Automated Selection and Visualisation of Statistical Hypothesis Tests.
visStatistics: The right test, visualised.
The R package visStatistics allows for rapid visualisation and statistical analysis of raw data. It automatically selects and visualises the most appropriate statistical hypothesis test between two vectors of class integer, numeric or factor.
This workflow is particularly suited for browser-based interfaces that rely on server-side R applications connected to secure databases, where users have no direct access, or for quick data visualisation, e.g. in statistical consulting projects.
Installation of latest stable version from CRAN
1. Install the package
install.packages("visStatistics")
2. Load the package
library(visStatistics)
Installation of the development version from GitHub
1.Install devtools from CRAN if not already installed:
install.packages("devtools")
2. Load the devtools package:
library(devtools)
3. Install the visStatistics package from GitHub:
install_github("shhschilling/visStatistics")
4. Load the visStatistics package:
library(visStatistics)
5. View help for the main function:
? visstat
Getting Started
The function visstat() accepts input in two ways:
# Standardised form (recommended):
visstat(x, y)
# Backward-compatible form:
visstat(dataframe, "name_of_y", "name_of_x")
In the standardised form, x and y must be vectors of class "numeric", "integer", or "factor".
In the backward-compatible form, "name_of_x" and "name_of_y" must be character strings naming columns in a data.frame named dataframe. These column must be of class "numeric", "integer", or "factor". This is equivalent to writing:
visstat(dataframe[["name_of_x"]], dataframe[["name_of_y"]])
To simplify the notation, throughout the remainder, data of class numeric or integer are both referred to by their common modenumeric, while data of class factor are referred to as categorical.
The interpretation of x and y depends on their classes:
If one is numeric and the other is a factor, the numeric must be passed as response
yand the factor as predictorx. This supports tests for central tendencies.If both are numeric, a simple linear regression model is fitted with
yas the response andxas the predictor.If both are factors, a test of association is performed (Chi-squared or Fisher’s exact). The test is symmetric, but the plot layout depends on which variable is supplied as
x.
visstat() selects the appropriate statistical test and generates visualisations accompanied by the main test statistics.
Examples
library(visStatistics)
Numerical response and categorical predictor
When the response is numerical and the predictor is categorical, test of central tendencies are selected.
Welch two sample t-test
InsectSprays data set — both input forms
insect_sprays_ab <- InsectSprays[InsectSprays$spray %in% c("A", "B"), ]
insect_sprays_ab$spray <- factor(insect_sprays_ab$spray)
# Standardised
visstat(insect_sprays_ab$spray, insect_sprays_ab$count)
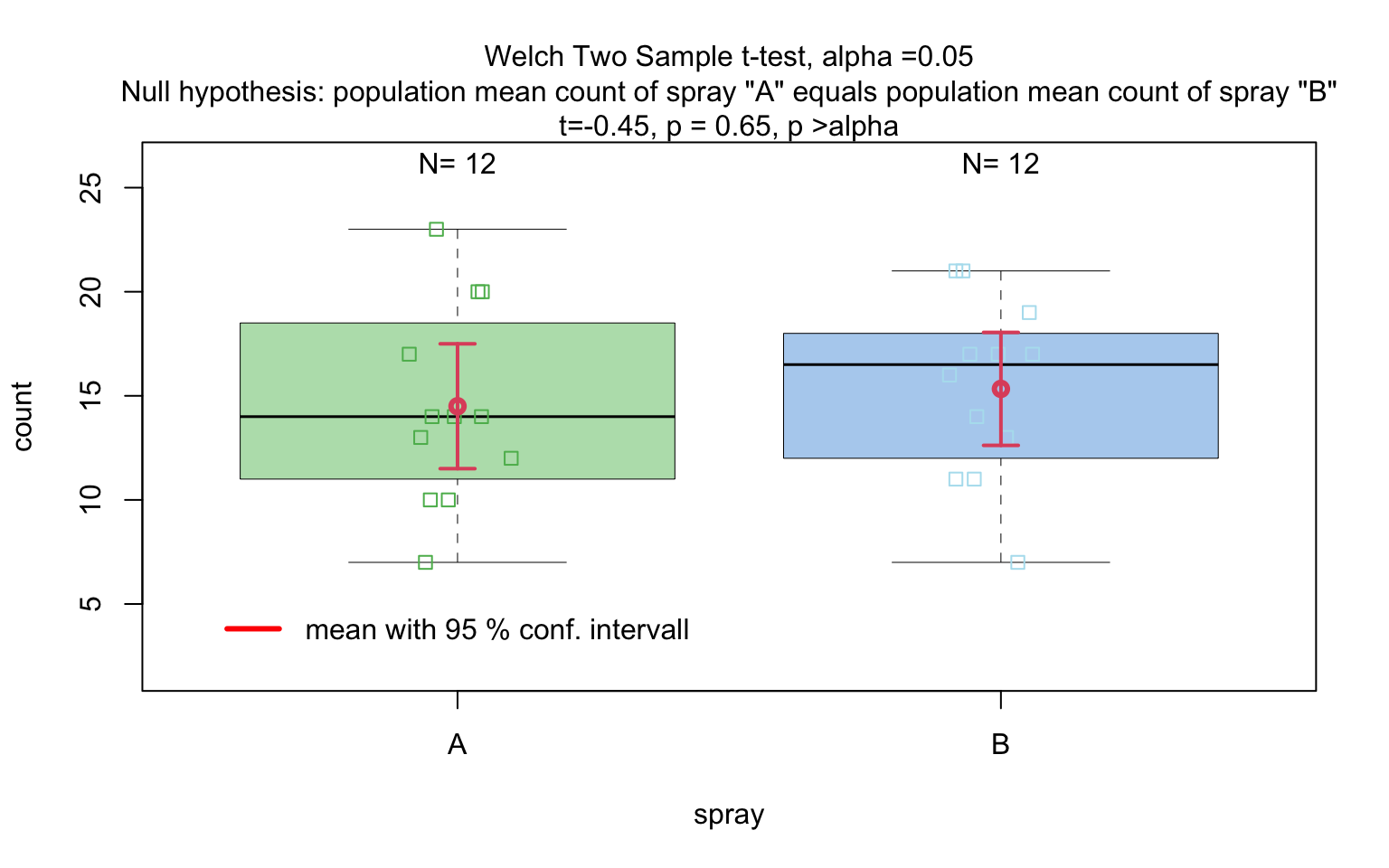
# Backward-compatible function call resulting in same output
# visstat(insect_sprays_ab,"count", "spray")
mtcars data set
mtcars$am <- as.factor(mtcars$am)
t_test_statistics <- visstat(mtcars$am, mtcars$mpg)
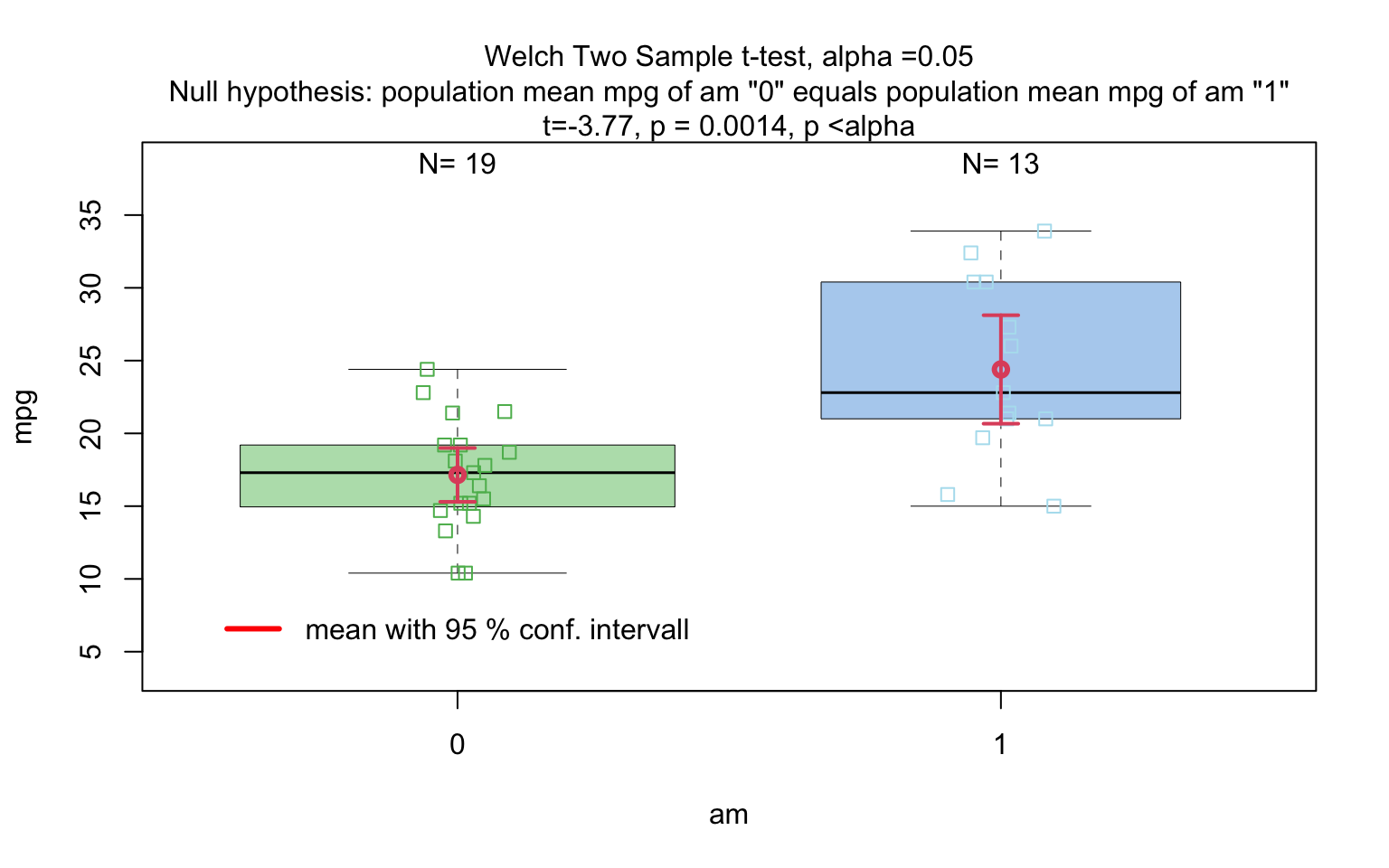
# t_test_statistics
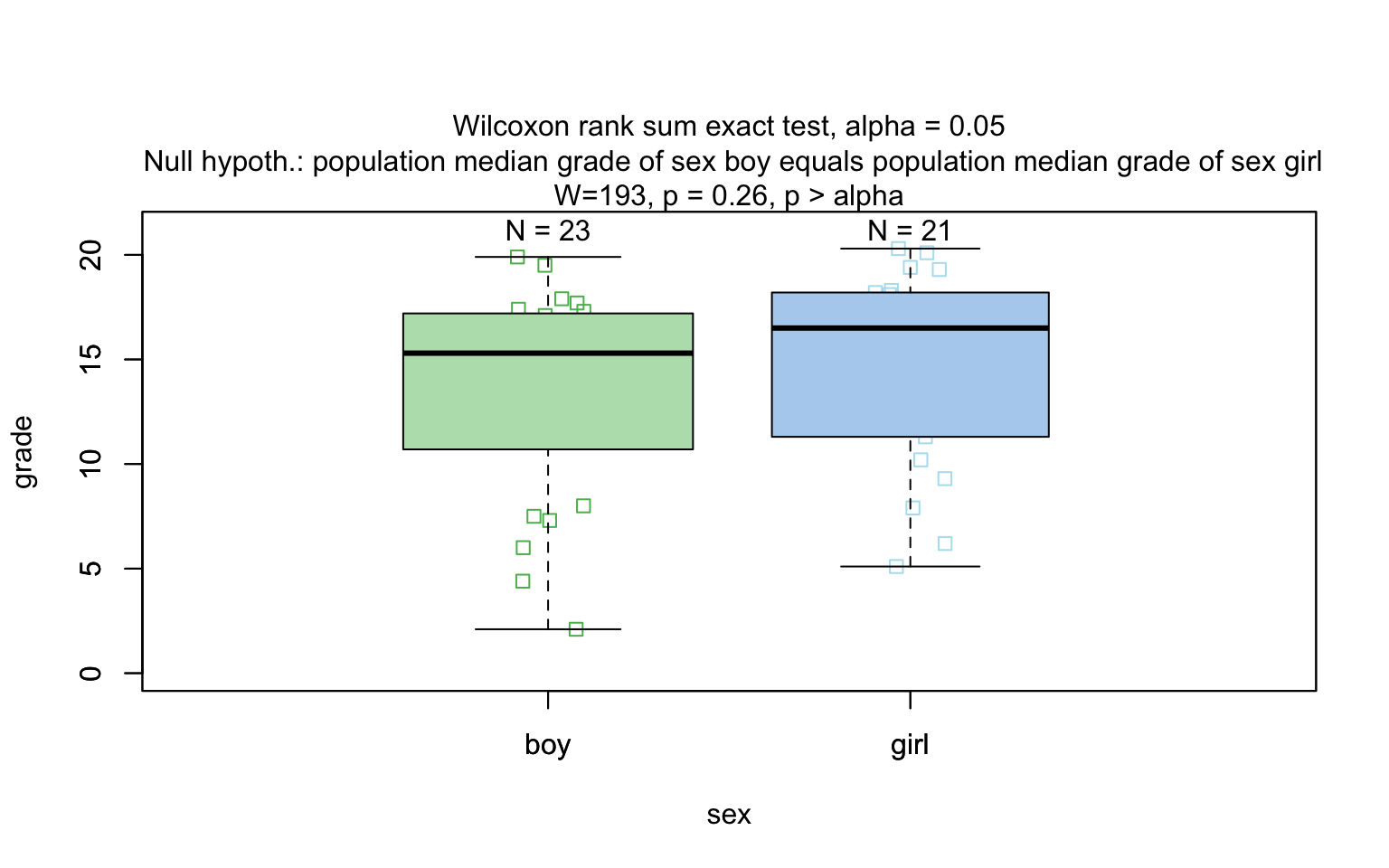
Wilcoxon rank sum test
grades_gender <- data.frame(
sex = factor(rep(c("girl", "boy"), times = c(21, 23))),
grade = c(
19.3, 18.1, 15.2, 18.3, 7.9, 6.2, 19.4, 20.3, 9.3, 11.3,
18.2, 17.5, 10.2, 20.1, 13.3, 17.2, 15.1, 16.2, 17.0, 16.5, 5.1,
15.3, 17.1, 14.8, 15.4, 14.4, 7.5, 15.5, 6.0, 17.4, 7.3, 14.3,
13.5, 8.0, 19.5, 13.4, 17.9, 17.7, 16.4, 15.6, 17.3, 19.9, 4.4, 2.1
)
)
wilcoxon_statistics <- visstat(grades_gender$sex, grades_gender$grade)
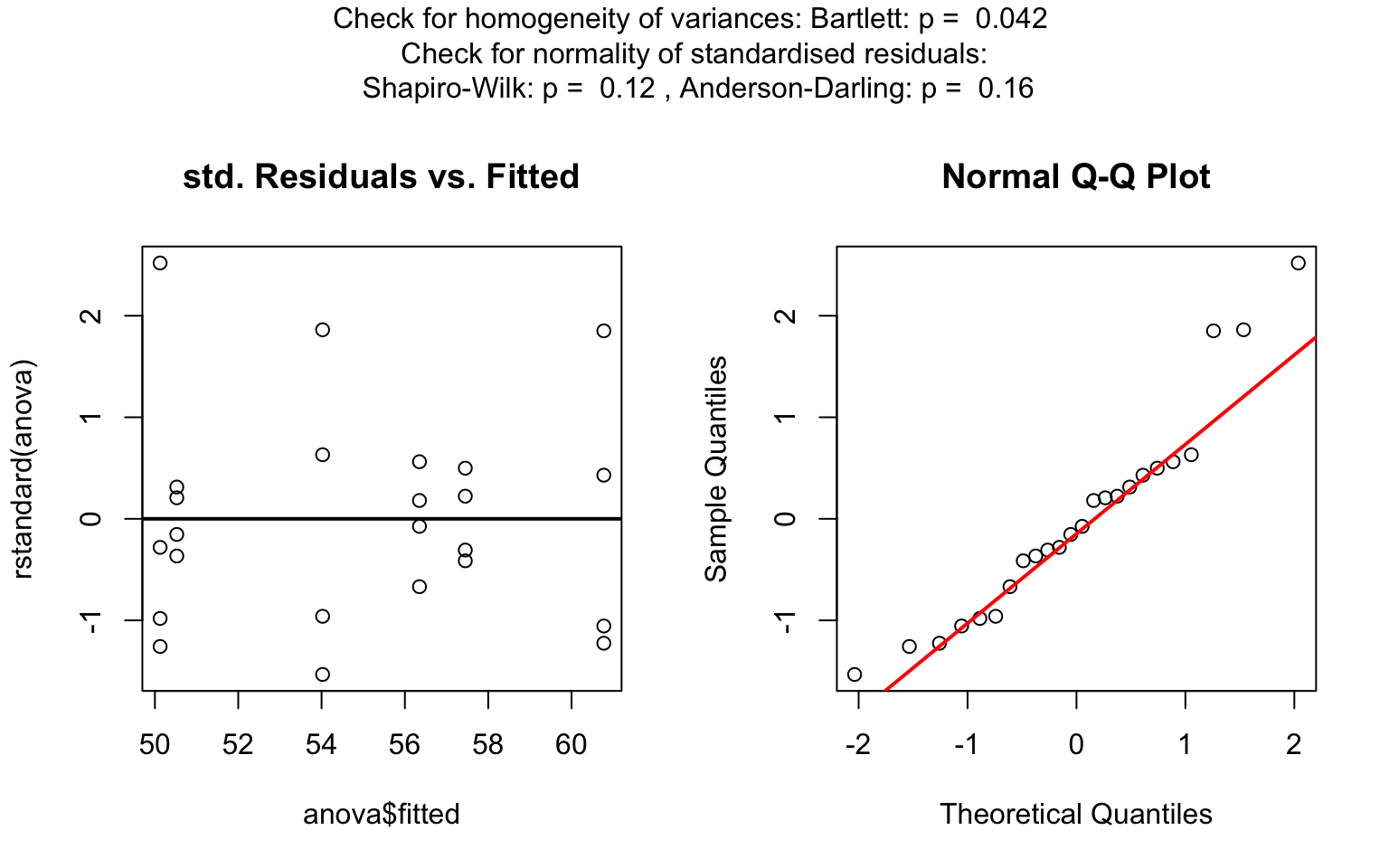
One-way test
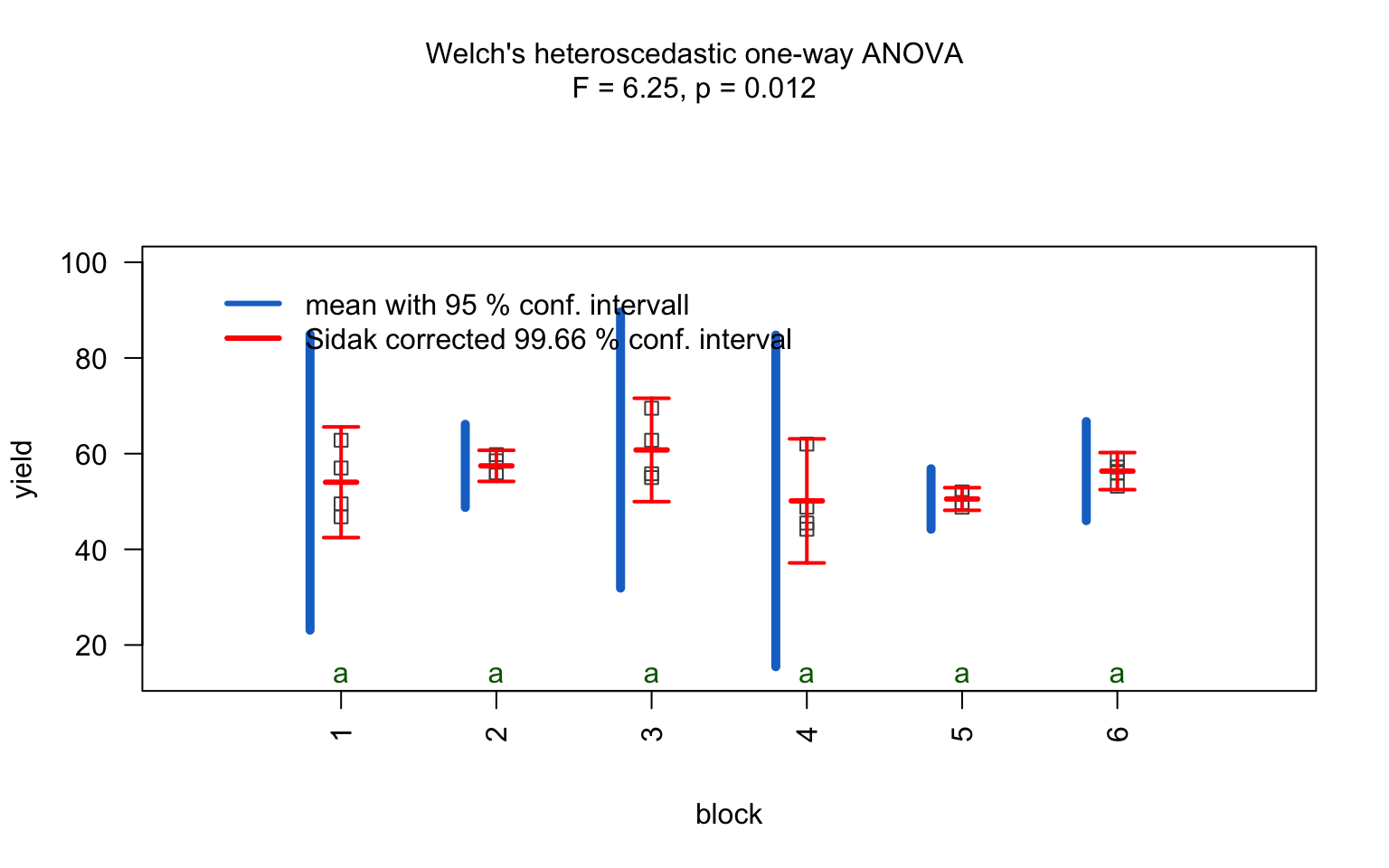
one_way_npk <- visstat(npk$block,npk$yield)
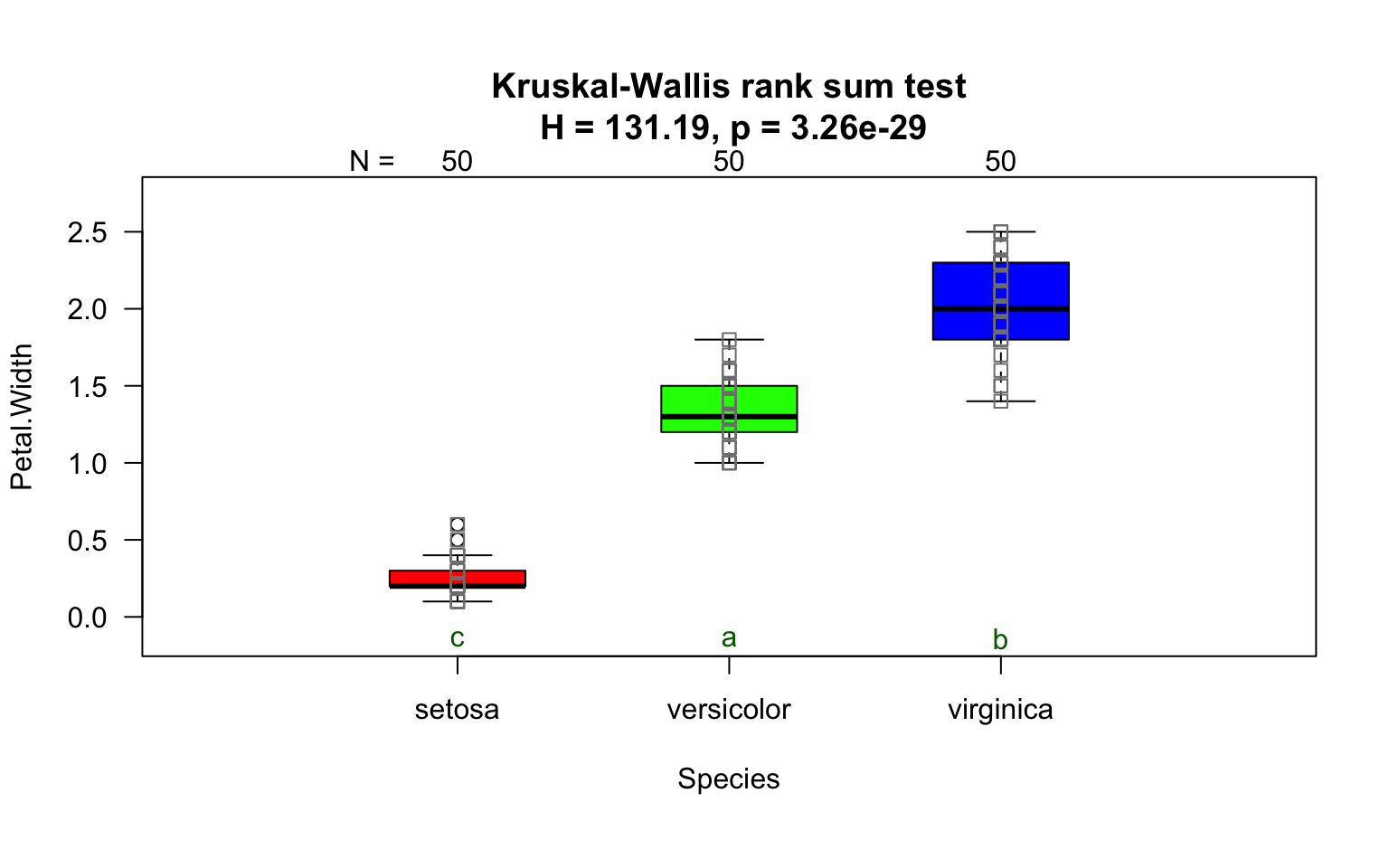
Kruskal-Wallis test
visstat(iris$Species, iris$Petal.Width)
 The generated graphs can be saved in all available formats of the
The generated graphs can be saved in all available formats of the Cairo package. Here we save the graphical output of type “pdf” in the plotDirectorytempdir():
visstat(
iris$Species,iris$Petal.Width,graphicsoutput = "pdf",plotDirectory = tempdir()
)
Numerical response and numerical predictor: Linear Regression
linreg_cars <- visstat(cars$speed ,cars$dist)
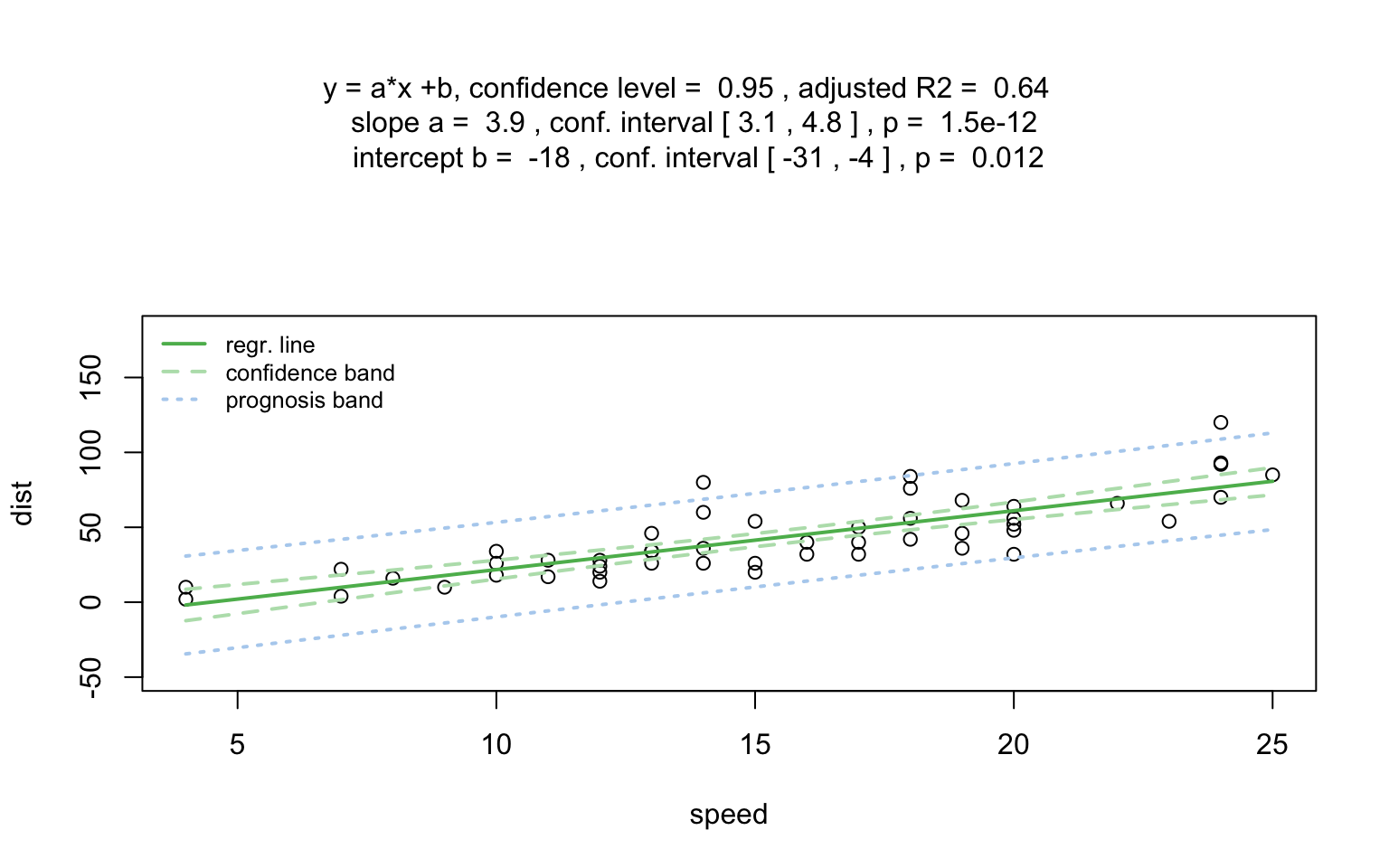
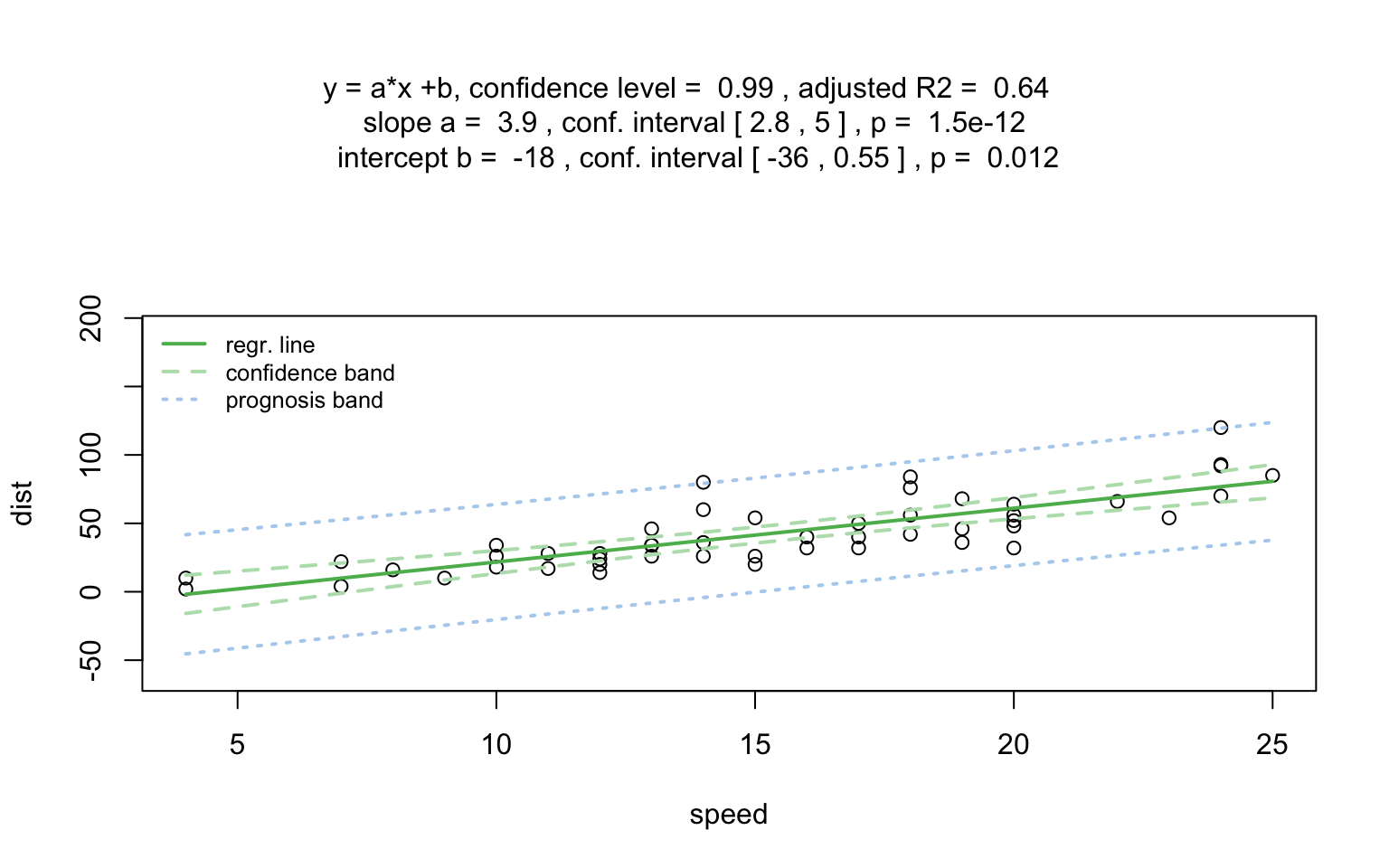
Increasing the confidence level conf.level from the default 0.95 to 0.99 leads two wider confidence and prediction bands:
Both varibles categorical
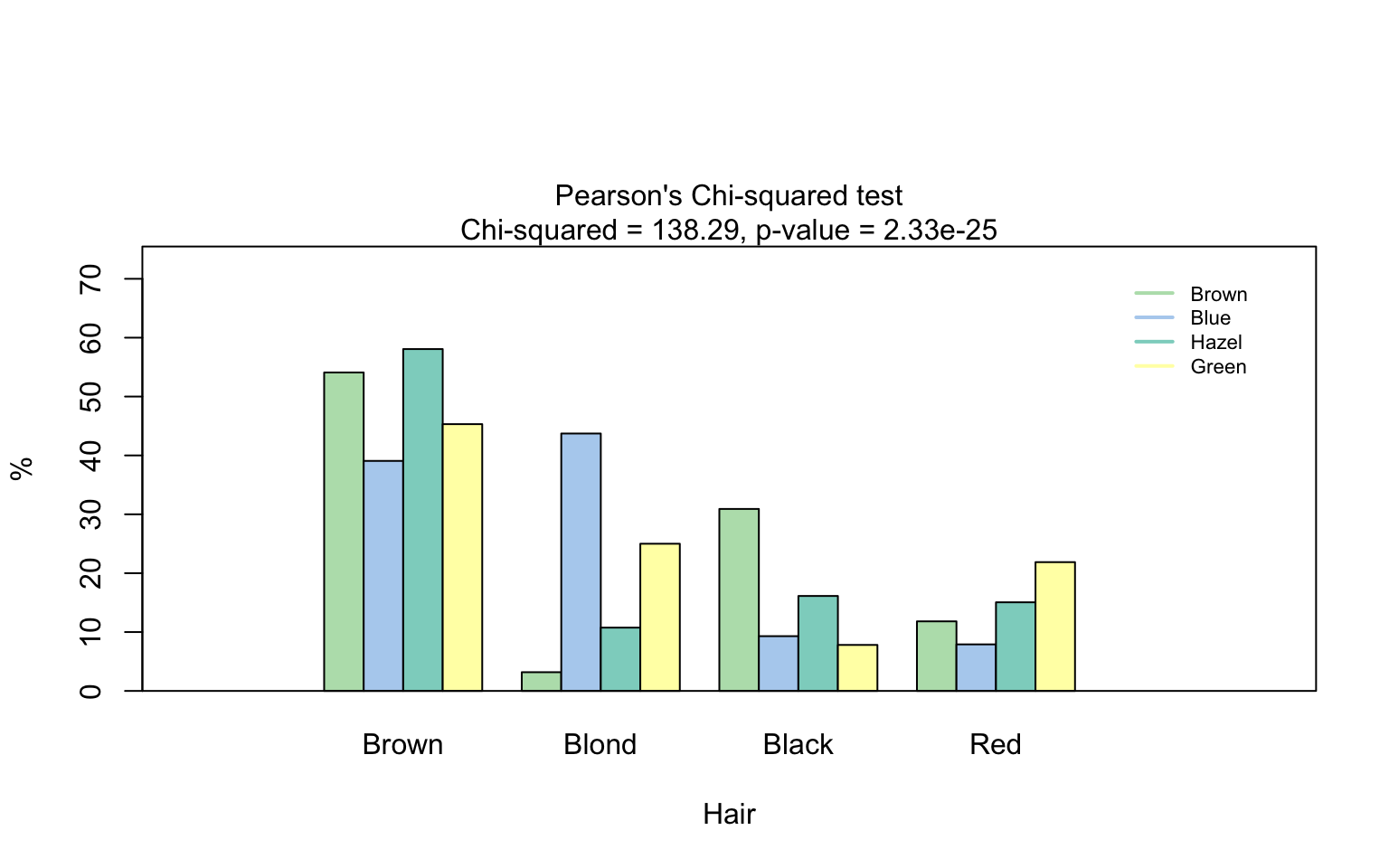
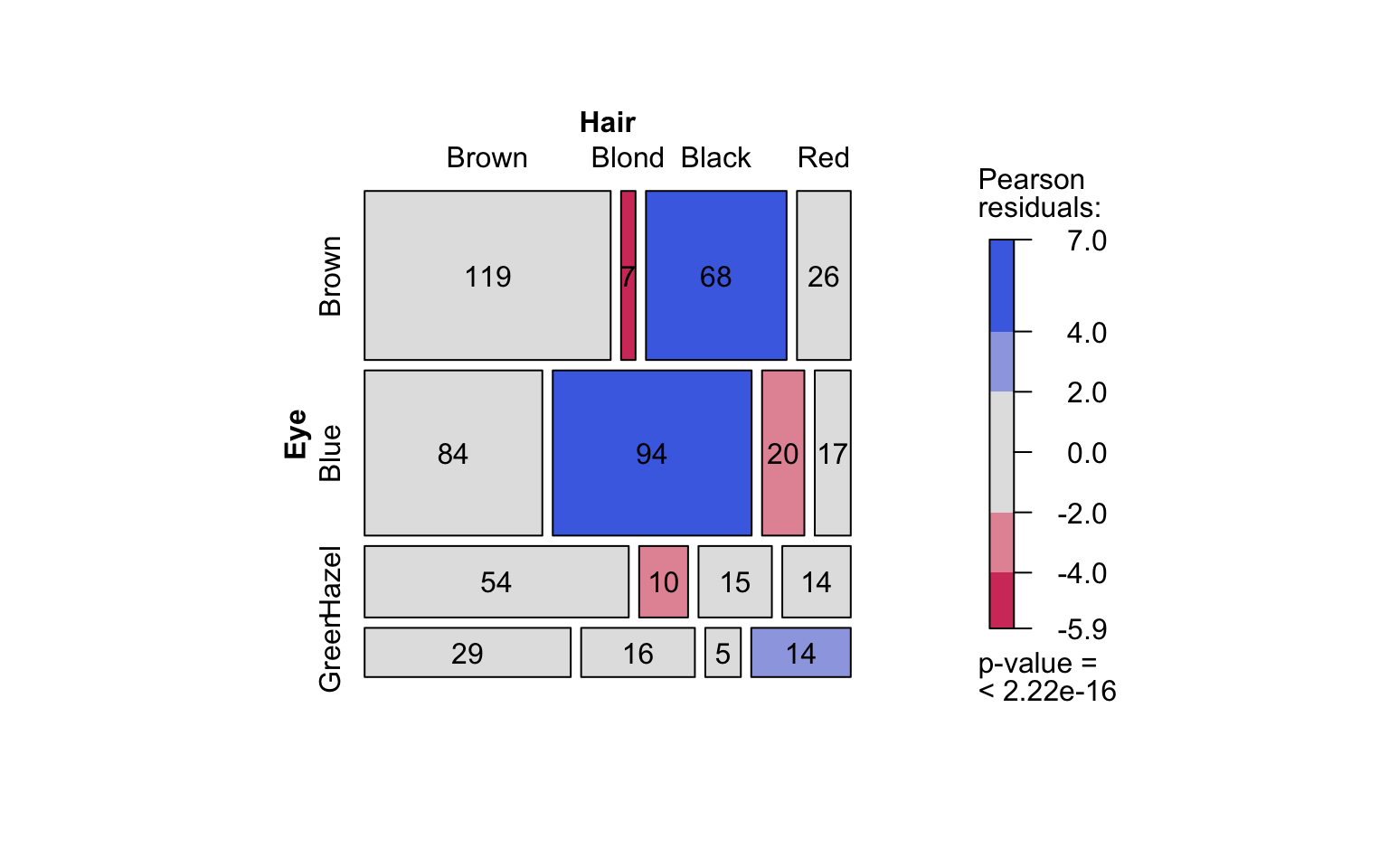
Pearson’s Chi-squared test
Count data sets are often presented as multidimensional arrays, so - called contingency tables, whereas visstat() requires a data.frame with a column structure. Arrays can be transformed to this column wise structure with the helper function counts_to_cases():
hair_eye_color_df <- counts_to_cases(as.data.frame(HairEyeColor))
visstat(hair_eye_color_df$Eye, hair_eye_color_df$Hair)
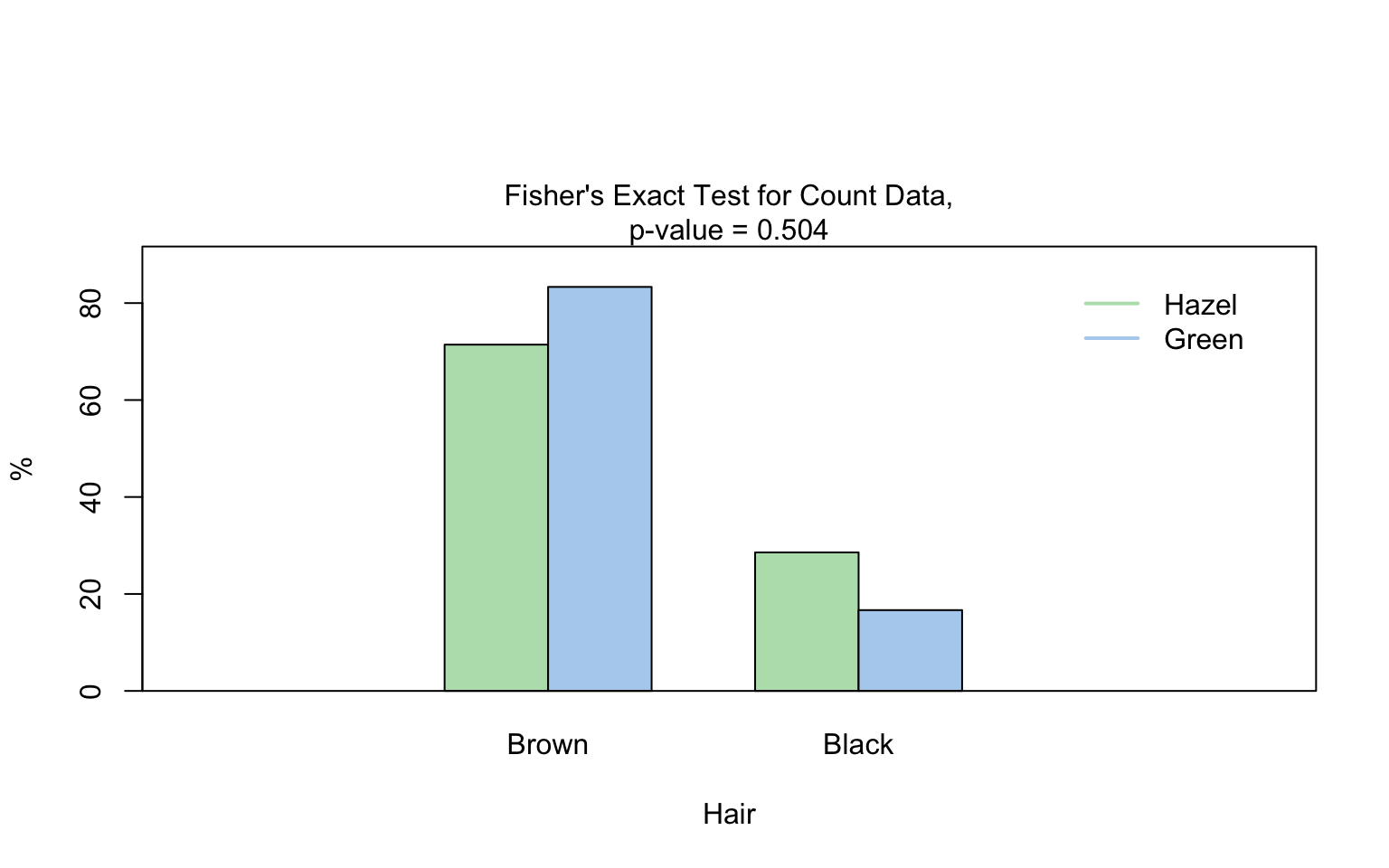
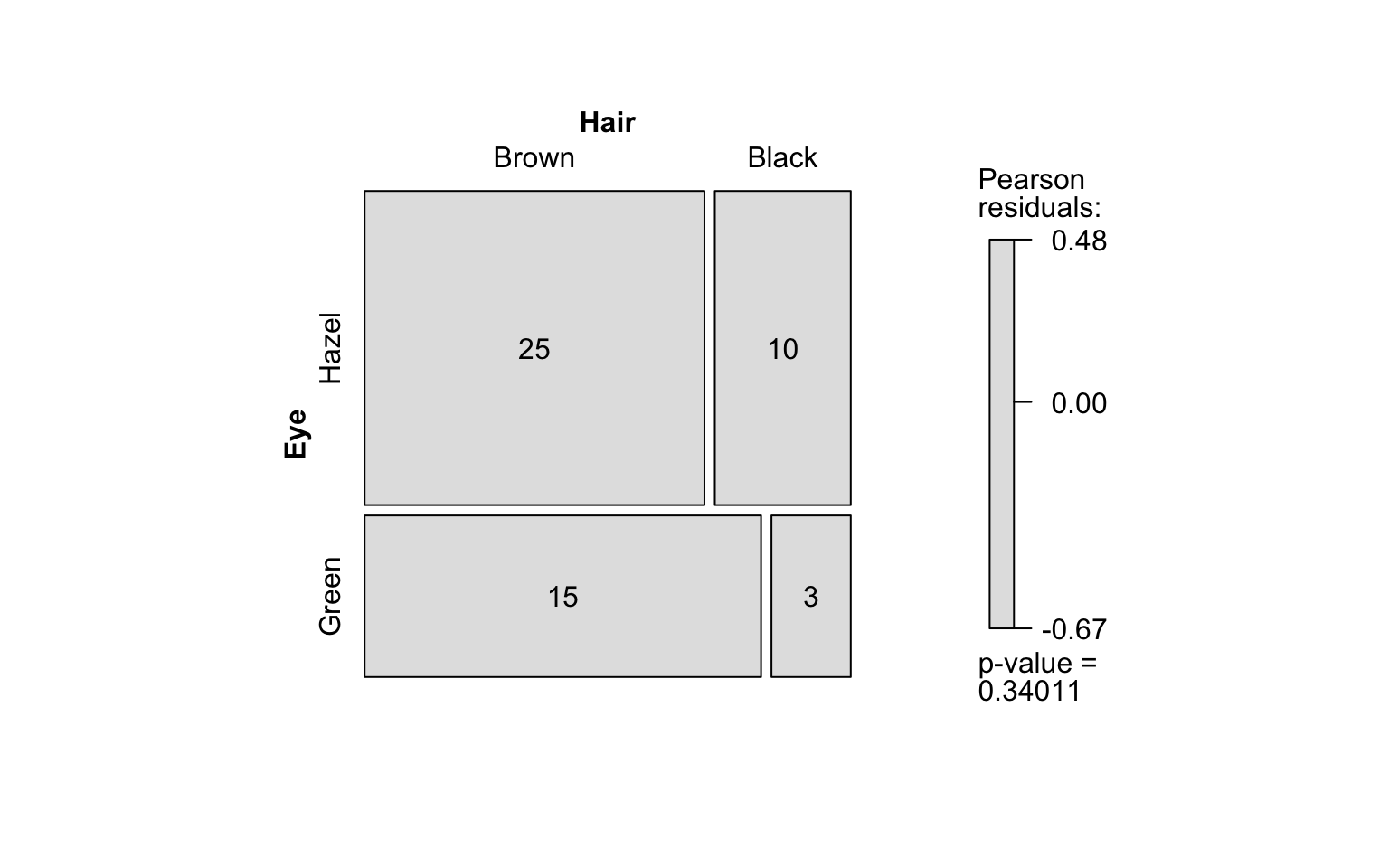
Fisher’s exact test
hair_eye_color_male <- HairEyeColor[, , 1]
# Slice out a 2 by 2 contingency table
black_brown_hazel_green_male <- hair_eye_color_male[1:2, 3:4]
# Transform to data frame
black_brown_hazel_green_male <- counts_to_cases(as.data.frame(black_brown_hazel_green_male))
# Fisher test
fisher_stats <- visstat(black_brown_hazel_green_male$Eye,black_brown_hazel_green_male$Hair)
Decision logic
The choice of statistical tests depends on whether the data of the selected columns are numeric or categorical, the number of levels in the categorical variable, and the distribution of the data. The function prioritizes interpretable visual output and tests that remain valid under the the following decision logic:
Numerical response and categorical predictor
When the response is numeric and the predictor is categorical, a statistical hypothesis test of central tendencies is selected.
If the categorical predictor has exactly two levels, Welch’s t - test (
t.test()), is applied whenever both groups contain more than 30 observations, with the validity of the test supported by the approximate normality of the sampling distribution of the mean under the central limit theorem [@Rasch:2011vl @Lumley2002dsa]. For smaller samples, group - wise normality is assessed using the Shapiro - Wilk test (shapiro.test()) at the significance levelα. If both groups are found to be approximately normally distributed according to the Shapiro - Wilk test, Welch’s t-test is applied; otherwise, the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (wilcox.test()) is used.For predictors with more than two levels, an ANOVA model (
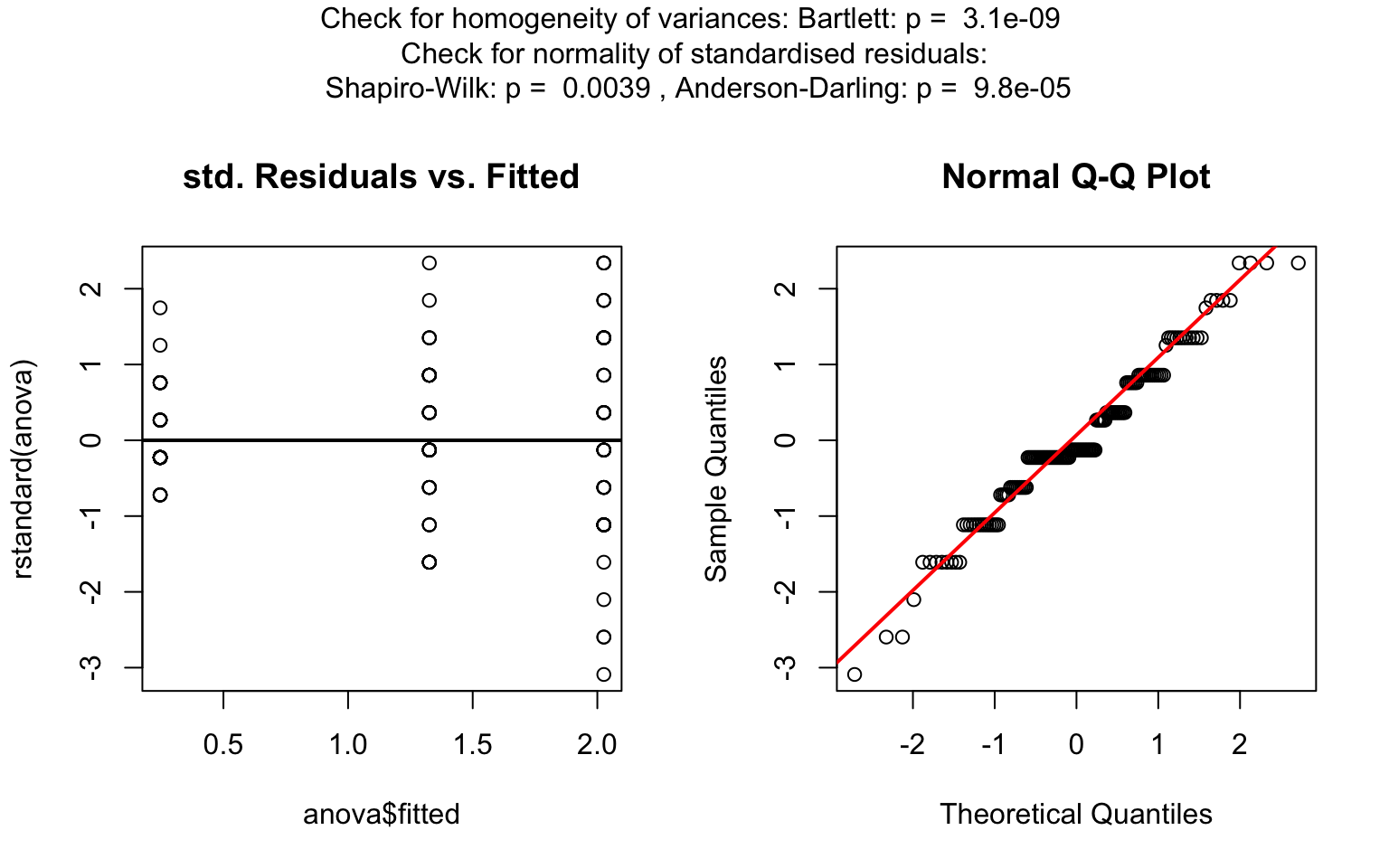
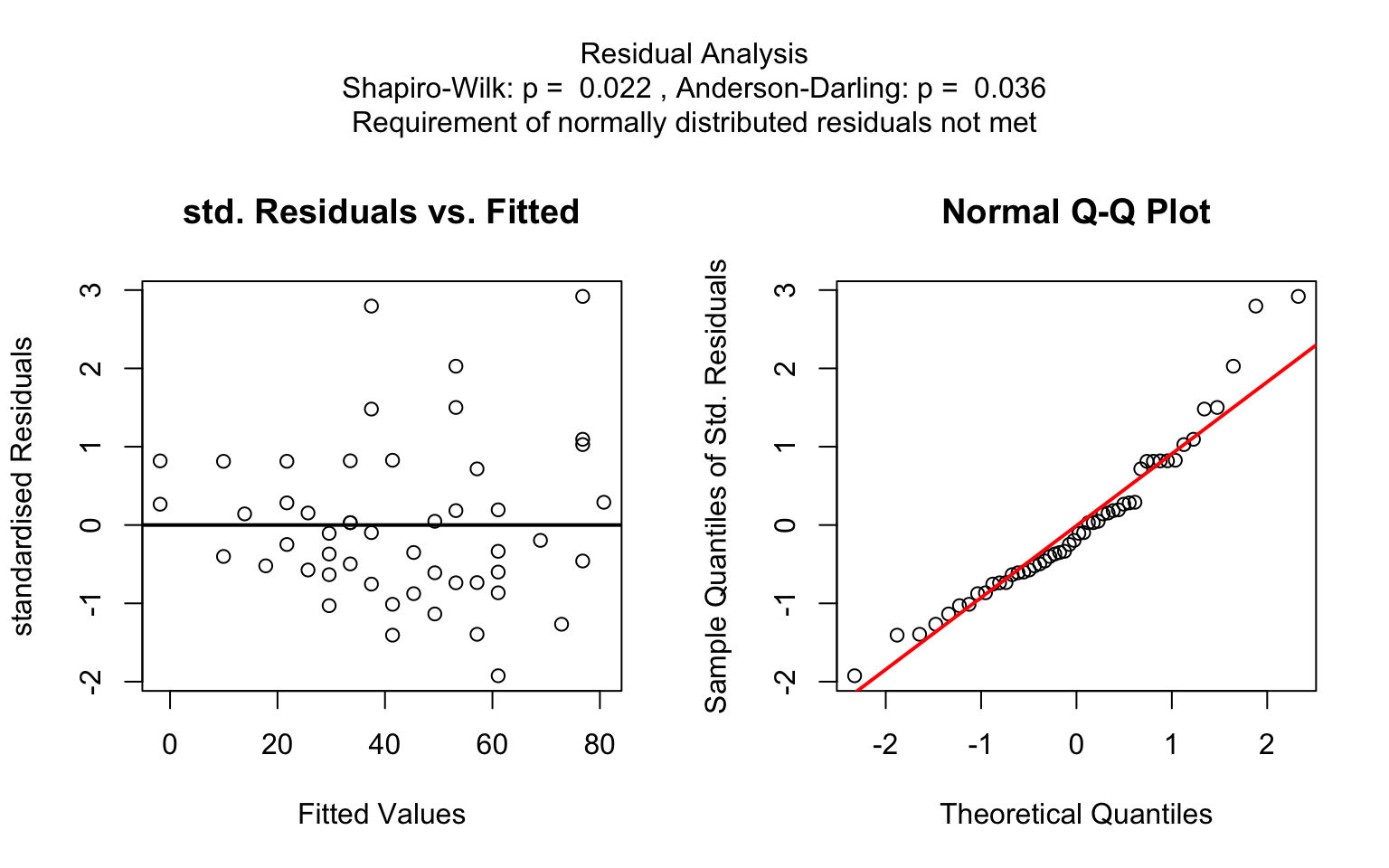
aov()) is initially fitted. The normality of residuals is evaluated using both the Shapiro–Wilk test (shapiro.test()) and the Anderson–Darling test (ad.test()); residuals are considered approximately normal if at least one of the two tests yields a result exceeding the significance threshold α. If this condition is met, Bartlett’s test (bartlett.test()) is then used to assess homoscedasticity. When variances are homogeneous (p > α), ANOVA is applied with Tukey’s HSD (TukeyHSD()) for post-hoc comparison. If variances differ significantly (p ≤ α), Welch’s one - way test (oneway.test()) is used, also followed by Tukey’s HSD. If residuals are not normally distributed according to both tests (p ≤ α), the Kruskal-Wallis test (kruskal.test()) is selected, followed by pairwise Wilcoxon tests (pairwise.wilcox.test()). A graphical overview of the decision logic used is provided in below figure.
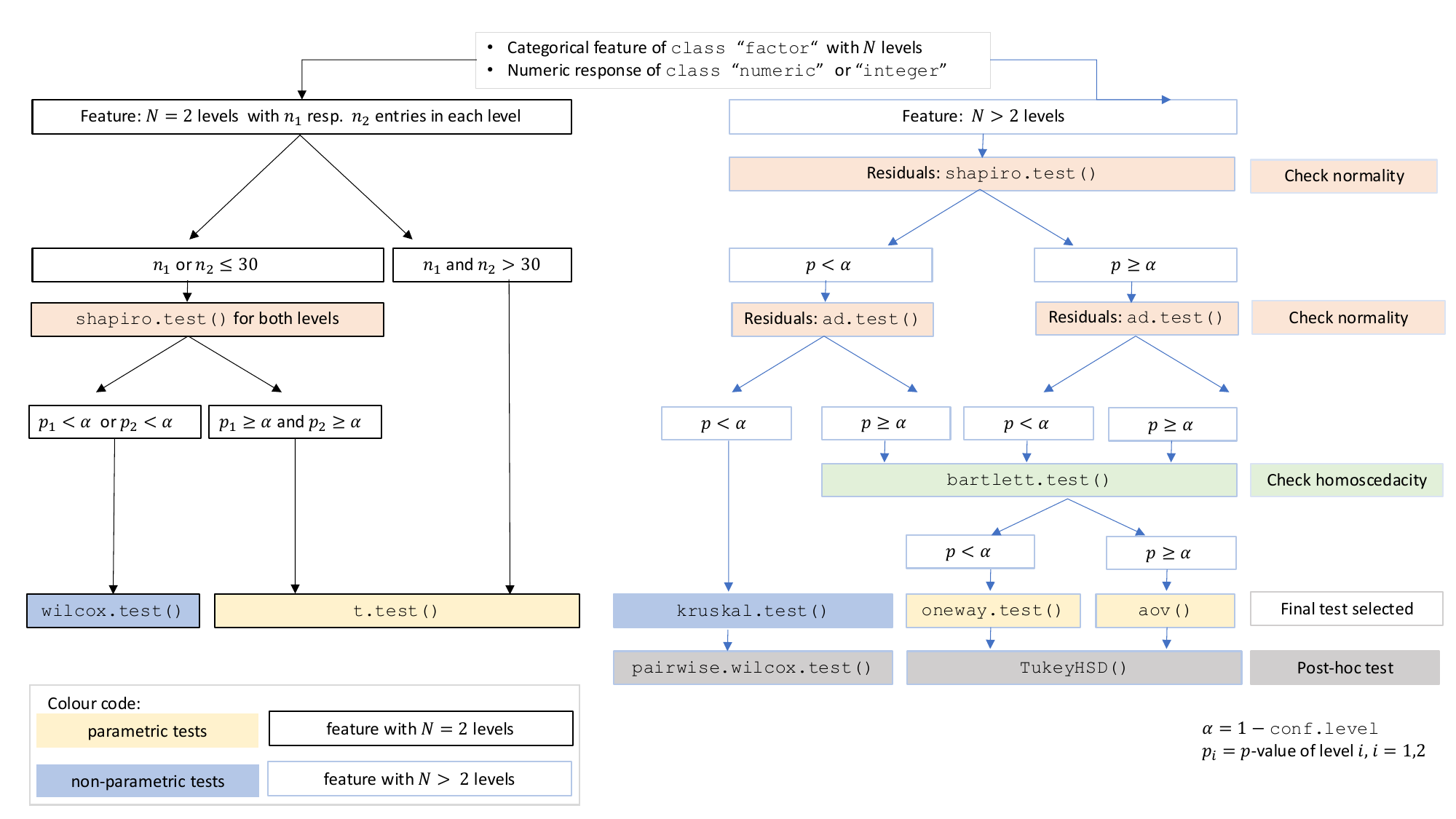
Decision tree used to select the appropriate statistical test for a categorical predictor and numeric response, based on the number of factor levels, normality, and homoscedasticity.
Numerical response and numerical predictor: Linear Regression
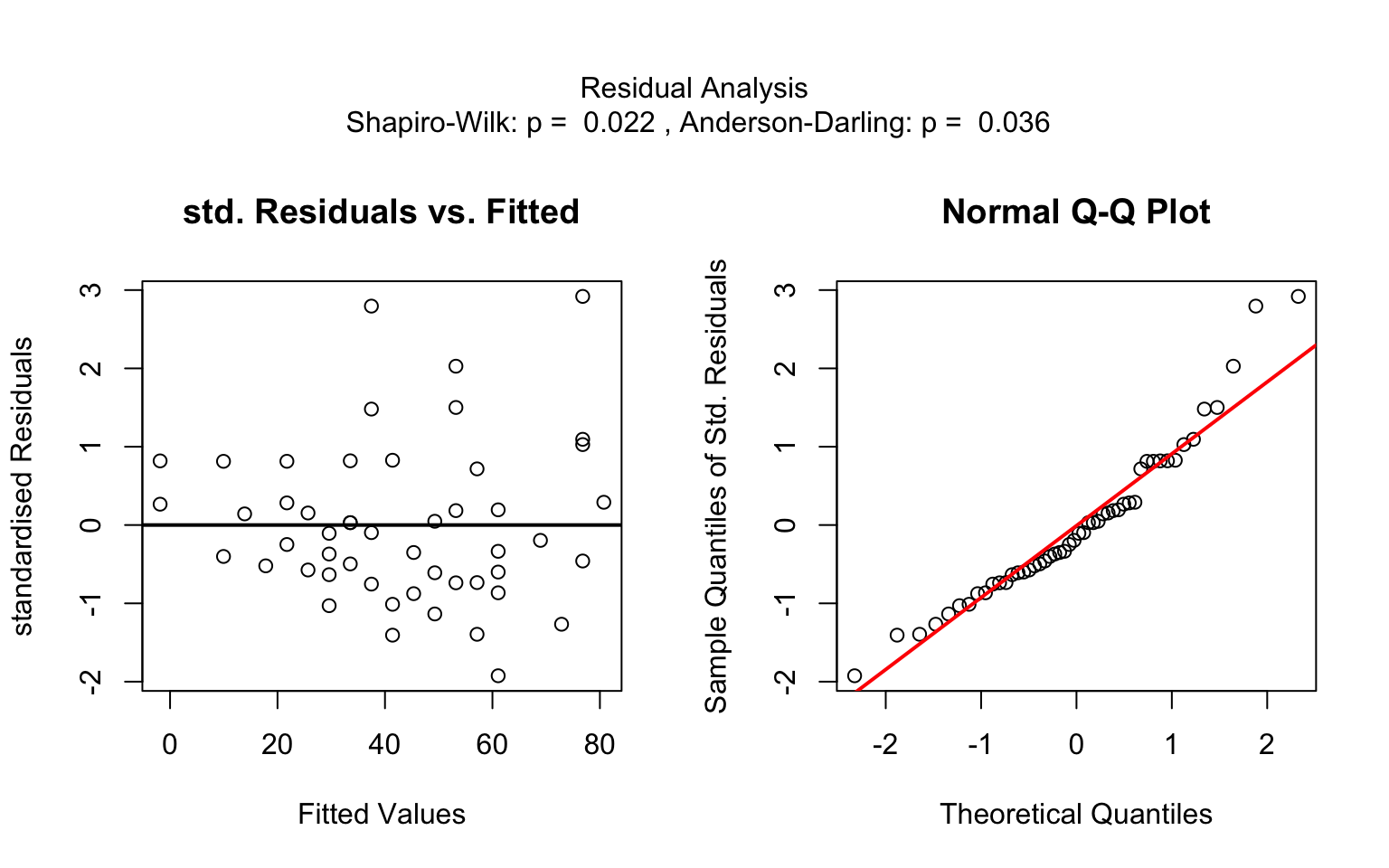
When both the response and predictor are numeric, a simple linear regression model (lm()) is fitted and analysed in detail, including residual diagnostics, formal tests, and the plotting of fitted values with confidence bands. Note that only one explanatory variable is allowed, as the function is designed for two-dimensional visualisation.
Both variables categorical
When both variables are categorical, no direction is assumed (though one is still referred to as the for consistency). visstat() tests the null hypothesis that both variables are independent using either chisq.test() or fisher.test(). The choice of test is based on Cochran’s rule [@Cochran], which advises that theχ2approximation is reliable only if no expected cell count is zero and no more than 20 percent of cells have expected counts below 5.
For a more detailed description of the underlying decision logic see
vignette("visStatistics")
Limitations
The main purpose of this package is a decision-logic based automatic visualisation of statistical test results. Therefore, except for the user-adjustable conf.level parameter, all statistical tests are applied using their default settings from the corresponding base R functions. As a consequence, paired tests are currently not supported and visstat() does not allow to study interactions terms between the different levels of an independent variable in an analysis of variance. Focusing on the graphical representation of tests, only simple linear regression is implemented, as multiple linear regressions cannot be visualised.
Implemented tests
Numerical response and categorical predictor
Main tests
t.test(), wilcox.test(), aov(), oneway.test(), kruskal.test()
Normality assumption check
shapiro.test() and ad.test()
Homoscedasticity assumption check
bartlett.test()
Post-hoc tests-TukeyHSD() (used following aov()and oneway.test())
pairwise.wilcox.test()(used followingkruskal.test())
Numerical response and numerical predictor
When both the response and predictor are numerical, a simple linear regression model is fitted:lm()
Note that multiple linear regression models are not implemented, as the package focuses on the visualisation of data, not model building. ### Categorical response and categorical predictor
When both variables are categorical, visstat() tests the null hypothesis of independence using one of the following:-chisq.test() (default for larger samples) - fisher.test() (used for small expected cell counts based on Cochran’s rule)