Incrementally Build Complex Plots using Natural Semantics.
WHeatmap 
WHeatmap designs a set of languages and a layer system that allows arbitrary positioning of heatmaps programmatically.
It makes plotting complex heatmaps using plain English such as TopOf, RightOf and BottomLeftOf etc.
To install from github using devtools,
library(devtools)
install_github('zwdzwd/wheatmap')
library(wheatmap)
For example, the following complex layout
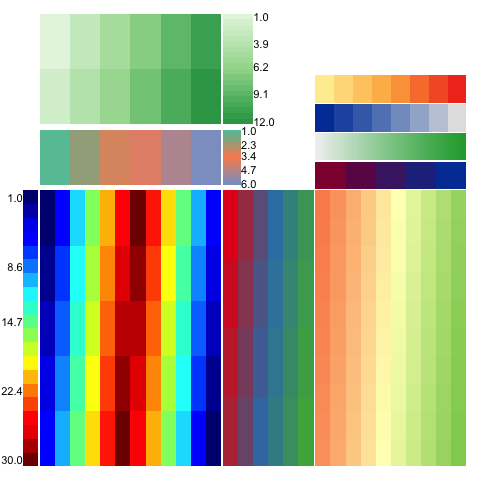
can be generated simply by
WHeatmap(matrix(1:12,nrow=2), cmp=CMPar(brewer.name='Greens'), name='a') +
WHeatmap(matrix(1:6,nrow=1), Beneath(pad=0.05), cmp=CMPar(brewer.name='Set2'), name='b') +
WHeatmap(matrix(c(1:30,30:1),nrow=5), Beneath(pad=0.05), 'c', cmp=CMPar(cmap='jet')) +
WHeatmap(matrix(1:24,nrow=4), RightOf('c'), 'd', cmp=CMPar(brewer.name='Set1')) +
WLegendV('c', LeftOf('c', pad=0.01), yticklabel.side='l') +
WLegendV('b', RightOf('b', width=0.1)) +
WLegendV('a', RightOf('a')) +
WHeatmap(matrix(1:100, nrow=10), RightOf('d'), cmp=CMPar(brewer.name='RdYlGn')) +
WColorBarH(matrix(5:1), TopOf(), cmp=CMPar(colorspace.name = 'diverge_hcl')) +
WColorBarH(matrix(50:1), TopOf(), cmp=CMPar(colorspace.name = 'terrain_hcl')) +
WColorBarH(matrix(1:8), TopOf(), cmp=CMPar(colorspace.name = 'sequential_hcl')) +
WColorBarH(matrix(1:8), TopOf(), cmp=CMPar(brewer.name = 'YlOrRd'))
One who is really obssessed with %>% can do something like
library(magrittr)
WHeatmap(cc$mat, name='h1') %>% add(WColorBarV(row.data, LeftOf('h1'), 'c1'))
The layout looks like
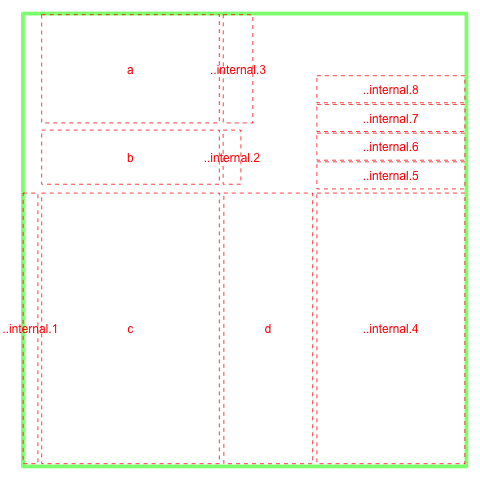
In order to cross-refer panels in the plot, one has to use a unique name. This name can be given through the name= option and user has to make sure the uniqueness of the names from existing objects in the plot. If not specified, wheatmap can generate a unique name and that name is visible from ly() function. A special NULL tag can be used to refer to the last plotted object.
More User guides:
Acknowledgement
- The internal
grid.dendrogram()function is adapted fromComplexHeatmappackage.