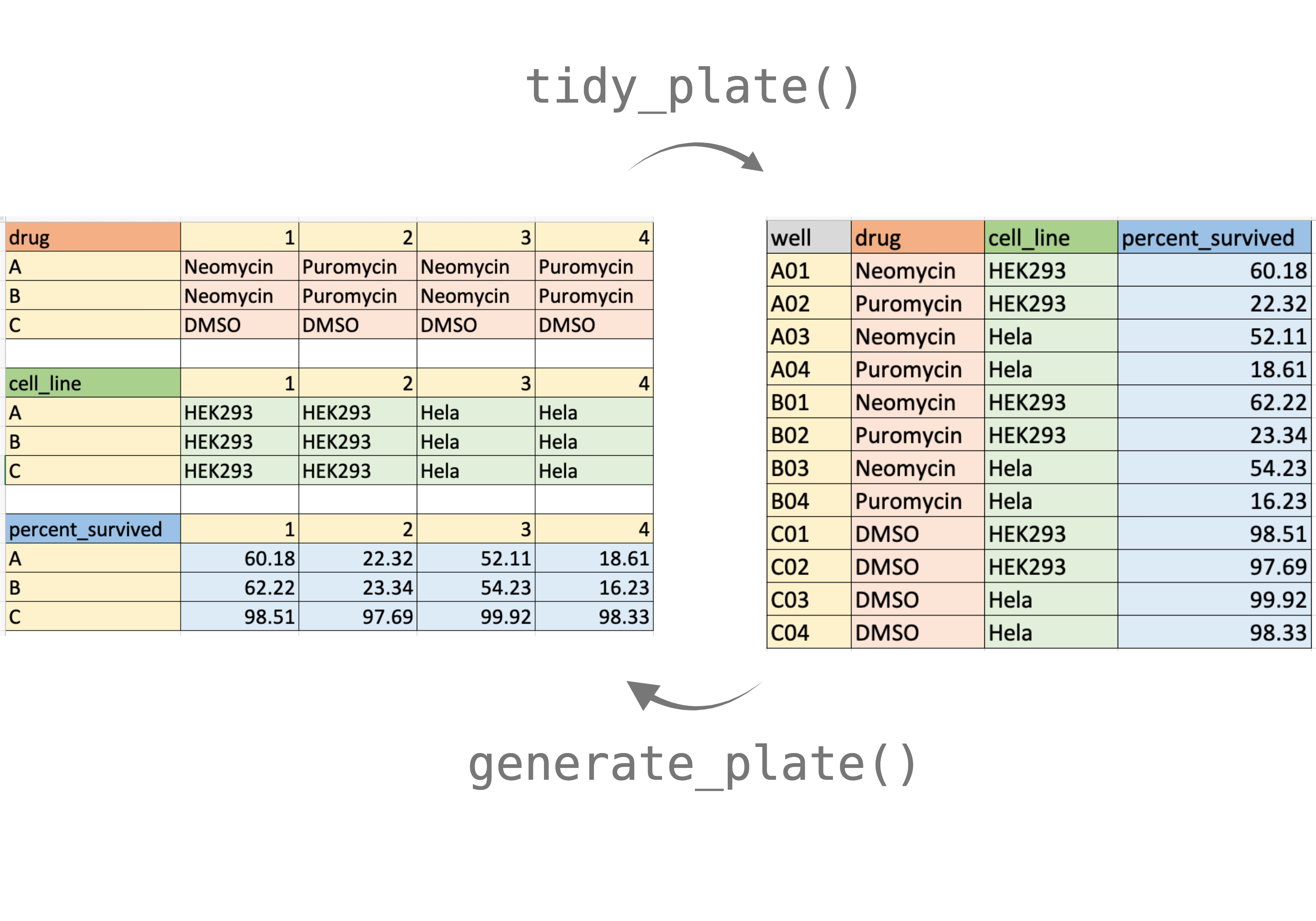
This figure demonstrates how to format the 12-well plate input file. Colors are for visualization purposes only.
Installation
To install tidyplate from CRAN:
install.packages("tidyplate")
You can install the development version of tidyplate from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("shubhamdutta26/tidyplate")
Formating the input data
The input xlsx or csv should be formatted in a specific way:
- Top left corner must hold the name for that plate.
- Column names should be: 1, 2, 3, and so on and so forth.
- Row names should be: A, B, C, and so on and so forth.
- There must be an empty row between each plate.
Usage
This is an example which shows you how to use the tidyplate. If the input file is an xlsx file it reads the first sheet by default. Users can specify sheet using the sheet argument for an xlsx file. Users can also specify the variable name of column where well ids will be stored (defaults to “well”). Please make sure that well_id argument does not match individual plate names in the input file.
First check if the input file is valid or not:
library(tidyplate)
file <- system.file("extdata",
"example_12_well.xlsx",
package = "tidyplate")
check_plate(file) # No error for valid file
#> example_12_well.xlsx: OK; Plate type: 12-well
incorrect_file <- system.file("extdata",
"incorrect_format.csv",
package = "tidyplate")
check_plate(incorrect_file) # Error type displayed
#> Error:
#> ! Verify row and column ids in incorrect_format.csv.
#> ℹ Expected column ids: 1, 2, 3, and so on.
#> ℹ Expected row ids: A, B, C, and so on.
#> ℹ Use the `build_plate()` function to build an empty template.
As mentioned above, the formatting of the input file is very important. A csv or excel template for each plate type can be created using the build_plate function:
build_plate(plate_type = 96,
n_plates = 2,
file_type = "xlsx") # default is csv
If you want to retrieve the names of individual plates:
view_plate_names(file)
#> [1] "drug" "cell_line" "percent_survived"
Read and import the file as a tibble:
data <- tidy_plate(file)
#> Plate type: 12-well
head(data)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 4
#> well drug cell_line percent_survived
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int>
#> 1 A01 Neomycin HEK293 60
#> 2 A02 Puromycin HEK293 NA
#> 3 A03 Neomycin Hela 52
#> 4 A04 Puromycin Hela 18
#> 5 B01 Neomycin HEK293 62
#> 6 B02 Puromycin HEK293 23
Conversely, a dataframe or tibble can be re-exported back to a plate shaped csv or xlsx file:
generate_plate(data, well_id = "well", plate_type = 12, file = "plate.csv")
For more information on how to use functions on multiple files or multi-sheet excel files read the vignette("advanced").
Cite
To cite package ‘tidyplate’ in publications use:
Dutta S (2024). tidyplate: Transform Microplate Data into Tibbles. R package version 2.0.1.9000, <https://www.shubhamdutta.com/tidyplate/.