Description
Exploit Data Leakages in Time Series Forecasting Competitions.
Description
Forecasting competitions are of increasing importance as a mean to learn best practices and gain knowledge. Data leakage is one of the most common issues that can often be found in competitions. Data leaks can happen when the training data contains information about the test data. For example: randomly chosen blocks of time series are concatenated to form a new time series, scale-shifts, repeating patterns in time series, white noise is added in the original time series to form a new time series, etc. 'tsdataleaks' package can be used to detect data leakages in a collection of time series.
README.md
tsdataleaks
R Package for detecting data leakages in time series forecasting competitions.
Installation
The development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("thiyangt/tsdataleaks")
library(tsdataleaks)
Example
To demonstrate the package functions, I created a small data set with 4 time series.
set.seed(2020)
a <- rnorm(15)
d <- rnorm(10)
lst <- list(
a = a,
b = c(a[10:15]+rep(8,6), rnorm(10), a[1:5], a[1:5]),
c = c(rnorm(10), -a[1:5]),
d = d,
e = d)
find_dataleaks: Exploit data leaks
library(tsdataleaks)
library(magrittr)
library(tidyverse)
library(viridis)
# h - I assume test period length is 5 and took that as wind size, h.
f1 <- find_dataleaks(lstx = lst, h=5, cutoff=1)
f1
$a
.id start end
2 b 2 6
$b
.id start end
1 a 1 5
2 b 17 21
4 c 11 15
$c
.id start end
1 a 1 5
2 b 17 21
3 b 22 26
$d
.id start end
5 e 6 10
$e
.id start end
4 d 6 10
Interpretation: The first element in the list means the last 5 observations of the time series a correlates with time series b observarion from 2 to 6.
viz_dataleaks: Visualise the data leaks
viz_dataleaks(f1)
[[1]]

[[2]]
[[2]]$a
.id start end
2 b 2 6
[[2]]$b
.id start end
1 a 1 5
2 b 17 21
4 c 11 15
[[2]]$c
.id start end
1 a 1 5
2 b 17 21
3 b 22 26
[[2]]$d
.id start end
5 e 6 10
[[2]]$e
.id start end
4 d 6 10
reason_dataleaks
Display the reasons for data leaks and evaluate usefulness of data leaks towards the winning of the competition
r1 <- reason_dataleaks(lstx = lst, finddataleaksout = f1, h=5)
r1
[[1]]
series1 .id start end dist_mean dist_sd is.useful.leak dist_cor
1 a b 2 6 -8.0 0.0 useful 1
2 b a 1 5 0.0 0.0 useful 1
3 b b 17 21 0.0 0.0 useful 1
4 b c 11 15 -1.7 2.6 not useful -1
5 c a 1 5 1.7 2.6 useful -1
6 c b 17 21 1.7 2.6 useful -1
7 c b 22 26 1.7 2.6 not useful -1
8 d e 6 10 0.0 0.0 not useful 1
9 e d 6 10 0.0 0.0 not useful 1
reason
1 add constant
2 exact match
3 exact match
4 multiply by -1 or negative constant value
5 multiply by -1 or negative constant value
6 multiply by -1 or negative constant value
7 multiply by -1 or negative constant value
8 exact match
9 exact match
[[2]]

A list without naming element
a = rnorm(15)
lst <- list(
a,
c(a[10:15], rnorm(10), a[1:5], a[1:5]),
c(rnorm(10), a[1:5])
)
f1 <- find_dataleaks(lst, h=5)
viz_dataleaks(f1)
#> [[1]]
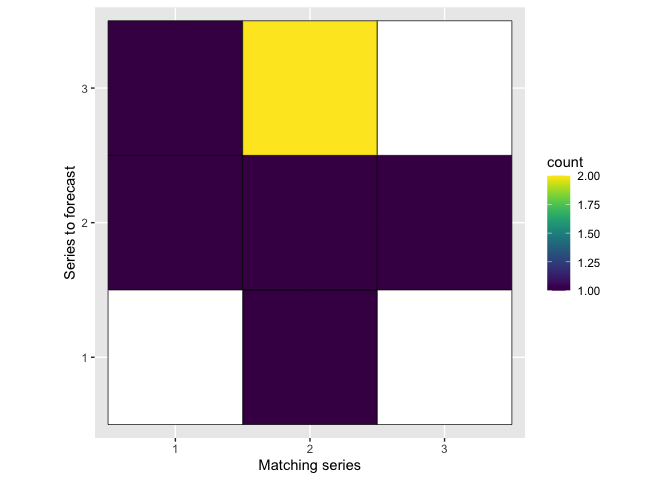
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [[2]]$`1`
#> .id start end
#> 2 2 2 6
#>
#> [[2]]$`2`
#> .id start end
#> 1 1 1 5
#> 2 2 17 21
#> 4 3 11 15
#>
#> [[2]]$`3`
#> .id start end
#> 1 1 1 5
#> 2 2 17 21
#> 3 2 22 26
reason_dataleaks(lst, f1, h=5)
#> [[1]]
#> series1 .id start end dist_mean dist_sd is.useful.leak dist_cor reason
#> 1 1 2 2 6 0 0 useful 1 exact match
#> 2 2 1 1 5 0 0 useful 1 exact match
#> 3 2 2 17 21 0 0 useful 1 exact match
#> 4 2 3 11 15 0 0 not useful 1 exact match
#> 5 3 1 1 5 0 0 useful 1 exact match
#> 6 3 2 17 21 0 0 useful 1 exact match
#> 7 3 2 22 26 0 0 not useful 1 exact match
#>
#> [[2]]

Application to M-Competition data
M1 Competition - Yearly data
library(Mcomp)
data("M1")
M1Y <- subset(M1, "yearly")
M1Y_x <- lapply(M1Y, function(temp){temp$x})
m1y_f1 <- find_dataleaks(M1Y_x, h=6, cutoff = 1)
m1y_f1
#> $YAF17
#> .id start end
#> 22 YAM6 9 14
#>
#> $YAM6
#> .id start end
#> 16 YAF17 16 21
#>
#> $YAM28
#> .id start end
#> 78 YAI21 16 21
#>
#> $YAB3
#> .id start end
#> 18 YAM2 14 19
#>
#> $YAB4
#> .id start end
#> 17 YAM1 15 20
#>
#> $YAI21
#> .id start end
#> 43 YAM28 16 21
#>
#> $YAG29
#> .id start end
#> 137 YAC15 6 11
viz_dataleaks(m1y_f1)
#> [[1]]
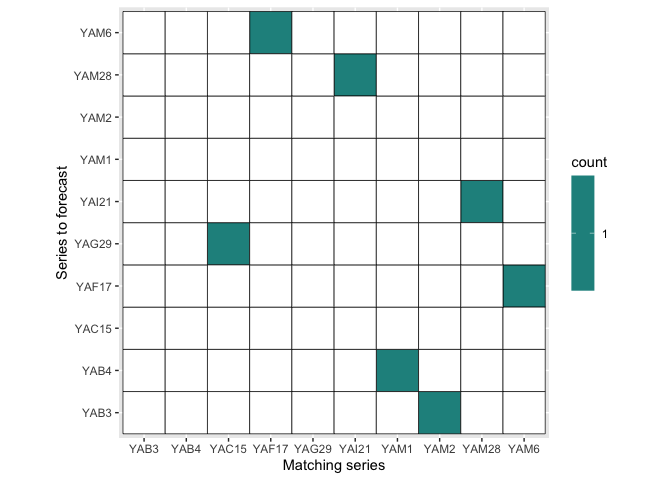
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [[2]]$YAF17
#> .id start end
#> 22 YAM6 9 14
#>
#> [[2]]$YAM6
#> .id start end
#> 16 YAF17 16 21
#>
#> [[2]]$YAM28
#> .id start end
#> 78 YAI21 16 21
#>
#> [[2]]$YAB3
#> .id start end
#> 18 YAM2 14 19
#>
#> [[2]]$YAB4
#> .id start end
#> 17 YAM1 15 20
#>
#> [[2]]$YAI21
#> .id start end
#> 43 YAM28 16 21
#>
#> [[2]]$YAG29
#> .id start end
#> 137 YAC15 6 11
reason_dataleaks(M1Y_x, m1y_f1, h=6, ang=90)
#> [[1]]
#> series1 .id start end dist_mean dist_sd is.useful.leak dist_cor
#> 1 YAF17 YAM6 9 14 5.4 0.4 not useful 1
#> 2 YAM6 YAF17 16 21 -5.4 0.4 not useful 1
#> 3 YAM28 YAI21 16 21 0.0 0.0 not useful 1
#> 4 YAB3 YAM2 14 19 0.0 0.0 useful 1
#> 5 YAB4 YAM1 15 20 0.0 0.0 useful 1
#> 6 YAI21 YAM28 16 21 0.0 0.0 not useful 1
#> 7 YAG29 YAC15 6 11 -36815.7 6159.2 useful 1
#> reason
#> 1 other transformation
#> 2 other transformation
#> 3 exact match
#> 4 exact match
#> 5 exact match
#> 6 exact match
#> 7 other transformation
#>
#> [[2]]
