Comparison of Trees using a Tree Defining Polynomial.
treenomial
Overview
The package treenomial is an application of polynomials that uniquely describe trees. It provides tools for tree analysis and comparison based on polynomials. The core functions are:
treeToPoly(): convert rooted unlabeled binary trees to tree distinguishing polynomials described with coefficient matricespolyToDistMat(): construct a distance matrix from multiple coefficient matrices using a distance measure
For the mathematical description of the tree defining polynomial see:
Liu, Pengyu. “A tree distinguishing polynomial.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.03332 (2019).
Installation
To install using CRAN:
install.packages("treenomial")
For the development version:
library(devtools)
install_github("mattgou1d/treenomial")
Example tree and polynomial
Consider a three tip tree:
library(ape)
library(treenomial)
threeTipTree <- rtree(3, rooted = T)
plot.phylo(threeTipTree, use.edge.length = F, show.tip.label = F, direction = "downwards")
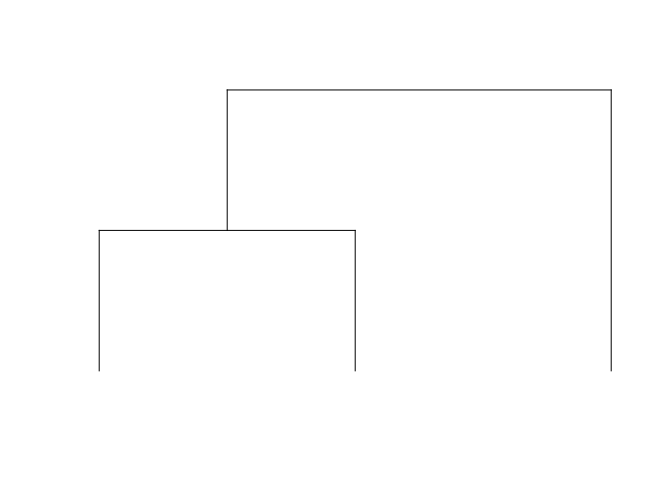
It’s polynomial is x^3+xy+y which can equivalently be described with a coefficient matrix where the element in the ith row, jth column represents the y^(i-1) * x^(j-1) coefficient:
treeToPoly(threeTipTree, varLabels = T)
#> x^0 x^1 x^2 x^3
#> y^0 0 0 0 1
#> y^1 1 1 0 0
#> y^2 0 0 0 0
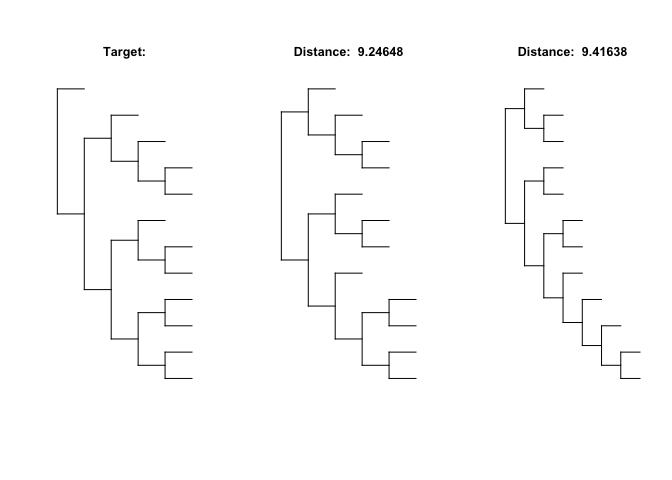
Using the coefficients of the polynomials, distances between trees can be compared, below the two closest trees to a random target tree are found from a random sample:
# random 12 tip target tree
target <- rtree(12)
# random sample of 100 trees
sample <- rmtree(100,12)
minInfo <- plotExtremeTrees(target,sample, n = 2, comparison = "min", type = "d")